Abstract
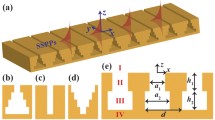
Talbot effect in a metallic groove array is observed numerically based on finite element method (FEM) and verified theoretically based on non-paraxial approximation. Grooves in the metallic layer are separated from backside with a narrow gap that is smaller than surface plasmon (SP) penetration depth in metal. At certain circumstances, SPs tunnel through the gap and constructively interfere beneath the metallic layer. In propagation pattern, called Talbot carpet, self-images at certain distances in a periodic row parallel the metallic layer are formed. The distance, called Talbot distance, is coincident with non-paraxial approximation result. To evaluate the periodicity of revivals, new parameters such as R-square, contrast, and image size are introduced. Afterwards, influence of the structural parameters such as groove size, period, and gap thickness on the light intensity is analyzed and proper values for near-infrared wavelength range is determined. We anticipate that our finding reveals better understanding of SP tunneling and paves a way toward utilization of this effect in Talbot effect attributed applications, particularly image processing.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fresnel A (1819) Mémoire sur la diffraction de la lumière. Da P 339 a P 475 1 Tav Ft AQ 210:339
Talbot HF (1836) LXXVI. Facts relating to optical science. No. IV. London Edinburgh Philos Mag J Sci 9:401–407
Rayleigh L (1881) XXV. On copying diffraction-gratings, and on some phenomena connected therewith. London, Edinburgh, Dublin Philos Mag J Sci 11:196–205
Liu L (1989) Talbot and Lau effects on incident beams of arbitrary wavefront, and their use. Appl Opt 28:4668–4678
Stuerzebecher L, Harzendorf T, Vogler U, Zeitner UD, Voelkel R (2010) Advanced mask aligner lithography: fabrication of periodic patterns using pinhole array mask and Talbot effect. Opt Express 18:19485–19494
Gao H, Hyun JK, Lee MH, Yang JC, Lauhon LJ, Odom TW (2010) Broadband plasmonic microlenses based on patches of nanoholes. Nano Lett 10:4111–4116
Maddaloni P, Paturzo M, Ferraro P, Malara P, De Natale P, Gioffrè M et al (2009) Mid-infrared tunable two-dimensional Talbot array illuminator. Appl Phys Lett 94:121105
Song YG, Han BM, Chang S (2001) Force of surface plasmon-coupled evanescent fields on Mie particles. Opt Commun 198:7–19
Maier SA (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and applications. In: Springer Science & Business Media
Bavil MA, Liu Z, Zhou WW, Li CB, Cheng BW (2017) Photocurrent enhancement in Si-Ge photodetectors by utilizing surface plasmons. Plasmonics 12:1709–1715
Bavil MA, Deng Q, Zhou Z (2014) Extraordinary transmission through gain-assisted silicon-based nanohole arrays in telecommunication regimes. Opt Lett 39:4506–4509
Zhi GA, Jin HS, He C, Guo FS, Jia KS, Yu YS et al (2016) Nanoplasmonic-gold-cylinder-array-enhanced terahertz source. J Semicond 37:123002
Hess O, Pendry JB, Maier SA, Oulton RF, Hamm JM, Tsakmakidis KL (2012) Active nanoplasmonic metamaterials. Nat Mater 11:573–584
Wang J, Yang G, Zhang Q, Gao S, Zhang R, Zheng Y (2017) Localized surface plasmon-enhanced deep-UV light-emitting diodes with Al/Al2O3 asymmetrical nanoparticles. Plasmonics 12:843–848
Wang J, Yang G, Ye X, Zhang Q, Gao S, Chen G (2017) Tailoring the multiple Fano resonances in nanobelt plasmonic cluster. Plasmonics 12:1641–1647
Li W, Li H, Gao B, Yu Y (2017) Investigation on the plasmon Talbot effect of finite-sized periodic arrays of metallic nanoapertures. Sci Rep 7:45573
Shi XY, Yang W, Xing H, Chen X (2015) Discrete plasmonic Talbot effect in finite metal waveguide arrays. Opt Lett 40:1635–1638
Wang Y, Zhou K, Zhang X, Yang K, Wang Y, Song Y, Liu S (2010) Discrete plasmonic Talbot effect in subwavelength metal waveguide arrays. Opt Lett 35:685–687
Cherukulappurath S, Heinis D, Cesario J, van Hulst NF, Enoch S, Quidant R (2009) Local observation of plasmon focusing in Talbot carpets. Opt Express 17:23772–23784
Chowdhury MH, Catchmark JM, Lakowicz JR (2007) Imaging three-dimensional light propagation through periodic nanohole arrays using scanning aperture microscopy. Appl Phys Lett 91:1–4
Dennis MR, Zheludev NI, García de Abajo FJ (2007) The plasmon Talbot effect. Opt Express 15:9692–9700
Iwanow R, May-Arrioja DA, Christodoulides DN, Stegeman GI, Min Y, Sohler W (2005) Discrete Talbot effect in waveguide arrays. Phys Rev Lett 95:1–4
Zhao WS, Eldaiki OM, Yang RX, Lu ZL (2010) Deep subwavelength waveguiding and focusing based on designer surface plasmons. Opt Express 18(20):21498–21503
Maradudin AA, Leskova TA (2009) The Talbot effect for a surface plasmon polariton. New J Phys 11:33004
Van Oosten D, Spasenović M, Kuipers L (2010) Nanohole chains for directional and localized surface plasmon excitation. Nano Lett 10:286–290
Palik ED (1998) Handbook of optical constants of solids, vol 3. Academic press, Cambridge
Zhang W, Zhao C, Wang J, Zhang J (2009) An experimental study of the plasmonic Talbot effect. Opt Express 17:19757–19762
Hua Y, Suh JY, Zhou W, Huntington MD, Odom TW (2012) Talbot effect beyond the paraxial limit at optical frequencies. Opt Express 20:14284–14291
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Zamani, Dr. Gudarzi, and Dr. Deng for their kind and warm assistance during discussion on the related physical concept and numerical programming.
Funding
This work is supported by the 111 Project (D17021), Program for Changjiang Scholars, Innovative Research Team in University (PCSIRT, IRT_16R07) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant no. 61675195].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afshari-Bavil, M., Luo, X., Li, C. et al. The Observation of Plasmonic Talbot Effect at Non-Illumination Side of Groove Arrays. Plasmonics 13, 2387–2394 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-018-0765-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-018-0765-8