Abstract
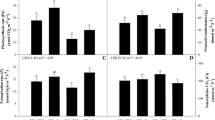
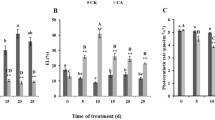
We evaluated the effect of TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) on metabolic and molecular traits involved in photosynthesis of two chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) genotypes (Sel96Th11439, cold tolerant genotype, and ILC533, cold susceptible one) during cold stress (4°C). The data analysis showed that hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content increased more extremely under cold in susceptible plants than in tolerant ones. TiO2 NPs caused a significant decrease in H2O2 content so that tolerant plants showed lower H2O2 content than susceptible ones. This decrease often was accompanied with higher metabolic potential for photosynthesis particularly in tolerant plants. Under thermal treatments, TiO2 NPs significantly increased the activity of Rubisco compared to control plants although its activity decreased significantly under cold comparison with optimum temperature. Along with a decreasing in H2O2 content, more photosynthetic activity at the transcription levels of CaLRubisco, CaSRubisco and Cachlorophyll a/b-binding protein genes in a simultaneous manner particularly in plants treated with TiO2 NPs ensure the acclimation of plants to survival or recovery. Under such status, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) activity increased particularly in tolerant plants compared to susceptible ones as well as in plants treated with TiO2 NPs compared to control plants, indicating probably an increase in energy efficiency through different mechanisms like malate. Thus, chickpea tolerance responses to cold stress may occur after TiO2 NPs application on plants through managing the pressure of temperature decline damage and altered metabolism for plant growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Chl:
-
chlorophyll
- NPs:
-
nanoparticles
- PEPC:
-
phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
References
Castiglione, M.R., Giorgetti, L., Cremonini, R., Bottega, S., and Spanò, C., Impact of TiO2 nanoparticles on Vicia narbonensis L.: potential toxicity effects, Protoplasma, 2014, vol. 251, pp. 1471–1479.
Mohammadi, R., Maali-Amiri, R., and Abbasi, A., Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on chickpea response to cold stress, Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 2013, vol. 152, pp. 403–410.
Mohammadi, R., Maali-Amiri, R., and Mantri, N., Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on oxidative damage and antioxidant defense systems in chickpea seedlings during cold stress, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2014, vol. 61, pp. 768–775.
Zhou, B., Sanz-Sáes, Á., Elazab, A., Shen, T., Sánchez-Bragado, R., Bort, J., Serret, M.D., and Araus, J.L., Physiological traits contributed to the recent increase in yield potential of winter wheat from Henan province, China, J. Integr. Plant Biol., 2014, vol. 56, pp. 492–504.
Parry, M.A.J., Reynolds, M., Salvucci, M.E., Raines, C., Andralojc, P.J., Zhu, X.G., Price, G.D., Condon, A.G., and Furbank, R.T., Raising yield potential of wheat. II. Increasing photosynthetic capacity and efficiency, J. Exp. Bot., 2011, vol. 62, pp. 453–467.
Galmés, J., Perdomo, J.A., Flexas, J., and Whitney, S.M., Photosynthetic characterization of Rubisco transplantomic lines reveals alterations on photochemistry and mesophyll conductance, Photosynth. Res., 2013, vol. 115, pp. 153–166.
Flexas, J., Bota, J., Loreto, F., Cornic, G., and Sharkey, T., Diffusive and metabolic limitations to photosynthesis under drought and salinity in C3 plants, Plant Biol., 2004, vol. 6, pp. 269–279.
Kazemi-Shahandashti, S.S., Maali-Amiri, R., Zeinali, H., Khazaei, M., Talei, A., and Ramezanpour, S.S., Effect of short-term cold stress on oxidative damage and transcript accumulation of defense-related genes in chickpea seedlings, J. Plant Physiol., 2014, vol. 171, pp. 1106–1116.
Kramer, D.M. and Evans, J.R., The importance of energy balance in improving photosynthetic productivity, Plant Physiol., 2011, vol. 155, pp. 70–78.
Xuming, W., Fengqing, G., Linglan, M., Jie, L., Sitao, Y., Ping, Y., and Fashui, H., Effects of nanoanatase on ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase mRNA expression in spinach, Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 2008, vol. 126, pp. 280–289.
Singh, D., Kumar, S., Singh, S.C., Lal, B., and Singh, N.B., Applications of liquid assisted pulsed laser ablation synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles on germination, growth and biochemical parameters of Brassica oleracea var. capitata, Sci. Adv. Mather., 2012, vol. 4, pp. 522–531.
Ghosh, M., Bandyopadhyay, M., and Mukherjee, A., Genotoxicity of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticle at two trophic levels: plant and human lymphocytes, Chemosphere, 2010, vol. 81, pp. 1253–1262.
Lilley, R.M. and Walker, D.A., An improved spectrophotometric assay for ribulosebisphosphate carboxilase, Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 1974, vol. 385, pp. 226–229.
Sayre, R.T. and Kennedy, R.A., Photosynthetic enzyme activities and localization in Mollugo veticillata populations differing in the levels of C3 and C4 cycle operation, Plant Physiol., 1979, vol. 64, pp. 293–299.
Nazari, M.R., Habibpour F., Mehraban, F., Maali Amiri, R., and Zeinali H., Haneghah, H. Change in antioxidant responses against oxidative damage in black chickpea following cold acclimation, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2012, vol. 59, pp. 183–189.
Livak, K.J. and Schmittgen, T.D., Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–CT method, Methods, 2001, vol. 25, pp. 402–408.
Lei, Z., Mingyu, S., Xiao, W., Chao, L., Chunxiang, Q., Liang, C., Hao, H., Xiaoqing, L., and Fashui, H., Antioxidant stress is promoted by nano-anatase in spinach chloroplasts under UV-B radiation, Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 2008, vol. 121, pp. 69–79.
Backhausen, J.E., Kitzmann, C., Horton, P., and Scheibe, R., Electron acceptors in isolated intact spinach chloroplasts act hierarchically to prevent overreduction and competition for electrons, Photosynth. Res., 2000, vol. 64, pp. 1–13.
He, Y., Yu, C., Zhou, L., Chen, Y., Liu, A., Jin, J., Hong, J., Qi, Y., and Jiang, D., Rubisco decrease is involved in chloroplast protrusion and Rubisco-containing body formation in soybean (Glycine max) under salt stress, Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2014, vol. 74, pp. 118–124.
Flexas, J., Ribas-Carbó, V., Bota, J., Galméj M., Henkle, M., Martinez-Cañellas s., and Medrano, H., Decreased Rubisco activity during water stress is not induced by decreased relative water content but related to conditions of low stomatal conductance and chloroplast CO2 concentration, New Phytol., 2006, vol. 172, pp. 73–82.
Parry, M.A.J., Madgwick, P.J., Carvalho, J.F.C., and Andralojc, P.J., Prospects for increasing photosynthesis by overcoming the limitations of Rubisco, J. Agric. Sci., 2007, vol. 145, pp. 31–43.
Parry, M.A.J., Keys, A.J., Madgwick, P.J., CarmoSilva, A.E., and Andralojc, P.J., Rubisco regulation: a role for inhibitors, J. Exp. Bot., 2008, vol. 59, pp. 1569–1580.
Gao, F., Liu, C., Qu, C., Zheng, L., Yang, F., Su, M., and Hong, F., Was improvement of spinach growth by nano-TiO2 treatment related to the changes of Rubisco activase? Biometals, 2008, vol. 21, pp. 211–217.
Suzuki, Y. and Makino, A., Translational down-regulation of RBCL is operative in the coordinated expression of Rubisco genes in senescent leaves in rice, J. Exp. Bot., 2013, vol. 64, pp. 1145–1152.
Liu, H.M., Fang, L., Che, Y.S., Wu, F.Z., and Yang, C.P., Protein expression patterns in two Spiraea species in response to cold treatment, Mol. Biol. Rep., 2014, vol. 41, pp. 4533–4547.
Hahn, M. and Walbot, V., Effects of cold-treatment on protein synthesis and mRNA levels in rice leaves, Plant Physiol., 1989, vol. 91, pp. 930–938.
Xia, Y., Ning, Z., Bai, G., Li, R., Yan, G., Siddique, K.H., Baum, M., and Guo, P., Allelic variations of a light harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding protein gene (Lhcb1) associated with agronomic traits in barley, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7: e37573.
González, M.C., Sánchez, R., and Cejudo, F.J., Abiotic stresses affecting water balance induce phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase expression in roots of wheat seedlings, Planta, 2003, vol. 216, pp. 985–992.
Ermolayev, V., Weschke, W., and Manteuffel, R., Comparison of Al-induced gene expression in sensitive and tolerant soybean cultivars, J. Exp. Bot., 2003, vol. 54, pp. 2745–2756.
Soussi, M., Lluch, C., Ocana, A., and Norero, A., Comparative study of nitrogen fixation and carbon metabolism in two chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars under salt stress, J. Exp. Bot., 1999, vol. 50, pp. 1701–1708.
Chia, D.W., Yoder, T.J., Reiter, W.D., and Gibson, S.I., Fumaric acid: an overlooked form of fixed carbon in Arabidopsis and other plant species, Planta, 2000, vol. 211, pp. 743–751.
Ryšlavá, H., Müller, K., Semorádová, Š., Synková, H., and Čeřovská, N., Photosynthesis and activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in Nicotiana tabacum L. leaves infected by potato virus A and potato virus Y, Photosynthetica, 2003, vol. 41, pp. 357–363.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasanpour, H., Maali-Amir, R. & Zeinali, H. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on metabolic limitations to photosynthesis under cold in chickpea. Russ J Plant Physiol 62, 779–787 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443715060096
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443715060096