Summary.
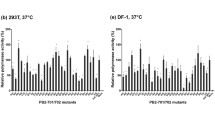
X-31(H3N2) virus, which is a high yielding reassortant between A/PR/8/34(H1N1) and A/Aichi/68(H3N2), is currently used as a backbone strain for influenza vaccine production. The sequence of the current X-31 virus was determined from cloned cDNA of 6 internal RNA genes, and was compared with the original sequence of the A/PR/8/34 virus. 71 point mutations were accumulated in the six internal viral genes (PB2, PB1, PA, NP, M and NS). These nucleotide changes encode 23 amino acid substitutions in seven viral proteins (PB2, PB1, PA, M1, M2, NS1 and NS2). Among three polymerase genes, a significantly low mutation frequency was observed in PA gene as compared to PB2 and PB1. The mutation frequency at the nucleotide level was significantly low in NP gene without any amino acid substitution, being only about 20% of those observed in 5 other internal genes. The unequal distribution of mutations among different viral proteins may correlate with individual role of each protein in viral growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received March 21, 2000 Accepted August 4, 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K., Youn, J., Kim, H. et al. Identification and characterization of mutations in the high growth vaccine strain of influenza virus. Arch. Virol. 146, 369–377 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050170181
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050170181