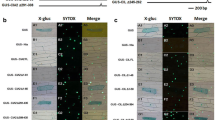
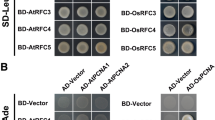
Abstract
TFIIA has initially been identified as a component of transcription initiation complex of RNA polymerase II. Its role in transcription has been controversial. In this paper, we report the characterization and functional analysis of both the Arabidopsis TFIIA large and small subunits. Sequence analysis revealed that Arabidopsis TFIIA is structurally more related to animal than to yeast counterparts. Arabidopsis has at least two genes for the large subunit and one for the small subunit. Both types of genes are constitutively transcribed in various plant organs. The proteins encoded by the cDNA interact each other in yeast 2-hybrid system. Only the N-terminal part of the large subunit is necessary for the interaction with the small subunit. Recombinant Arabidopsis TFIIA polypeptides bind to TBP-DNA complex in gel shift assays. The large subunit of TFIIA can stimulate transcription in yeast and in plant cells when fused to a DNA-binding domain binding to cis sequences upstream of a minimal promoter. This trans-activating activity is localized to a 35 amino acid segment within the evolutionarily unconserved central region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aible DT, Hansen KE, Mueller CGF, Lane WS, Throner J, Hahn S: Mot1, a globle repressor of RNA polymerase II transcription, inhibits TBP binding to DNA by an ATP-dependent mechanism. Genes Dev 8: 857–867(1994).
Baldwin DA, Gurley WB: Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding transcription factor IIB from Arabidopsis and soybean. Plant J 10: 561–568(1996).
Buratowski S, Hahn S, Sharp PA: Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNApolymerase II. Cell 56: 549–561 (1989).
Burley SK, Roeder RG: Biochemistry and structural biology of transcription factor IID (TFIID). Annu Rev Biochem 65: 769–799(1996).
Cortes P, Flores O, Reinberg D: Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: Purification and analysis of transcription factor IIA and identification of transcription factor III. Mol Cell Biol 12: 413–421(1992).
DeJong J, Roeder RG: A single cDNA hTFIIA/α encodes both the p35 and p19 subunits of human TFIIA. Genes Dev 7: 2220–2234(1993).
Emami KH, Jain A, Smale ST: Mechanism of synergy between TATA and initiator: Synergistic binding of TFIID following a putative TFIIA-induced isomerization. Genes Dev 11: 3007–3019 (1997).
Gasch A, Hoffmann S, Horikoshi M, Roeder RG, Chua NH: Arabidopsis thaliana contains two genes for TFIID. Nature 346: 390–394(1990).
Ge H, Roeder RG: Purification, cloning, and characterization of a human coactivator, PC4, that mediates transcriptional activation of class II genes. Cell 78: 513–523(1994).
Geiger JH, Hahn S, Lee S, Sigler PB: Crystal structure of the yeast TFIIA/TBP/DNA complex. Science 272: 830–836 (1996).
Guarente L: Transcriptional coactivators in yeast and beyond. Trends Biochem Sci 20: 517–521(1995).
Hansen SK, Tjian R: TAFs and TFIIA mediate differential utilization of the tandem Adh promoters. Cell 82: 565–575 (1995).
Inostroza JA, Mermelstein FH, Ha I, Lane WS, Reinberg D: Dr1, a TATA-binding associated prosphoprotein and inhibitor of class II gene transcription. Cell 70: 477- 489 (1992).
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW: GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6: 3901–3907(1987).
Kang JJ, Aible DT, Ranish JA, Hahn S: Analysis of yeast transcription factor TFIIA: Distinct functional regions and a polymerase II-specific role in basal and activated transcription. Mol Cell Biol 15: 1234–1243(1995).
Kobayashi N, Boyer TG, Berk AJ: A class of activation domains interacts directly with TFIIA and stimulates TFIIATFIID-promoter complex assembly. Mol Cell Biol 15: 6465–6473 (1995).
Koleske AJ, Sharp P: The RNA polymerase II holoenzyme and its implications for gene regulation. Trends Biochem Sci 20: 113–116(1995).
Lieberman PM, Ozer J, Gursel DB: Requirement for transcription factor IIA (TFIIA)-TFIID recruitment by an activator depends on promoter structure and template competition. Mol Cell Biol 17: 6624–6632(1997).
Ma D, Waranabe H, Mermelstein F, Admon A, Oguri K, Sun X, Wada T, Imai T, Shiroya T, Reinberg D, Handa H: Isolation of a cDNA encoding the largest subunit of TFIIA reveals functions important for activated transcription. Genes Dev 7: 2246–2257(1993).
Matsui T, Segall J, Weil A, Roeder RG: Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem 255: 11992–11996(1980).
Orphanides G, Lagrange T, Reinberg D: The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev 10: 2657–2683 (1996).
Oze J, Moore PA, Bolden AH, Lee A, Rosen CA, Leiberman PM: Molecular cloning of the small ( ) subunit of human TFIIA reveals functions critical for activated transcription. Genes Dev 8: 2324–2335(1994).
Ptashne M, Gann A: Transcriptional activation by recruitment. Nature 386: 569–577(1997).
Ranish JA, Lane WS, Hahn S: Isolation of two genes that encode subunits of the yeast transcription factor IIA. Science 255: 1127–1129(1992).
Ranish JA, Hahn S: Transcription: basal factors and activation. Curr Opin Genet Dev 6: 151–158(1996).
Roeder RG: The role of general initiation factors in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem Sci 21: 327–335 (1996).
Sambrook J, Fritsch RF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Saier F, Tjian R: Mechanisms of transcriptional activation: differences and similarities between yeast, Drosophila, and man. Curr Opin Genet Dev 7: 176–181(1997).
Shykind BM, Kim J, Sharp PA: Activation of the TFIID-TFIIA complex with HMG-2. Genes Dev 9: 1354–1365(1995).
Sun X, Ma D, Sheldon M, Yeung K, Reinberg D: Reconstitution of human TFIIA activity from recombinant polypeptides: a role in TFIID-mediated transcription. Genes Dev 8: 2336–2348(1994).
Tan S, Hunziker Y, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ: Crystal structure of a yeast TFIIA/TBP/DNA complex. Nature 381: 127–134 (1996).
Tjian R, Maniatis T: Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell 77: 5–8(1994).
Triezenberg SJ:Structure and function of transcriptional activation domains. Curr Opin Genet Dev 5: 190–196(1995).
Verrijzer CP, Tjian R: TAFs mediate transcriptional activation and promoter selectivity. Trends Biochem Sci 21: 338–342 (1996).
Yokomori K, Admon A, Goodrich JA, Chen JL, Tjian R: Drosophila TFIIA-L is processed into two subunits that are associated with the TBP/TAF complex. Genes Dev 7: 2235–2245 (1993).
Yokomori K, Zeidler MP, Chen JL, Verrijzer CP, Mlodzic M, Tjian R: Drosophila TFIIA directs cooperative DNA binding with TBP and mediates transcription activation. Genes Dev 8: 2313–2323(1994).
Zawel L, Reinberg D: Advances in RNA polymerase II transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol 4: 488–495(1992).
Zawel L, Reinberg D: Common themes in assembly and function of eukaryotic transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem 64: 533–561(1995).
Zeidler MP, Yokomori K, Tjian R, Mlodzik M: Drosophila TFIIA-S is up-regulated and required during Ras-mediated photoreceptor determination. Genes Dev 10: 50–59(1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YF., Le Gourierrec, J., Torki, M. et al. Characterization and functional analysis of Arabidopsis TFIIA reveal that the evolutionarily unconserved region of the large subunit has a transcription activation domain. Plant Mol Biol 39, 515–525 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006139724849
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006139724849