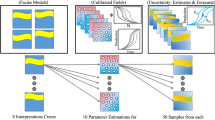
Abstract
In this paper, the application of a population-based sampling algorithm, i.e., differential evolution, in the geological well testing of a multi-layered faulted reservoir model is discussed. In this sense, the available multiple well test datasets are used to calibrate the geological model parameters rather than fitting simplified analytical models. In the exercise studied in this paper, the parameter space includes a range of geostatistical, petrophysical, and structural parameters. The differential evolution algorithm starts with an initial random population from the ranges of input variables and progresses with successive evaluation of the static models’ transient tests. The static models’ input parameters are perturbed to generate new populations, which can finally match the truth model well test derivative with lower misfits. The ensemble of population models (samples) along with the misfit values are used to highlight the value of well test data in reducing the uncertainty in the parameter space. A Bayesian framework is employed to implement the Markov chain Monte Carlo (McMC) methods to estimate the posterior distributions of the parameters. The results are confirmed by the sample-based Sobol sensitivity indices, which rank the influential parameters. To reduce the computational cost of the McMC and sensitivity indices, a cross-validated proxy model (i.e., Multivariate Adaptive Regression Spline) is constructed. The effect of different variants of differential evolution algorithm on the geological well test matching is also discussed. This paper provides a workflow for quantitative integration of well test data into the reservoir characterization workflow.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuchuk, F.J., Hollaender, F., Onur, M., Ramakrishnan, T.S.: Pressure transient formation and well testing:Convolution, Deconvolution and Nonlinear Estimation Elsevier Science Ltd (2010)
Landa, J.L., Kamal, M.M., Jenkins, C.D., Horne, R.N.: Reservoir characterization constrained to well test data: a field example. Paper presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Denver, Colorado 6-9 October (1996)
Hamdi, H.: Illumination of channelised fluvial reservoirs using geological well testing and seismic modelling. Unpub. PhD Thesis, Heriot-Watt University, p 247 (2012)
Corbett, P.W.M., Hamdi, H., Gurav, H.: Layered fluvial reservoirs with internal fluid cross flow: a well-connected family of well test pressure transient responses. Pet. Geosci. 18, 231–238 (2012)
Corbett, P.W.M., Geiger-Boschung, S., Borges, L.P., Garayev, M., Gonzalez, J.G., Valdez, C.: Limitations in numerical well test modelling of fractured carbonate rocks. Paper presented at the SPE EUROPEC/EAGE Annual Conference and Exhibition, Barcelona, Spain, 01 (2010)
Corbett, P.W.M., Mesmari, A., Stewart, G.: A method for using the naturally-occurring negative geoskin in the description of fluvial reservoirs (1996)
Massonnat, G.J., Bandiziol, D.: Interdependence between geology and well test interpretation. Paper presented at the SPE annual technical conference and exhibition, Dallas, Texas, 01 (1991)
Zheng, S., Corbett, P., Stewart, G.: The impact of variable formation thickness on pressure transient behavior and well test permeability in fluvial meander loop reservoirs. Paper presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Denver, Colorado, 01 (1996)
Hamdi, H., Ruelland, P., Bergey, P., Corbett, P.W.M.: Using geological well testing in the improved selection of appropriate reservoir models. Petroleum Geoscience (2013)
Landa, J.L.: Integration of well testing into reservoir characterization. In: Kamal, M.M (ed.) : Transient well testing, vol. 23, p 849. Society of Petroleum Engineers, USA (2009)
Corbett, P.W.M.: Petroleum geoengineering: integration of static and dynamic models, vol 12.DISC No. 12. EAGE/SEG (2009)
Bourdet, D.: Well test analysis—the use of advanced interpretation models. Elsevier (2002)
Zheng, S.Y., Corbett, P.W.M., Emery, A.: Geological interpretation of well test analysis: a case study from a fluvial reservoir in the Gulf of Thailand. J. Pet. Geol. 26(1), 49–64 (2003). doi:10.1111/j.1747-5457.2003.tb00017.x
Boutaud de la Combe, J.-L., Akinwumni, O., Dumay, C.D., Tachon, M.: Use of DST for effective dynamic appraisal: case studies from deep offshore West Africa and associated methodology. In: Paper presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Dallas, Texas, 01 (2005)
Ehlig-Economides, C.A., Joseph, J.A., Ambrose Jr. R.W., Norwood, C.: A modern approach to reservoir testing (includes associated papers 22220 and 22327). SPE J. Pet. Technol. 42(12) (1990). doi: 10.2118/19814-pa
Gok, I., Onur, M., Kuchuk, F.J.: Estimating formation properties in heterogeneous reservoirs using 3D interval pressure transient test and geostatistical data. Paper presented at the SPE Middle East Oil and Gas Show and Conference, Kingdom of Bahrain, 01 (2005)
Robertson, E., Corbett, P.W.M., Hurst, A., Satur, N., Cronin, B.T.: Synthetic well test modelling in a high net-to-gross outcrop system for turbidite reservoir description. Pet. Geosci. 8(1), 19–30 (2002). doi: 10.1144/petgeo.8.1.19
Bard, Y.: Nonlinear Parameter Estimation. Academic Press, NY (1974)
Gilman, J.R., Ozgen, C.: Reservoir simulation: history matching and forecasting. Society of petroleum engineers, Richardson, TX (2013)
Poli, R., Kennedy, J., Blackwell, T.: Particle swarm optimization. Swarm Intell. 1(1), 33–57 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11721-007-0002-0 10.1007/s11721-007-0002-0
Hajizadeh, Y., Christie, M.A., Demyanov, V.: Ant colony optimization for history matching. Paper presented at the EUROPEC/EAGE Conference and Exhibition, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8-11 (2009)
Storn, R., Price, K.: Differential evolution—a simple and efficient adaptive scheme for global optimization over continuous spaces. In: Technical Report TR-95-012. Berkeley (1995)
Oliver, D., Chen, Y.: Recent progress on reservoir history matching: a review. Comput. Geosci 15(1), 185–221 (2011). doi:10.1007/s10596-010-9194-2
Evensen, G.: Sequential data assimilation with a nonlinear quasi-geostrophic model using Monte Carlo methods to forecast error statistics. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 99(C5), 10143–10162 (1994). doi:10.1029/94JC00572
Bazargan, H., Christie, M., Tchelepi, H.: Efficient Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling using polynomial chaos expansion. Paper presented at the SPE Reservoir Simulation Symposium, The Woodlands, Texas, USA 18-20 February
Heidari, L., Gervais, V., Ravalec, M.L., Wackernagel, H.: History matching of petroleum reservoir models by the Ensemble Kalman Filter and parameterization methods. Comput. Geosci. 55(0), 84–95 (2013). doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2012.06.006
Lu, F., Morzfeld, M., Tu, X., Chorin, A.J.: Limitations of polynomial chaos expansions in the Bayesian solution of inverse problems. J. Comput. Phys. 282, 138–147 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.jcp.2014.11.010
Hajizadeh, Y., Christie, M.A., Demyanov, V.: Application of differential evolution as a new method for automatic history matching. Paper presented at the Kuwait International Petroleum Conference and Exhibition, Kuwait City, Kuwait,14-16 December
Wan, Z., Igusa, T.: Adaptive sampling for optimization under uncertainty. In: Proceedings of the 4th international symposium on uncertainty modelling and analysis, College Park, MD. p. 423. IEEE computer society, 943696 (2003)
Wetter, M., Wright, J.A.: A comparison of deterministic and probabilistic optimization algorithms for nonsmooth simulation based optimization. Build. Environ. 39(8), 989–999 (2004)
Nissen, V., Propach, J.: On the robustness of population-based versus point-based optimization in the presence of noise. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2(3), 107–119 (1998). doi:10.1109/4235.735433
Price, K., Storn, R.M., Lampinen, J.: Differential evolution: a practical approach to global optimization. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Bourdet, D., Whittle, T.M., Douglas, A.A., Pirard, Y.M.: A new set of type curves simplifies well test analysis. World Oil. 196(6), 95–106 (1983)
Ferraro, P., Verga, F.: Use of evolutionary algorithms in single and multi-objective optimization techniques for assisted history matching (2009)
Barker, J.W., Cuypers, M., Holden, L.: Quantifying uncertainty in production forecasts: another look at the PUNQ-S3 Problem. SPE J. 6(4), 433–441 (2001). doi:10.2118/74707-pa
Erbaş, D., Christie, M.: Comment la stratégie de l’échantillonnage affecte-t-elle les estimations d’incertitude ? Oil & Gas Science and Technology -. IFP Rev. 62(2), 155–167 (2007)
Alpak, F.O., Kats, F.v.: Stochastic history matching of a deepwater turbidite reservoir. Paper presented at the SPE Reservoir Simulation Symposium, The Woodlands, Texas, 2-4 (2009)
Kruschke, J.: Doing bayesian data analysis: A tutorial with R and Bugs. Academic Press (2010)
Gamerman, D.: Markov chain Monte Carlo: stochastic simulation for Bayesian inference. Chapman & Hall, London (1997)
Shonkwiler, R.W., Mendivil, F.: Explorations in monte carlo methods. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Tong, C.: PSUADE. In: Center for applied scientific computing lawrence livermore national laboratory, livermore, CA (2013)
Geman, S., Geman, D.: Stochastic relaxation, Gibbs distributions, and the Bayesian restoration of images. Pattern analysis and machine intelligence. IEEE Trans. PAMI 6(6), 721–741 (1984). doi:10.1109/TPAMI.1984.4767596
Koziel, S., Leifsson, L.: Surrogate-based modeling and optimization. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Forrester, A., Sobester, A., Keane, A.: Engineering design via surrogate modelling: A practical guide. Wiley, New York (2008)
Friedman, J.H.: Multivariate adaptive regression splines. Ann. Stat 19(1), 1–67 (1991). doi:10.2307/2241837
Zhan, C.-S., Song, X.-M., Xia, J., Tong, C.: An efficient integrated approach for global sensitivity analysis of hydrological model parameters. Environ. Model Softw. 41(0), 39–52 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2012.10.009
Balshi, M.S., McGuire, A.D., Duffy, P., Flannigan, M., Walsh, J., Melillo, J.: Assessing the response of area burned to changing climate in western boreal North America using a multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS) approach. Glob. Chang. Biol. 15(3), 578–600 (2009). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01679.x
Leathwick, J.R., Rowe, D., Richardson, J., Elith, J., Hastie, T.: Using multivariate adaptive regression splines to predict the distributions of New Zealand’s freshwater diadromous fish. Freshw. Biol. 50(12), 2034–2052 (2005). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2005.01448.x
Hamdi, H., Hajizadeh, Y., Azimi, J., Sousa, M.C.: Sequential Bayesian optimization coupled with differential evolution for geological well testing. Paper presented at the 76th EAGE Conference and Exhibition 2014 Amsterdam, the Netherlands,16–19 (2014)
Cheng, M.-Y., Cao, M.-T.: Accurately predicting building energy performance using evolutionary multivariate adaptive regression splines. Appl. Soft Comput. 22(0), 178–188 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2014.05.015
Hamdi, H., Jamiolahmady, M., Corbett, P.W.M.: Modeling the interfering effects of gas condensate and geological heterogeneities on transient pressure response. SPE J. 18(4), 656–669 (2013). doi: 10.2118/143613-pa
Deutsch, C.V.: Geostatistical reservoir modelling. Oxford University Press, New York (2002)
Doyen, P.: Seismic reservoir characterization: an earth modelling perspective. EAGE publications (2007)
Dubrule, O.: Geostatistics for seismic data integration in Earth models. Distinguished instructor series 6. Society of Exploration Geophysics, Tulsa, USA (2003)
Deutsch, C.V., Journel, A.G.: GSLIB: geostatistical software library and user’s guide. Oxford University Press, New York (1992)
Corbett, P.W.M., Hamdi, H., Gurav, H.: Layered fluvial reservoirs with internal fluid cross flow: a well-connected family of well test pressure transient responses. Pet. Geosci. 18, 219–229 (2012)
Chiles, J.P., Delfiner, P.: Geostatistics: modeling spatial uncertainty, vol. 713 of wiley series in probability and statistics. Wiley, New Jersey (2012)
Oliver, M.A., Webster, R.: Basic steps in geostatistics: the variogram and kriging. Springer, Berlin (2015)
Pyrcz, M.J., Deutsch, C.V.: Geostatistical reservoir modeling. Oxford University Press, London (2014)
Pedersen, M.E.H.: Good parameters for differential evolution. In: vol. Technical Report HL1002 (2010)
Hajizadeh, Y.: Population-based algorithms for improved history matching and uncertainty quantification of petroleum reservoirs Heriot-Watt University (2011)
Hamdi, H., Behmanesh, H., Clarkson, C.R., Costa Sousa, M.: Using differential evolution for compositional history-matching of a tight gas condensate well in the Montney Formation in western Canada. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering (in press) (2015)
Tvrdik, J.: Differential evolution: competitive setting of control parameters. In: Proceedings of the International Multiconference on Computer Science and Information Technology, 207–213 (2006). http://www.citeulike.org/user/andizuend/article/8501230
McKay, M.D., Beckman, R.J., Conover, W.J.: A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code. Technometrics 21(2), 239–245 (1979). doi: 10.2307/1268522
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45(1), 5–32 (2001). doi:10.1023/A:1010933404324
Kohavi, R.: A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 14th international joint conference on Artificial intelligence- volume 2,Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Elisseeff, A., Pontil, M.: Leave-one-out error and stability of learning algorithms with applications. In: Suykens, J., Horvath, G., Basu, S., Micchelli, C., Vandewalle, J. (eds.) Learning Theory and Practice. IOS Press, Amsterdam (2002)
Homma, T., Saltelli, A.: Importance measures in global sensitivity analysis of nonlinear models. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf 52(1), 1–17 (1996). doi:10.1016/0951-8320(96)00002-6
Sobol’, I.M.: On the distribution of points in a cube and the approximate evaluation of integrals. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 7(4), 86–112 (1967). doi:10.1016/0041-5553(67)90144-9
van Riel, N.A.W.: Dynamic modelling and analysis of biochemical networks: mechanism-based models and model-based experiments. Brief. Bioinform 7(4), 364–374 (2006)
Saltelli, A.: Sensitivity analysis for importance assessment. Risk Anal. 22(3), 579–590 (2002). doi: 10.1111/02724332.00040
Shukhman, B.V., Sobol’, I.M.: Integration with quasirandom sequences: numerical experience. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 06(02), 263–275 (1995). doi:10.1142/S0129183195000204
Bollen, K., Stine, R.: Direct and indirect effects: classical and bootstrap estimates of variability. Sociol. Methodol. 20, 115–140 (1990) http://www.citeulike.org/user/ctacmo/article/553224
Tong, C., Graziani, F.: A Practical global sensitivity analysis methodology for multi-physics applications. In: Graziani, F. (ed.) Computational Methods in Transport: Verification and Validation, vol. 62. Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering, 277-299. Springer Berlin Heidelberg (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamdi, H., Hajizadeh, Y. & Costa Sousa, M. Population-based sampling methods for geological well testing. Comput Geosci 19, 1089–1107 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-015-9522-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-015-9522-7