Abstract
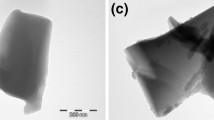
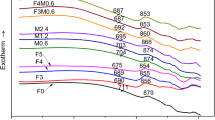
The research objective of the study was to increase the current understanding about how oxide compositions (CaO, MgO and SiO2 ratios) influence the (1) crystallization behaviour of starting frits, and subsequently (2) morphological features of diopside crystals, formed after wall tile industrial firing. It has been shown that the replacement of CaO and MgO at the expense of SiO2 causes a decrease in the crystallization temperature. The increase of CaO content also results in lower softening temperature and faster densification. SEM results of the glazes showed that spherical and needle-shape diopside crystals were formed during heating. While increase of MgO content results in finer needle-shape crystals, increase of CaO results in coarser spherical-shape crystals. Although all the glaze formulations showed a high whiteness index, lower densification and higher crystallization in the glazes caused an unfired matt appearance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leonelli, C., Manfredini, T., Siligardi, C.: New tile glaze families based on glass ceramic systems. International Ceramics Journal. 31–35 (2002), April)
Quinteiro E, Boschi AO, Leonelli C, Manfredini T, Siligardi C. Glass-ceramic Systems Compatible with the Firing Conditions Used in the Ceramic Tile Industry. In: Proceedings of Qualicer 2002, Castellon, Spain. (2002), 301–311
Yekta, B.E., Alizadeh, P., Rezazadeh, L.: Floor tile glass-ceramic glaze for improvement of glaze surface properties. J Eur Ceram Soc. 26, 3809–3812 (2006)
Kara F, Cavac M., Diopside Based White Porcelain Tiles. In: Proceedings of Qualicer 2002, Castellon, Spain.(2002); P 161–164
Cavac, M., Kara, F.: High strength diopside containing porcelain tiles. Key Eng Mater. 264-268, 1487–1490 (2004)
Cavac M, Kara F., Alternatif Duvar Karosu Angop Kompozisyonları. In: Proceedings of V. Ceramics Congress with International Participations, (2001), P 123
Reinosa, J.J., Rubio-Marcos, F., Solera, E., Bengochea, M.A., Fernandez, J.F.: Sintering behaviour of nanostructured glass-ceramic glazes. Ceram Int. 36, 1845–1850 (2010)
Rezvani, M., Eftekhari-Yekta, B., Solati-Hashjin, M., Marghussian, V.K.: Effect of Cr2O3, Fe2O3 and TiO2 Nucleants on the crystallization behaviour of SiO2-Al2O3-CaO-MgO(R2O) glass-ceramics. Ceram Int. 31, 75–80 (2005)
Baldi, G., Generali, E., Leonelli, C., Manfredini, T., Pellacani, G., Siligardi, C.: Effects of nucleating agents on diopside crystallization in new glass-ceramics for tile-glaze application. J Mater Sci. 30, 3251–3255 (1995)
Khater, G.: Influence of Cr2O3, LiF, CaF2, and TiO2 Nucleants on the crystallization behavior and microstructure of glass-ceramics based on blast-furnace slag. Ceram Int. 37, 2193–2199 (2011)
Romero, M., Rincon, J., Acosta, A.m.: Effect of iron oxide content on the crystallization of a diopside glass-ceramic glaze. J Eur Ceram Soc. 22, 883–890 (2002)
Alizadeh, P., Marghussian, V.K.: Effect of nucleating agents on the crystallization behaviour and microstructure of SiO2–CaO–MgO (Na2O) glass-ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc. 20, 775–782 (2000)
Guo, X., Cai, X., Song, J., Yang, G., Yang, H.: Crystallization and microstructure of CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 glass ceramics containing complex nucleating agents. J Non-Cryst Solids. 405, 63–37 (2014)
Tulyaganov, D.U., Agathopoulos, S., Ventura, J.M., Karakassides, M.A., Fabrichnaya, O., Ferreira, J.M.F.: Synthesis of glass-ceramics in the CaO–MgO–SiO2 system with B2O3, P2O5, Na2O and CaF2 additives. J Eur Ceram Soc. 26, 1463–1471 (2006)
Torres, F., Alarcon, J.: Pyroxene-based glass-ceramics as glazes for floor tiles. J Eur Ceram Soc. 25, 349–355 (2005)
Torres, F.J., Alarcon, J.: Mechanism of crystallization of pyroxene-based glass-ceramic glazes. J Eur Ceram Soc. 347, 45–51 (2004)
Abdel-Hameed, S.A.M., El-kheshen, A.A.: Thermal and chemical properties of diopside-wollastonite glass-ceramics in the SiO2-CaO-MgO system from raw materials. Ceram Int. 29, 265–269 (2003)
Ma, J., Chen, C.Z., Wang, D.G., Shao, X., Wang, C.Z., Zhang, H.M.: Effect of MgO addition on the crystallization and in vitro bioactivity of glass ceramics in the CaO–MgO–SiO2–P2O5 system. Ceram Int. 38, 6677–6684 (2012)
Fröberg, L., Kronberg, T., Hupa, L., Hupa, M.: Influence of firing parameters on phase composition of raw glazes. J Eur Ceram Soc. 27, 1671–1675 (2007)
Fröberg, L., Hupa, L., Hupa, M.: Corrosion of the crystalline phases of matte glazes in aqueous solutions. J Eur Ceram Soc. 29, 7–14 (2009)
Xiao H, Cheng Y, Yu L, Liu HA study on the preparation of CMAS glass–ceramics by in situ crystallization. Materials science and engineering (2006), A 431, 191–195
Pekkan, K., Karasu, B.: Zircon-free frits suitable for single fast-firing opaque wall tile glazes and their industrial productions. J Eur Ceram Soc. 29, 1571–1578 (2009)
Rasteiro M. G, Gassman T, Santos R, Antunes E, Crystalline phase characterization of glass-ceramic glazes. Ceramics International (2006)
Branda, F., Arcobello-Varlese, F., Costantini, A., Luciani, G.: Effect of the substitution of M2O3 (M = La, Y, In, Ga, Al) for CaO on the bioactivity of 2.5CaO.2SiO2 glass. Biomaterials. 23, 711–716 (2002)
Salman, S.M., Darwish, H., Mahdy, E.A.: The influence of Al2O3, MgO and ZnO on the crystallization characteristics and properties of lithium calcium silicate glasses and glass-ceramics. Mater Chem Phys. 112, 945–953 (2008)
Alizadeh, P., Marghussian, V.K.: The effect of compositional changes on the crystallization behaviour and mechanical properties of diopside-wollastonite glass-ceramics in the SiO2-CaO-MgO (Na2O) system. J Eur Ceram Soc. 20, 765–773 (2000)
Ma, J., Chen, C.Z., Wang, D.G., Shi, J.Z.: Textural and structural studies of Sol-gel derived SiO2-CaO-P2O5-MgO glasses by substitution of MgO for CaO. Mater Sci Eng. 30, 886–890 (2010)
Chen, G.-H.: Effect of replacement of MgO by CaO on sintering, crystallization and properties of MgO–Al2O3–SiO2 system glass-ceramics. J Mater Sci. 42, 7239–7244 (2007)
Acknowledgments
The financial support from Turkish State Planning Organization through the Industrial Doctorate Programme for this project and Yurtbay Seramik Company are also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suvaci, E., Yildiz, B. Roles of CaO, MgO and SiO2 on crystallization and microstructure development in diopside-based glass-ceramic glazes under industrial fast-firing condition. J Aust Ceram Soc 53, 75–81 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-016-0011-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-016-0011-9