Abstract
Purpose
To provide preliminary data about efficacy and safety of plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF) eye-drops in neurotrophic keratitis (NK) and to analyze the possible influence of certain variables on treatment outcomes.
Methods
This retrospective study included patients with stages 2–3 of NK treated with PRGF eye-drops. Primary endpoint was the resolution time of corneal ulcer defect. Outcome measures including percentage of ulcer closure at 4 weeks, Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI), Best-Corrected Visual Acuity (BCVA) and Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) were also evaluated before and after treatment with PRGF. The influence of some patients’ clinical variables on results was assessed. Safety assessment was also performed reporting all adverse events.
Results
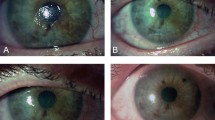
Thirty-eight treated eyes in a total of thirty-one patients were evaluated, of which five cases had no prior response to autologous serum treatment. Most cases (97.4%) achieved the complete resolution of corneal defect/ulcer. Mean resolution time was 11.4 weeks (SD = 13.7). A statistical significant (p < 0.05) reduction in OSDI (60.9%), VAS frequency (59.9%), VAS severity (57.0%) and improvement in BCVA (52.8%) was observed. The results were stratified according to the pathology stage and to the identified potential effect modifiers variables. Only one adverse event was reported in one patient (2.6%).
Conclusions
PRGF eye-drops could be a safe and effective therapeutic option for patients with stages 2–3 of NK, showing high rates of corneal defect/ulcer resolution in short times, either in reducing signs and symptoms of NK, and therefore preventing the progression of NK to greater ocular complications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sacchetti M, Lambiase A (2014) Diagnosis and management of neurotrophic keratitis. Clin Ophthalmol 8:571–579
Bonini S, Rama P, Olzi D, Lambiase A (2003) Neurotrophic keratitis. Eye 17(8):989–995
Cavanagh HD, Colley AM (1989) The molecular basis of neurotrophic keratitis. Acta Ophthalmol Suppl (Oxf) 192:115–134
Lambiase A, Rama P, Aloe L, Bonini S (1999) Management of neurotrophic keratopathy. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 10(4):270–276
Yoon KC, You IC, Im SK, Jeong TS, Park YG, Choi J (2007) Application of umbilical cord serum eyedrops for the treatment of neurotrophic keratitis. Ophthalmology 114(9):1637–1642
Versura P, Buzzi M, Giannaccare G, Terzi A, Fresina M, Velati C, Campos EC (2016) Targeting growth factor supply in keratopathy treatment: comparison between maternal peripheral blood and cord blood as sources for the preparation of topical eye drops. Blood Transfus 14(2):145–151
Versura P, Buzzi M, Giannaccare G, Grillini M, Terzi A, Pagliaro P, Campos EC (2014) Cord blood serum-based eye drops: the impact of donor haematological and obstetric factors on the variability of epidermal growth factor levels. Blood Transfus 12(Suppl 1):44–50
Shen EP, Hu F-R, Lo S-C, Chen Y-M, Sun Y-C, Lin C-T, Chen W-L (2011) Comparison of corneal epitheliotrophic capacity among different human blood-derived preparations. Cornea 30(2):208–214
Jeng BH, Dupps WJ (2009) Autologous serum 50% eyedrops in the treatment of persistent corneal epithelial defects. Cornea 28(10):1104–1108
Matsumoto Y, Dogru M, Goto E, Ohashi Y, Kojima T, Ishida R, Tsubota K (2004) Autologous serum application in the treatment of neurotrophic keratopathy. Ophthalmology 111(6):1115–1120
Anitua E, Zalduendo MM, Prado R, Alkhraisat MH, Orive G (2015) Morphogen and proinflammatory cytokine release kinetics from PRGF-Endoret fibrin scaffolds: evaluation of the effect of leukocyte inclusion. J Biomed Mater Res A 103(3):1011–1020
Anitua E, Zalduendo M, Troya M, Padilla S, Orive G (2015) Leukocyte inclusion within a platelet rich plasma-derived fibrin scaffold stimulates a more pro-inflammatory environment and alters fibrin properties. PLoS ONE 10(3):1–19
Anitua E, Sanchez M, Merayo-Lloves J, De la Fuente M, Muruzabal F, Orive G (2011) Plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF-Endoret) stimulates proliferation and migration of primary keratocytes and conjunctival fibroblasts and inhibits and reverts TGF-beta1-Induced myodifferentiation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(9):6066–6073
Anitua E, Muruzabal F, Alcalde I, Merayo-Lloves J, Orive G (2013) Plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF-Endoret) stimulates corneal wound healing and reduces haze formation after PRK surgery. Exp Eye Res 115:153–161
Anitua E, Muruzabal F, De la Fuente M, Merayo-Lloves J, Orive G (2014) Effects of heat-treatment on plasma rich in growth factors-derived autologous eye drop. Exp Eye Res 119:27–34
Anitua E, Muruzabal F, Pino A, Merayo-Lloves J, Orive G (2013) Biological stability of plasma rich in growth factors eye drops after storage of 3 months. Cornea 32(10):1380–1386
Anitua E, Pelacho B, Prado R, Aguirre JJ, Sánchez M, Padilla S, Aranguren XL, Abizanda G, Collantes M, Hernandez M, Perez-Ruiz A, Peñuelas I, Orive G, Prosper F (2015) Infiltration of plasma rich in growth factors enhances in vivo angiogenesis and improves reperfusion and tissue remodeling after severe hind limb ischemia. J Control Release 202:31–39
Bendinelli P, Matteucci E, Dogliotti G, Corsi MM, Banfi G, Maroni P, Desiderio MA (2010) Molecular basis of anti-inflammatory action of platelet-rich plasma on human chondrocytes: mechanisms of NF-kB inhibition via HGF. J Cell Physiol 225(3):757–766
Anitua E, Alonso R, Girbau C, Aguirre JJ, Muruzabal F, Orive G (2012) Antibacterial effect of plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF®-Endoret®) against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis strains. Clin Exp Dermatol 37:652–657
Drago L, Bortolin M, Vassena C, Romanò CL, Taschieri S, Del Fabbro M (2014) Plasma components and platelet activation are essential for the antimicrobial properties of autologous platelet-rich plasma: an in vitro study. PLoS ONE 9(9):e107813
Chikama TI, Fukuda K, Morishige N, Nishida T (1998) Treatment of neurotrophic keratopathy with substance-P-derived peptide (FGLM) and insulin-like growth factor I. Lancet 351(9118):1783–1784
Bonini S, Lambiase A, Rama P, Caprioglio G, Aloe L (2000) Topical treatment with nerve growth factor for neurotrophic keratitis. Ophthalmology 107:1347–1351
Benowitz LI, Popovich PG (2011) Inflammation and axon regeneration. Curr Opin Neurol 24(6):577–583
Shaheen BS, Bakir M, Jain S (2014) Corneal nerves in health and disease. Surv Ophthalmol 59(3):263–285
Geerling G, Maclennan S, Hartwing D (2004) Autologous serum eye drops for ocular surface disorders. Br J Ophthalmol 88(11):1467–1474
Schnabel LV, Mohammed HO, Miller BJ, McDermott WG, Jacobson MS, Santangelo KS, Fortier LA (2007) Platelet rich plasma (PRP) enhances anabolic gene expression patterns in flexor digitorum superficialis tendons. J Orthop Res 25(2):230–240
Yoon K-C, Jeong I-Y, Park Y-G, Yang S-Y (2007) Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in tears of patients with dry eye syndrome. Cornea 26(4):431–437
Freire V, Andollo N, Etxebarria J, Durán JA, Morales M-C (2012) In vitro effects of three blood derivatives on human corneal epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53(9):5571–5578
Anitua E, Prado R, Orive G (2015) Closing regulatory gaps: new ground rules for platelet-rich plasma. Trends Biotechnol 33(9):492–495
Anitua E, Muruzabal F, De la Fuente M, Merayo-Lloves J, Orive G (2014) Effects of heat-treatment on plasma rich in growth factors-derived autologous eye drop. Exp Eye Res 119:27–34
Anitua E, de la Fuente M, Muruzabal F, Riestra A, Merayo-Lloves J, Orive G (2015) Plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF) eye drops stimulates scarless regeneration compared to autologous serum in the ocular surface stromal fibroblasts. Exp Eye Res 135:118–126
Anitua E, Muruzabal F, Tayebba A, Riestra A, Perez VL, Merayo-Lloves J, Orive G (2015) Autologous serum and plasma rich in growth factors in ophthalmology: preclinical and clinical studies. Acta Ophthalmol 93:1–10
Anitua E, Muruzabal F, de la Fuente M, Merayo J, Duran J, Orive G (2016) Plasma rich in growth factors for the treatment of ocular surface diseases. Curr Eye Res 41(7):875–882
Merayo-Lloves J, Sanchez-Avila RM, Riestra AC, Anitua E, Begona L, Orive G, Fernandez-Vega L (2016) Safety and efficacy of autologous plasma rich in growth factors eye drops for the treatment of evaporative dry eye. Ophthalmic Res 56(2):68–73
Merayo-Lloves J, Sanchez RM, Riestra AC, Anitua E, Begona L, Orive G, Fernandez-Vega L (2015) Autologous plasma rich in growth factors eyedrops in refractory cases of ocular surface disorders. Ophthalmic Res 55(2):53–61
Kim KM, Shin Y-T, Kim HK (2012) Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on persistent corneal epithelial defect after infectious keratitis. Jpn J Ophthalmol 56(6):544–550
Semeraro F, Forbice E, Romano V, Angi M, Romano MR, Filippelli ME, Di Iorio R, Costagliola C (2014) Neurotrophic keratitis. Ophthalmologica 231(4):191–197
Aifa A, Gueudry J, Portmann A, Delcampe A, Muraine M (2012) Topical treatment with a new matrix therapy agent (RGTA) for the treatment of corneal neurotrophic ulcers. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53(13):8181–8185
Brignole-Baudouin F, Warnet JM, Barritault D, Baudouin C (2013) RGTA-based matrix therapy in severe experimental corneal lesions: safety and efficacy studies. J Fr Ophtalmol 36(9):740–747
Kymionis GD, Liakopoulos DA, Grentzelos MA, Diakonis VF, Klados NE, Tsoulnaras KI, Tsilimbaris MK, Pallikaris IG (2014) Combined topical application of a regenerative agent with a bandage contact lens for the treatment of persistent epithelial defects. Cornea 33(8):868–872
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Virginia Cuadrado for her support with the English grammar. This study received funding from the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness of the Spanish Government, within the project denominated SURFEYE (reference RTC-2014-2375-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): E.A. is the Scientific Director of and GO, LB, and FM are scientists at BTI Biotechnology Institute, a dental implant company, that investigates in the fields of oral implantology and PRGF-Endoret technology. The other authors: RSA, JMLL, ACR, LFVC declare no conflict of interest in developing this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanchez-Avila, R.M., Merayo-Lloves, J., Riestra, A.C. et al. Treatment of patients with neurotrophic keratitis stages 2 and 3 with plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF-Endoret) eye-drops. Int Ophthalmol 38, 1193–1204 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0582-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0582-7