Abstract
Background
Although research on pediatric intracranial aneurysms is well documented, studies of pediatric intracranial distal arterial aneurysms (PIDAAs) remain scarce.
Methods
All pediatric patients (≤ 18 years) with intracranial aneurysms located distally to the M2 segment of the middle cerebral artery (MCA), A2 segment of the anterior cerebral artery, P2 segment of the posterior cerebral artery, and other cerebral arteries distal to the main branch who were treated at our center between January 2012 and April 2017 were retrospectively reviewed.
Results
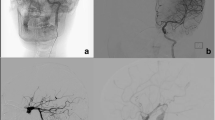
Thirty-five PIDAAs were observed in 35 patients with a mean age of 9.2 ± 5.9 years and a male ratio of 71.4% (n = 25). Sudden onset of severe headache was the most common symptom (n = 22, 62.9%), followed by seizures (n = 21, 60%). Twenty-seven patients (77.1%) had ruptured aneurysms, and 18 of them (66.7%) exhibited combined lobe intracerebral hematoma. MCA was the most common site (n = 23, 65.7%). Large or giant aneurysms were observed in 16 patients (45.7%). Eight patients (22.9%) had pseudoaneurysms, six of whom (75%) reported a head trauma history. Thirty patients (85.7%) had favorable outcomes at the end of the 6-month follow-up. Kaplan-Meier 6-month seizure curves revealed a significantly higher decrease in seizure rates in the surgical group than in the endovascular group (P = 0.036).
Conclusions
PIDAAs constitute a high proportion of pediatric intracranial aneurysms. PIDAAs are associated with an increased risk of seizures, a predilection for the MCA, and a high incidence of pseudoaneurysms with head trauma history. Surgical intervention is of greater benefit than endovascular treatment in controlling the risk of seizures.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PIDAAs:
-
Pediatric intracranial distal arterial aneurysms
- MCA:
-
Middle cerebral artery
- IRB:
-
Institutional Review Board
- ACA:
-
Anterior cerebral artery
- PCA:
-
Posterior cerebral artery
- GCS:
-
Glasgow Coma Score
- LOS:
-
Length of stay
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CTA:
-
Computed tomographic angiography
- DSA:
-
Digital subtraction angiography
- mRS:
-
Modified Rankin Scale
- ICU:
-
Intensive care unit
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- CI:
-
Confidence intervals
- PICA:
-
Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
References
Abla AA, Ducruet AF, Spetzler RF, Crowley RW, McDougall CG, Albuquerque FC (2012) High-flow bypass and tandem microsurgical-endovascular occlusion of recurrent proximal middle cerebral artery aneurysms in a pediatric patient. J Neurosurg Pediatr 10:365–369. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.8.PEDS12101
Bhaisora KS, Behari S, Godbole C, Phadke RV (2016) Traumatic aneurysms of the intracranial and cervical vessels: a review. Neurol India 64(Suppl):S14–S23. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.178032
Bigi S, Fischer U, Wehrli E, Mattle HP, Boltshauser E, Burki S, Jeannet PY, Fluss J, Weber P, Nedeltchev K, El-Koussy M, Steinlin M, Arnold M (2011) Acute ischemic stroke in children versus young adults. Ann Neurol 70:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22427
Choi KS, Chun HJ, Yi HJ, Ko Y, Kim YS, Kim JM (2009) Seizures and epilepsy following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage : incidence and risk factors. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 46:93–98. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2009.46.2.93
Connolly ES Jr, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, Derdeyn CP, Dion J, Higashida RT, Hoh BL, Kirkness CJ, Naidech AM, Ogilvy CS, Patel AB, Thompson BG, Vespa P, American Heart Association Stroke C, Council on Cardiovascular R, Intervention, Council on Cardiovascular N, Council on Cardiovascular S, Anesthesia, Council on Clinical C (2012) Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 43:1711–1737. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0b013e3182587839
Eddleman C, Nikas D, Shaibani A, Khan P, Dipatri AJ Jr, Tomita T (2007) HydroCoil embolization of a ruptured infectious aneurysm in a pediatric patient: case report and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 23:707–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0264-7
Ellamushi H, Thorne L, Kitchen N (1999) Unruptured cerebral aneurysms causing seizure disorder (report of two cases). Seizure 8:310–312. https://doi.org/10.1053/seiz.1999.0290
Fulkerson DH, Voorhies JM, Payner TD, Leipzig TJ, Horner TG, Redelman K, Cohen-Gadol AA (2011) Middle cerebral artery aneurysms in children: case series and review. J Neurosurg Pediatr 8:79–89. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.4.PEDS10583
Garg K, Singh PK, Sharma BS, Chandra PS, Suri A, Singh M, Kumar R, Kale SS, Mishra NK, Gaikwad SK, Mahapatra AK (2014) Pediatric intracranial aneurysms—our experience and review of literature. Childs Nerv Syst 30:873–883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2336-9
Gemmete JJ, Toma AK, Davagnanam I, Robertson F, Brew S (2013) Pediatric cerebral aneurysms. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 23:771–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nic.2013.03.018
Gonzales-Portillo GA, Valdivia JM (2006) Uncommon presentation of pediatric ruptured intracranial aneurysm after radiotherapy for retinoblastoma. Case report. Surg Neurol 65:391–395, discussion 395-396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2005.07.074
Harder EE, Ohye RG, Knepp MD, Owens ST (2014) Pediatric giant right atrial aneurysm: a case series and review of the literature. Congenit Heart Dis 9:E70–E77. https://doi.org/10.1111/chd.12079
Hart Y, Sneade M, Birks J, Rischmiller J, Kerr R, Molyneux A (2011) Epilepsy after subarachnoid hemorrhage: the frequency of seizures after clip occlusion or coil embolization of a ruptured cerebral aneurysm: results from the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial. J Neurosurg 115:1159–1168. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.6.JNS101836
Heiskanen O (1989) Ruptured intracranial arterial aneurysms of children and adolescents. Surgical and total management results. Childs Nerv Syst 5:66–70
Honda M, Nagamine T, Yamashiro K, Shimoji T (2008) An intracranial pseudoaneurysm in the distal middle cerebral artery in a child. Pediatr Neurosurg 44:426–429. https://doi.org/10.1159/000149914
Huang J, McGirt MJ, Gailloud P, Tamargo RJ (2005) Intracranial aneurysms in the pediatric population: case series and literature review. Surg Neurol 63:424–432; discussion 432-423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2004.11.023
Juszkat R, Jonczyk-Potoczna K, Stanislawska K, Bartkowska-Sniatkowska A, Rosada-Kurasinska J, Liebert W, Moskal J (2015) Endovascular treatment of an adolescent patient with a ruptured intracranial aneurysm—case report and review of literature. Pol J Radiol 80:10–12. https://doi.org/10.12659/PJR.891344
Krings T, Geibprasert S, terBrugge KG (2010) Pathomechanisms and treatment of pediatric aneurysms. Childs Nerv Syst 26:1309–1318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-009-1054-9
Krishna H, Wani AA, Behari S, Banerji D, Chhabra DK, Jain VK (2005) Intracranial aneurysms in patients 18 years of age or under, are they different from aneurysms in adult population? Acta Neurochir 147:469–476; discussion 476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0481-y
Leibrock LG, Bennett DR, Bloch S (1983) Complex partial seizures associated with unruptured thrombosed basilar artery apex aneurysm. Surg Neurol 19:17–20
Liang J, Bao Y, Zhang H, Wrede KH, Zhi X, Li M, Ling F (2009) The clinical features and treatment of pediatric intracranial aneurysm. Childs Nerv Syst 25:317–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-008-0725-2
Lin CL, Dumont AS, Lieu AS, Yen CP, Hwang SL, Kwan AL, Kassell NF, Howng SL (2003) Characterization of perioperative seizures and epilepsy following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 99:978–985. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2003.99.6.0978
Liu P, Yang M, Cai M, Qin J, Pan L (2016) Treatment of pediatric traumatic intracranial pseudoaneurysm using endovascular covered stent: three case reports. World Neurosurg 88(693):e691–e696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2015.12.037
Lyon KA, Arrey EN, Haider AS, Jeevan DS, Benardete EA (2017) Endovascular treatment of a large ruptured middle cerebral artery bifurcation aneurysm in a 5-week-old infant: case report. J Neurosurg Pediatr 20:357–363. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.5.PEDS17116
Martin K, Vanhouwelingen L, Butter A (2011) The significance of pseudoaneurysms in the nonoperative management of pediatric blunt splenic trauma. J Pediatr Surg 46:933–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2011.02.031
Mehrotra A, Nair AP, Das KK, Srivastava A, Sahu RN, Kumar R (2012) Clinical and radiological profiles and outcomes in pediatric patients with intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg Pediatr 10:340–346. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.7.PEDS11455
Meljnikov I, Vulekovic P, Cigic T, Borisev V, Milojevic A, Iduski S (2012) Treatment of pediatric patient with ruptured intracranial aneurysm—case report. Med Pregl 65:331–336
Meyer FB, Sundt TM Jr, Fode NC, Morgan MK, Forbes GS, Mellinger JF (1989) Cerebral aneurysms in childhood and adolescence. J Neurosurg 70:420–425. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1989.70.3.0420
Motohashi O, Kameyama M, Imaizumi S, Mino M, Naganuma H, Ishii K, Onuma T (2004) A distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysm in infant: disappearance and reappearance of the aneurysm. J Clin Neurosci 11:86–88
Nimjee SM, Smith TP, Kanter RJ, Ames W, Machovec KA, Grant GA, Zomorodi AR (2015) Rapid ventricular pacing for a basilar artery pseudoaneurysm in a pediatric patient: case report. J Neurosurg Pediatr 15:625–629. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.11.PEDS14290
Patil A, Menon GR, Nair S (2013) Unruptured anterior communicating artery aneurysms presenting with seizure: report of three cases and review of literature. Asian J Neurosurg 8:164. https://doi.org/10.4103/1793-5482.121693
Proust F, Toussaint P, Garnieri J, Hannequin D, Legars D, Houtteville JP, Freger P (2001) Pediatric cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 94:733–739. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2001.94.5.0733
Raju BS, Purohit AK, Murthy SR, Sundaram C, Sanjay T (2001) Traumatic distal anterior cerebral artery aneurysm in a child: a case report. Neurol India 49:295–298
Rhoney DH, Tipps LB, Murry KR, Basham MC, Michael DB, Coplin WM (2000) Anticonvulsant prophylaxis and timing of seizures after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology 55:258–265
Sim SY, Shin YS, Yoon SH (2008) Endovascular internal trapping of traumatic pericallosal pseudoaneurysm with hydrogel-coated self-expandable coil in a child: a case report. Surg Neurol 69:418–422; discussion 422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2007.02.042
Sorteberg A, Dahlberg D (2013) Intracranial non-traumatic aneurysms in children and adolescents. Curr Pediatr Rev 9:343–352. https://doi.org/10.2174/221155281120100005
Sun L, Li M, Zhang H, Du J, Ling F (2011) Trapping with high-flow bypass for a traumatic giant pseudoaneurysm of the supraclinoid carotid artery in an adolescent: case report. Childs Nerv Syst 27:681–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1397-x
Thompson BG, Brown RD Jr, Amin-Hanjani S, Broderick JP, Cockroft KM, Connolly ES Jr, Duckwiler GR, Harris CC, Howard VJ, Johnston SC, Meyers PM, Molyneux A, Ogilvy CS, Ringer AJ, Torner J, American Heart Association Stroke Council CoC, Stroke N, Council on E, Prevention, American Heart A, American Stroke A (2015) Guidelines for the management of patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 46:2368–2400. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0000000000000070
Ulahannan TJ (1998) Epileptic seizures due to cerebral artery aneurysm. J R Soc Med 91:325
Wojtacha M, Bazowski P, Mandera M, Krawczyk I, Rudnik A (2001) Cerebral aneurysms in childhood. Childs Nerv Syst 17:37–41
Yi HJ, Kim KM, Ko Y, Kim YS, Oh SJ, Oh SH (2006) A spontaneous giant pseudoaneurysm presenting with chronic headache in adolescent. Childs Nerv Syst 22:295–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-005-1198-1
Young WF, Pattisapu JV (2000) Ruptured cerebral aneurysm in a 39-day-old infant. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 102:140–143
Funding
This study was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2012017yjsy200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the parents or legal guardians of all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Comments
Pediatric intracranial aneurysms are rare, and most publications are relatively small case series with a wide spectrum of aneurysm morphology and clinical presentation. Consequently, reported results are in part conflicting; however, there is consensus in that pediatric aneurysms represent an independent condition different from their adult counterparts. Hence, fusiform and dissecting peripheral aneurysms are much more common in children than in adults. The strong side of this report is that it strictly focusses on this typical morphological entity within pediatric aneurysm cases. It is thereby a valuable addition to the somewhat limited literature on pediatric aneurysms.
Angelika Sorteberg
Oslo, Norway
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, R., Zhang, S., Guo, R. et al. Pediatric intracranial distal arterial aneurysms: report of 35 cases. Acta Neurochir 160, 1633–1642 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-018-3574-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-018-3574-0