Abstract
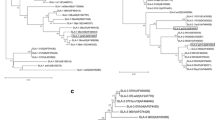
To study the molecular characteristics of swine leukocyte antigen (SLA) class I from the Hebao pig, a rare inbreed in China, a pair of primers was designed to amplify the SLA-2 gene (SLA-2-HB) and then the molecular characteristics of the gene were analyzed by computer. After cloning, sequencing and computer analysis, four SLA-2-HB alleles were found, all of 1119 bp. Sites 3–1097 were an open reading frame encoding 364 amino acids with two sets of intra-chain disulfide bonds comprising four cysteines situated in sites 125, 188, 227 and 283. By alignment of SLA-2-HB sequences with other SLA-2 alleles in the DNA Data Bank of Japan/European Molecular Biology Laboratory/GenBank database, nine key variable amino acid sites were found in the extracellular domain of the SLA-2-HB alleles at sites 23(F), 24(I), 43(A), 44(K), 50(Q), 73(N), 95(I), 114(R) and 216(S), which could be used to differentiate other SLA-2 alleles. The amino acid identities between SLA-2-HB and other SLA-2, SLA-3 and SLA-1 alleles were 87.1–97.0%, 85.0–93.9% and 83.3–88.6%, respectively. The phylogenetic tree of SLA-2-HB showed that it was relatively independent of the other SLA-2 genes. Furthermore, the SLA-2-HB alleles were similar to HLA-B15 and HLA-A2 functional domains and preserved some functional sites of HLA-A2. It was concluded that SLA-2-HB is an allele of SLA-2 and that the Hebao pig might have evolved independently in China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Oosterhout, C., A New Theory of MHC Evolution: Beyond Selection on the Immune Genes, Proc. Biol. Sci., 2009, vol. 276, pp. 657–665.
Trowsdale, J. and Campbell, R.D., Complexity in the Major Histocompatibility Complex, Eur. J. Immunogenet., 1992, vol. 19, pp. 45–55.
Vaiman, M., Renard, C., LaFage, P., et al., Evidence for a histocompatibility system in swine (SL-A). Transplantation, 1970, vol. 10, pp. 155–164.
Renard, C., Hart, E., Sehra, H., et al., The Genomic Sequence and Analysis of the Swine Major Histocompatibility Complex, Genomics, 2006, vol. 88, pp. 96–110.
Ho, C.S., Lunney, J.K., Ando, A., et al., Nomenclature for Factors of the SLA System, Update 2008, Tissue Antigens, 2009, vol. 73, pp. 307–315.
Chardon, P., Rogel-Gaillard, C., Peelman, L., et al., Physical Organization of the Pig Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Region, Immunogenetics, 1999, vol. 50, pp. 344–348.
Smith, D.M., Lunney, J.K., Martens, G.W., et al., Nomenclature for Factors of the SLA Class-I System, 2004, Tissue Antigens, 2005, vol. 65, pp. 136–149.
Ando, A., Kawata, H., Shigenari, A., et al., Genetic Polymorphism of the Swine Major Histocompatibility Complex (SLA) Class I Genes, SLA-1, -2 and -3, Immunogenetics, 2003, vol. 55, pp. 583–593.
Matsumura, M., Fremont, D.H., Peterson, P.A., et al., Emerging Principles for the Recognition of Peptide Antigens by MHC Class I Molecules, Science, 1992, vol. 257, pp. 927–934.
Meyer-Olson, D., Brady, K.W., Bartman, T.M., et al., Fluctuations of Functionally Distinct CD8+ T-cell Clonotypes Demonstrate Flexibility of the HIV-Specific TCR Repertoire, Blood, 2006, vol. 107, pp. 2373–2383.
Sun, J., Leahy, D.J., and Kavathas, P.B., Interaction between CD8 and Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I Mediated by Multiple Contact Surfaces That Include the Alpha 2 and Alpha 3 Domains of MHC Class I, J. Exp. Med., 1995, vol. 182, pp. 1275–1280.
Salter, R.D., Benjamin, R.J., Wesley, P.K., et al., A Binding Site for the T-Cell Co-Receptor CD8 on the Alpha 3 Domain of HLA-A2, Nature, 1990, vol. 345, pp. 41–46.
Gao, F.S., Fang, Q.M., Li, Y.G., et al., Reconstruction of a Swine SLA-I Protein Complex and Determination of Binding Nonameric Peptides Derived from the Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus, Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol., 2006, vol. 113, pp. 328–338.
Yan, R.Q., Li, X.S., Yang, T.Y., and Xia, C., Characterization of BF2 and beta2m in Three Chinese Chicken Lines, Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol., 2005, vol. 108, pp. 417–425.
Gao, F.S., Xu, C.B., Long, Y.H., and Xia, C., Secondary Structure and 3D Homology Modeling of Swine Leukocyte Antigen Class 2 (SLA-2) Molecules, Immunobiology, 2009, vol. 214, pp. 475–482.
Bjorkman, P.J., Saper, M. A., Samraoui, B., et al., Structure of the Human Class I Histocompatibility Antigen, HLA-A2, Nature, 1987, vol. 329, pp. 506–512.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, F.S., Bai, J., Zhang, X.H. et al. Molecular characteristics of the SLA-2 gene from Chinese Hebao pigs. Russ J Genet 48, 224–229 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795412010073
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1022795412010073