Summary
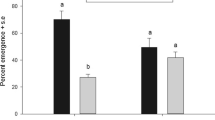
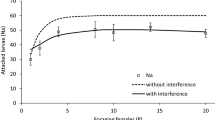
One of the most controversial putative cases of host race formation in insects is that of the apple maggot fly, Rhagoletis pomonella (Diptera: Tephritidae). A principal cause of the controversy is lack of relevant data. In laboratory and field enclosure experiments, we compared the host acceptance behavior of sympatric populations of flies originating from naturally infested hawthorn (the native host) and apple (an introduced host) in Amherst, Massachusetts or East Lansing, Michigan. In general, hawthorn fruit were accepted for ovipositional attempts nearly equally by apple and hawthorn origin females, whereas apples were accepted much more often by apple than hawthorn origin females. Similarly, males of apple and hawthorn origin exhibited about equal duration of residence on hawthorn fruits as sites at which to acquire potential mates, while males of apple origin tended to reside substantially longer than males of hawthorn origin on apples. Irrespective of fly origin, both sexes always responded more positively to hawthorn fruit than to apples. Because all flies assayed were naive (ruling out effects of prior host experience of adults) and because tests revealed no influence of pre-imaginal fruit exposure on pattern of host fruit acceptance by females, the combined evidence suggests the phenotypic differences we observed in host response pattern between hawthorn and apple origin flies may have an underlying genetic basis. Further tests showed that while larval progeny of flies of each origin survived better in naturally growing hawthorn fruit than in naturally growing apples, there was no differential effect of fly origin on larval survival ability in either host. We discuss our findings in relation to restriction in gene flow between sympatric populations of R. pomonella and in relation to current models of host shifts in insects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali Niazee MT (1985) Opiine parasitoids of Rhagoletis pomonella and R. zephyria in the Willamette Valley, Oregon. Can Entomol 117:163–166
Averill AL, Prokopy RJ (1987) Intraspecific competition in the tephritid fruit fly Rhagoletis pomonella. Ecology 68:878–886
Bush GL (1966) Taxonomy, cytology and evolution of the genus Rhagoletis in North America. Bull Harvard Mus Comp Zool 134:431–562
Bush GL (1974) The mechanism of sympatric host race formation in the true fruit flies. In: White MJD (ed) Genetic Mechanisms of Speciation in Insects. Australian and New Zealand Book Co., Sydney. pp 3–23
Bush GL (1975a) Modes of animal speciation. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 6:339–364
Bush GL (1975b) Sympatric speciation in phytophagous parasitic insects. In: Price PW (ed), Evolutionary Strategies of Parasitic Insects. Plenum Press, London, pp 187–206
Bush GL, Diehl SR (1982) Hort shifts, genetic models of sympatric speciation, and the origin of parasitic insect species. In: Visser JH, Minks AK (eds) Proc. 5th Intern. Symp. Insect-Plant Relationships, PUDOC, Wageningen, Netherlands, pp 297–305
Carle SA, Averill AL, Rule GS, Reissig WH, Roelofs WL (1987) Variation in host fruit volatiles attractive to apple maggot fly, Rhagoletis pomonella. J Chem Ecol 13:795–805
Chapman PJ (1933) Viability of eggs and larvae of the apple maggot (Rhagoletis pomonella). Cornell Univ Tech Bull 206: p 19
Diehl SR (1984) The role of host plant shifts in the ecology and speciation of Rhagoletis flies, Ph.D thesis, Univ Texas p 256
Diehl SR, Bush GL (1984) An evolutionary and applied perspective of insect biotypes. Ann Rev Entomol 29:471–504
Diehl SR, Prokopy RJ (1986) Host selection behavior differences between the fruit fly sibling species Rhagoletis pomonella and R. mendax. Ann Entomol Soc Am 79:266–271
Diehl SR, Prokopy RJ, Henderson S (1986) The role of stimuli associated with branches and foliage in host selection by Rhagoletis pomonella. In: Cavalloro R (ed) Fruit Flies of Economic Importance, 84. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 191–196
Fein BL, Reissig WH, Roelofs WL (1982) Identification of apple volatiles attractive to the apple maggot, Rhagoletis pomonella. J Chem Ecol 8:1473–1487
Felsenstein J (1981) Skepticism toward Santa Rosalia, or why are there so few kinds of animals? Evolution 35:124–135
Fisher RA (1954) Statistical Methods for Research Workers. 12th ed. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh
Fitt GP (1986a) The influence of a shortage of hosts on the specificity of oviposition behavior in species of Dacus. Physiol Entomol 11:133–143
Fitt GP (1986b) The roles of adult and larval specialization in limiting the occurrence of five species of Dacus in cultivated fruits. Oecologia 69:101–109
Fox LR, Morrow PA (1981) Specialization: species property or local phenomenon? Science 211:887–893
Futuyma DJ (1983) Selective factors in the evolution of host choice by phytophagous insects. In: Ahmad SA (ed) Herbivorous Insects: Host Seeking Behavior and Mechanisms. Academic Press, New York, pp 227–244
Futuyma DJ, Mayer GC (1980) Non-allopatric speciation in animals. Syst Zool 29:254–271
Futuyma DJ, Peterson SC (1985) Genetic variation in the sue of resources by insects. Ann Rev Entomol 30:217–238
Futuyma DJ, Philippi TE (1987) Genetic variation and covariation in responses to host plants by Alsophila pometaria. Evolution 41:269–279
Futuyma DJ, Cort RP, Van Noordwijk I (1984) Adaptation to host plants in the fall cankerworm (Alsophila pometaria) and its bearing on the evolution of host affiliation in phytophagous insects. Am Nat 123:287–296
Girolami V, Strapazzon A, Crnjar R, Angioy AM, Pietra P, Stoffolano JG, Prokopy RJ (1986) Behavior and sensory physiology of Rhagoletis pomonella in relation to oviposition sitmulants and deterrents in fruit. In: Cavalloro R (ed) Fruit Flies of Economic Importance, 84. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 183–190
Goodman LA (1964) Simultaneous confidence intervals for contrasts among multinomial populations. Ann Math Stat 35:716–725
Grizzle JE, Starmer CF, Koch GG (1969) Analysis of categorical data by linear models. Biometrics 25:489–504
Hall JA (1939) Further observations on the biology of the apple maggot (Rhagoletis pomonella). Ann Rept Entomol Soc Ontario 69:53–58
Hall JA (1943) Notes on the dogwood fly, a race of Rhagoletis pomonella. Can Entomol 75:202–203
Hare JD, Kennedy GC (1986) Genetic variation in plant-insect associations: survival of Leptinotarsa decemlineata populations on Solanum carolinense. Evolution 40:1031–1043
Hoffmann AA (1985) Effects of experience on oviposition and attraction in Drosophila: comparing apples and oranges. Am Nat 126:41–51
Jaenike J (1981) Criteria for ascertaining the existence of host races. Am Nat 117:830–834
Jaenike J (1982) Environmental modification of oviposition behavior in Drosophila. Am Nat 119:784–802
Jaenike J (1985a) Parasite pressure and the evolution of amanitin tolerance in Drosophila. Evolution 39:1295–1301
Jaenike J (1985b) Genetic and environmental determinants of food preference in Drosophila tripunctata. Evolution 39:362–369
Jaenike J (1986a) Genetic complexity of host-selection behavior in Drosophila. Proc Nat Acad Sci 83:2148–2151
Jaenike J (1986b) Intraspecific variation for resource use in Drosophila. Biol J Linn Soc 27:47–56
Jaenike J, Grimaldi D (1983) Genetic variation for host preference within and among populations of Drosophila tripunctata. Evolution 37:1023–1033
Jeffries MJ, Lawton JH (1984) Enemy free space and the structure of ecological communities. Biol J Linn Soc 23:269–286
Jorgensen CD, Allred DB, Westcott RL (1986) Apple maggot adaptation for cherries in Utah. Great Basin Nat 46:173–174
Koch GG, Amara IA, Davis GW, Gillings DB (1982) A review of some statistical methods for covariance analysis of categorical data. Biometrics 38:563–595
Kondrashov AS, Mina MV (1986) Sympatric speciation: when is it possible? Biol J Linn Soc 27:201–223
Maxwell CW, Parsons EC (1968) The recapture of marked apple maggot adults in several orchards from one release point. J Ecol Entomol 61:1157–1159
Mayr E (1970) Populations, Species, and Evolution. Harvard Univ Press, Cambridge
Miller JR, Strickler KL (1984) Finding and accepting host plants. In: Bell WJ, Carde RT (eds) Chemical Ecology of Insects. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 127–157
Moericke V, Prokopy RJ, Berlocher S, Bush GL (1975) Visual stimuli eliciting attraction of Rhagoletis pomonella flies to trees. Entomol Exp Appl 18:497–507
Opp SB, Prokopy RJ (1986) Variation in laboratory oviposition by Rhagoletis pomonella in relation to mating status. Ann Entomol Soc Am 79:705–710
Owens ED, Prokopy RJ (1986) Relationship between reflectance spectra of host plant surfaces and visual detection of host fruit by Rhagoletis pomonella flies. Physiol Entomol 11:297–307
Papaj DR (1986) Shifts in foraging behavior by a Battus philenor population: field evidence for switching by individual butterflies. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 19:31–39
Papaj DR, Prokopy RJ (1986) Phytochemical basis of learning in Rhagoletis pomonella and other herbivorous insects. J Chem Ecol 12:1125–1143
Papaj DR, Rausher MD (1983) Individual variation in host location by phytophagous insects. In: Ahmad S (ed) Herbivorous Insects: Host Seeking Behavior and Mechanisms. Academic Press, New York, pp 77–124
Paterson HEH (1981) The continuing search for the unknown and unknowable: a critique of contemporary ideas on speciation. South African J Sci 77:113–119
Pickett AD (1937) Studies on the genus Rhagoletis with special reference to Rhagoletis pomonella. Canad J Res 15:53–75
Pickett AD, Neary ME (1940) Further studies on Rhagoletis pomonella. Scient Agric 20:551–556
Pree DJ (1977) Resistance to development of larvae of the apple maggot in crab apples. J Econ Entomol 70:611–614
Prokopy RJ (1966) Artificial oviposition devices for apple maggot. J Econ Entomol 59:231–232
Prokopy RJ (1968) Visual responses of apple maggot flies, Rhagoletis pomonella: orchard studies. Entomol Exp Appl 11:403–422
Prokopy RJ (1972) Evidence for a marking pheromone deterring repeated oviposition in apple maggot flies. Environ Entomol 1:326–332
Prokopy RJ (1977) Attraction of Rhagoletis flies to red spheres of different sizes. Canad Entomol 109:593–596
Prokopy RJ (1981) Oviposition-deterring pheromone system of apple maggot flies. In: Mitchell ER (ed) Management of Insect Pests with Semiochemicals. Plenum Publ Co, New York, pp 477–494
Prokopy RJ, Berlocher SH (1980) Establishment of Rhagoletis pomonella on rose hips in southern New England. Canad Entomol 51:1319–1320
Prokopy RJ, Bush GL (1972) Apple maggot infestation of pear. J Econ Entomol 65:597
Prokopy RJ, Bush GL (1973) Ovipositional responses to different sizes of artificial fruit by flies of Rhagoletis pomonella species group. Ann Entomol Soc Am 66:927–929
Prokopy RJ, Bennett EW, Bush GL (1971) Mating behavior in Rhagoletis pomonella. I. Site of assembly. Canad Entomol 103:1405–1409
Prokopy RJ, Moericke V, Bush GL (1973). Attraction of apple maggot flies to odor of apples. Envir Entomol 2:743–749
Prokopy RJ, Averill AL, Cooley SS, Roitberg CA, Kallet C (1982a) Variation in host acceptance pattern in apple maggot flies. In: Visser JH, Minks AK (eds) Proc. 5th Intern. Symp. Insect-Plant Relationships, PUDOC, Wageningen, Netherlands, pp 123–129
Prokopy RJ, Averill AL, Cooley SS, Roitberg CA (1982b) Associative learning in egglaying site selection by apple maggot flies. Science 218:76–77
Prokopy RJ, Kallet C, Cooley SS (1985) Fruit acceptance pattern of Rhagoletis pomonella flies from different geographic regions. Ann Entomol Soc Am 78:799–803
Prokopy RJ, Papaj DR, Cooley SS, Kallet C (1986) On the nature of learning in oviposition site acceptance by apple maggot flies. Anim Behav 34:98–107
Prokopy RJ, Aluja M, Green TA (1987) Dynamics of host odor and visual stimulus interaction in host finding behavior of apple maggot flies. In: Labeyrie V, Fabres G, Lachaise D (eds) Insects-Plants, Junk, Netherlands, pp 161–166
Rausher MD (1978) Search image for leaf shape in a butterfly. Science 200:1071–1073
Rausher MD (1984) The evolution of habitat preference in subdivided populations. Evolution 38:596–608
Reissig WH (1979) Survival of apple maggot larvae, Rhagoletis pomonella, in picked and unpicked apples. Canad Entomol 111:181–187
Reissig WH, Smith DC (1978) Bionomics of Rhagoletis pomonella in Crataegus. Ann Ent Soc Am 71:155–159
Rice WR (1984) Disruptive selection on habitat preference and the evolution of reproductive isolation: a simulation study. Evolution 38:1251–1260
Robert P (1985) A comparative study of some aspects of the reproduction of three Caryedon serratus strains in presence of its potential host plants. Oecologia 65:425–430
Roitberg BD, Cairl RS, Prokopy RJ (1985) Oviposition deterring pheromone influences dispersal distance in tephritid fruit flies. Entomol Exp Appl 35:217–220
Roitberg BD, Van Lenteren JC, Van Alphen JJM, Galis F, Prokopy RJ (1982) Foraging behavior of Rhagoletis pomonella, a parasite of hawthorn (Crataegus), in nature. J Anim Ecol 51:307–325
SAS Institute (1985) SAS user's guide: statistics: version 5. SAS Institute, Cary, N.C.
Shervis LJ, Boush GM, Koval CF (1970) Infestation of sour cherrics by the apple maggot: confirmation of a previously uncertain host status. J Econ Entomol 63:294–295
Smith DC, Prokopy RJ (1980) Mating behavior of Rhagoletis pomonella. VI. Site of early-season encounters. Canad Entomol 112:585–590
Stanek EJ III, Dichl SR, Dgetluck M, Stokes ME, Prokopy RJ (1987) Statistical methods for analyzing discrete responses of insects tested repeatedly. Environ Entomol 16:319–326
Stanton ML (1984) Short-term learning and the searching accuracy of egglaying butterflies. Anim Behav 32:33–40
Tabashnik BE, Wheelock H, Rainbolt JD, Watt WB (1981) Individual variation in oviposition preference in the butterfly, Colias eurytheme. Oecologia 50:225–230
Traynier RMM (1986) Visual learning in assays of sinigrin solution as an oviposition releaser for the cabbage butterfly, Pieris rapae. Entomol Exp Appl 40:25–33
Van den Water TPM (1983) A host race of the small ermine moth Yponomeuta padellus in Northern Europe. Netherlands J Zool 33:276–282
Vet LEM, Van Opzeeland K (1984) The influence of conditioning of olfactory microhabitat and host location in Asobara tabida and A. rufescens larval parasitoids of Drosophilidae. Oecologia 63:171–177
Via S (1986) Genetic covariance between oviposition preference and larval performance in an insect herbivore. Evolution 40:778–785
Walsh BD (1867) The apple worm and the apple maggot. J Hort 2:338–343
Wasserman SS (1986) Genetic variation in adaptation to foodplants among populations of the southern cowpea weevil Callosobruchus maculatus: evolution of oviposition preference. Entomol Exp Appl 42:201–212
Wasserman SS, Futuyma DJ (1981) Evolution of host plant utilization in laboratory populations of the southern cowpea weevil, Callosobruchus maculatus. Evolution 35:605–617
Wood TK, Guttman SI (1982) Ecological and behavioral basis for reproductive isolation in the sympatric Enchenopa binota complex. Evolution 36:233–242
Zwölfer H (1975) Arbildung und ökologische Differenzierung bei phytophagen Insekten. Verk Deutschen Zool Gesell 67:394–401
Zwölfer H, Bush GL (1984) Sympatrische and parapatrische Artbildung. Z Zool Syst Evol Forsch 22:211–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prokopy, R.J., Diehl, S.R. & Cooley, S.S. Behavioral evidence for host races in Rhagoletis pomonella flies. Oecologia 76, 138–147 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00379612
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00379612