Abstract
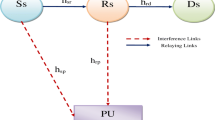
Cognitive radio (CR) is one of the candidate enabling technologies for future wireless communication systems. This paper is devoted to analyze the capacity of underlay cognitive multihop relaying over independent and non-identically distributed generalized-K fading channels. In doing so, we derive upper and lower-bounded expressions for the ergodic capacity and the outage probability of the secondary user (SU), respectively. By using these expressions, new insights in the performance of the cognitive multihop amplify-and-forward relaying are revealed. The obtained results provide interesting details on the joint effect of shadowing and multipath fading on the capacity of the SU in relay-assisted underlay CR networks. The analytical results are verified by Monte-Carlo simulations for different fading conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
FCC. (2002). Spectrum policy task force report. Report of Federal Communications Commission. Technical Report 02–135.
Mitola, J., & Maguire, G. Q. (1999). Cognitive radio: Making software radiosmore personal. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 6(4), 13–18.
Guizani, M. (2006). Wireless communications systems and networks. New York: Springer.
Van Der Meulen, E. C. (1971). Three-terminal communication channels. Advances in Applied Probability, 3(1), 120–154.
Sendonaris, A., Erkip, E., & Aazhang, B. (2003). User cooperation diversity. Part I. System description. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 51(11), 1927–1938.
Kramer, G., Gastpar, M., & Gupta, P. (2005). Cooperative strategies and capacity theorems for relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 51(9), 3037–3063.
Song, S., Son, K., Lee, H. W., & Chong, S. (2007). Opportunistic relaying in cellular network for capacity and fairness improvement. In IEEE GLOBECOM 2007-IEEE global telecommunications conference (pp. 4407–4412). IEEE.
Zhang, Q., Feng, Z., Yang, T., & Li, W. (2016). Optimal power allocation and relay selection in multi-hop cognitive relay networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 86(3), 1673–1692.
Simon, M. K., & Alouini, M. S. (2005). Digital communication over fading channels. Hoboken: Wiley.
Bithas, P. S., Efthymoglou, G. P., & Kalivas, D. S. (2014). Outage probability of cognitive relay networks over generalized fading channels with interference constraints. Procedia Computer Science, 40, 84–91.
Phan, H., Zepernick, H. J., & Tran, H. (2013). Impact of interference power constraint on multi-hop cognitive amplifyand-forward relay networks over Nakagami-m fading. IET Communications, 7(9), 860–866.
Kamga, G. N., Fredj, K. B., & Aïssa, S. (2015). Multihop cognitive relaying over composite multipath/shadowing channels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 64(8), 3807–3812.
Miridakis, N. I. (2015). On the ergodic capacity of underlay cognitive dual-hop AF relayed systems under nonidentical generalized-fading channels. IEEE Communications Letters, 19(11), 1965–1968.
Shankar, P. M. (2004). Error rates in generalized shadowed fading channels. Wireless Personal Communications, 28(3), 233–238.
Gradshteyn, I. S., & Ryzhik, I. M. (2014). Table of integrals, series, and products. Cambridge: Academic press.
Hasna, M. O., & Alouini, M. S. (2003). Outage probability of multihop transmission over Nakagami fading channels. IEEE Communications Letters, 7(5), 216–218.
Karagiannidis, G. K., Tsiftsis, T. A., & Mallik, R. K. (2006). Bounds for multihop relayed communications in Nakagami-m fading. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 54(1), 18–22.
Al-Ahmadi, S. (2014). The gamma–gamma signal fading model: A survey [wireless corner]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 56(5), 245–260.
Springer, M. D. (1979). The algebra of random variables. New York: Wiley.
Mathai, A. M., Saxena, R. K., & Haubold, H. J. (2009). The H-function: Theory and applications. New York: Springer.
Ghasemi, A., & Sousa, E. S. (2007). Fundamental limits of spectrum-sharing in fading environments. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 6(2), 649–658.
Prudnikov, A. P., & Marichev, O. I. (1998). Integrals and series: Special functions (Vol. 3). Milton Park: Gordon and Breach science publishers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoshafa, M.H., Al-Ahmadi, S. On the Capacity of Underlay Multihop Cognitive Relaying Over Generalized-K Composite Fading Channels. Wireless Pers Commun 96, 361–370 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4171-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4171-x