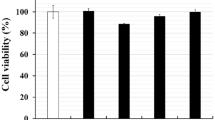
Abstract
Anisakis spp. is a parasitic nematode whose infective third-stage larvae may be found within the flesh of fish species commonly consumed by humans. Thorough cooking or freezing should render the fish safe for consumption; furthermore, marinating solutions containing biocidal agents might have a significant action against Anisakis larvae. Some studies suggest a relationship between some parasitic infections and development of inflammatory bowel disorders, and Anisakis infection might be a risk factor for stomach or colon cancer. The aim of our study was to investigate if crude extracts (CEs) obtained from Anisakis larvae marinated in a solution with added allyl isothiocyanate (ACE-AITC) and frozen, or from frozen only Anisakis larvae (ACE), can induce an inflammatory effect on in vitro differentiated colonic Caco-2 cells exposed or not to LPS. Caco-2 exposure to the two CEs induced a marked COX-2 expression and potentiated LPS-induced COX-2 overexpression, confirming that substances present in Anisakis larvae can induce an inflammatory response in the intestinal epithelium, possibly also exacerbating the effects of other inflammatory stimuli. ACE induced a marked decrease in caspase-3 activation, while AITC-ACE increased its activation. However, LPS-induced caspase-3 activation appeared lower in cells treated with ACE and with the lower concentration of AITC-ACE. Thus, it is evident that Anisakis CEs may affect various cell pathways crucial not only in the inflammatory process but also in cell growth and death. Thus, CEs obtained from nonviable Anisakis larvae retain or are otherwise provided with noxious properties able to induce a strong inflammation response in intestinal epithelial cells. Furthermore, their influence may persist also following pretreatment with the biocidal agent AITC, indicating that the harmful substances contained in crude extracts from Anisakis larvae are resistant to the thermal or biocidal agent treatments.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audicana MT, Kennedy MW (2008) Anisakis simplex: from obscure infectious worm to inducer of immune hypersensitivity. Clin Microbiol Rev 21:360–379. doi:10.1128/CMR.00012-07
Barbuzza O, Guarneri F, Galtieri G, Gangemi S, Vaccaro M (2009) Protein contact dermatitis and allergic asthma caused by Anisakis simplex. Contact Dermatitis 60:239–240. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2009.01519.x
Benet-Campos C, Cuéllar C, García-Ballesteros C, Zamora V, Gil-Borrás R, Catalán-Serra I, López-Chuliá F, Andreu-Ballester JC (2017) Determination of anti-Anisakis simplex antibodies and relationship with alphabeta and gammadelta lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with Crohn’s disease. Dig Dis Sci 62:934–943. doi:10.1007/s10620-017-4473-6
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Caradonna L, Amati L, Magrone T, Pellegrino NM, Jirillo E, Caccavo D (2000) Enteric bacteria, lipopolysaccharides and related cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease: biological and clinical significance. J Endotoxin Res 6:205–214
Carballeda-Sangiao N, Olivares F, Rodriguez-Mahillo AI, Careche M, Tejada M, Moneo I, Gonzalez-Munoz M (2014) Identification of autoclave-resistant Anisakis simplex allergens. J Food Prot 77:605–609. doi:10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-13-278
Cianciulli A, Calvello R, Cavallo P, Dragone T, Carofiglio V, Panaro MA (2012) Modulation of NF-kB activation by resveratrol in LPS treated human intestinal cells results in downregulation of PGE2 production and COX-2 expression. Toxicol In Vitro 26:1122–1128. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2012.06.015
Cimino F, Speciale A, Siracusa L, Naccari C, Saija A, Mancari F, Raciti R, Cristani M, Trombetta D (2014) Cytotoxic effects induced in vitro by organic extracts from urban air particulate matter in human leukocytes. Drug Chem Toxicol 37:32–39. doi:10.3109/01480545.2013.806529
Coussens LM, Werb Z (2002) Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420:860–867. doi:10.1038/nature01322
Daschner A, Alonso-Gomez A, Cabanas R, Suarez-de-Parga JM, Lopez-Serrano MC (2000) Gastroallergic anisakiasis: borderline between food allergy and parasitic disease-clinical and allergologic evaluation of 20 patients with confirmed acute parasitism by Anisakis simplex. J Allergy Clin Immunol 105:176–181
Deardorff TL, Jones RE, Kayes SG (1991) Adherence of eosinophils to the epicuticle of infective juveniles of Anisakis simplex (Nematoda: Anisakidae). J Helminthol Soc Wash 58:131–137
EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ) (2010) Scientific Opinion on risk assessment of parasites in fishery products EFSA Journal 8:1543-n/a doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1543
Ferrari D, Speciale A, Cristani M, Fratantonio D, Molonia MS, Ranaldi G, Saija A, Cimino F (2016) Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside inhibits NF-kB signalling in intestinal epithelial cells exposed to TNF-α and exerts protective effects via Nrf2 pathway activation. Toxicol Lett 264:51–58. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2016.10.014
Garcia-Perez JC, Rodriguez-Perez R, Ballestero A, Zuloaga J, Fernandez-Puntero B, Arias-Diaz J, Caballero ML (2015) Previous exposure to the fish parasite Anisakis as a potential risk factor for gastric or colon adenocarcinoma. Medicine (Baltimore) 94:e1699. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000001699
Giarratana F, Muscolino D, Panebianco F, Patania A, Benianti C, Ziino G, Giuffrida A (2015a) Activity of R(+) limonene against Anisakis Larvae. Ital J Food Saf 4:5499. doi:10.4081/ijfs.2015.5499
Giarratana F, Panebianco F, Muscolino D, Beninati C, Ziino G, Giuffrida A (2015b) Effect of allyl isothiocyanate against Anisakis larvae during the anchovy marinating process. J Food Prot 78:767–771. doi:10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-14-441
Guo H, Xu Y, Huang W, Zhou H, Zheng Z, Zhao Y, He B, Zhu T, Tang S, Zhu Q (2016) Kuwanon G preserves LPS-induced disruption of gut epithelial barrier in vitro Molecules 21 doi:10.3390/molecules21111597
Gutierrez-Ramos R, Guillen-Bueno R, Madero-Jarabo R, Cuellar del Hoyo C (2000) Digestive haemorrhage in patients with anti-Anisakis antibodies. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:337–343
Messina CM, Pizzo F, Santulli A, Buselic I, Boban M, Orhanovic S, Mladineo I (2016) Anisakis pegreffii (Nematoda: Anisakidae) products modulate oxidative stress and apoptosis-related biomarkers in human cell lines. Parasit Vectors 9:607. doi:10.1186/s13071-016-1895-5
Minciullo PL, Cascio A, David A, Pernice LM, Calapai G, Gangemi S (2012) Anaphylaxis caused by helminths: review of the literature. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 16:1513–1518
Mineta S, Shimanuki K, Sugiura A, Tsuchiya Y, Kaneko M, Sugiyama Y, Akimaru K, Tajiri T (2006) Chronic anisakiasis of the ascending colon associated with carcinoma. J Nippon Med Sch 73:169–174
Mohammadi R, Hosseini-Safa A, Ehsani Ardakani MJ, Rostami-Nejad M (2015) The relationship between intestinal parasites and some immune-mediated intestinal conditions. Gastroenterology and hepatology from bed to bench 8:123–131
Murata R, Suzuki J, Sadamasu K, Kai A (2011) Morphological and molecular characterization of Anisakis larvae (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in Beryx splendens from Japanese waters. Parasitol Int 60:193–198. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2011.02.008
Nieuwenhuizen N, Lopata AL, Jeebhay MF, Herbert DR, Robins TG, Brombacher F (2006) Exposure to the fish parasite Anisakis causes allergic airway hyperreactivity and dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 117:1098–1105. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2005.12.1357
Nieuwenhuizen NE (2016) Anisakis—immunology of a foodborne parasitosis. Parasite Immunol 38:548–557. doi:10.1111/pim.12349
Polimeno L, Loiacono M, Pesetti B, Mallamaci R, Mastrodonato M, Azzarone A, Annoscia E, Gatti F, Amoruso A, Ventura MT (2010) Anisakiasis, an underestimated infection: effect on intestinal permeability of Anisakis simplex-sensitized patients. Foodborne Pathog Dis 7:809–814. doi:10.1089/fpd.2009.0484
Purello-D'Ambrosio F, Pastorello E, Gangemi S, Lombardo G, Ricciardi L, Fogliani O, Merendino RA (2000) Incidence of sensitivity to Anisakis simplex in a risk population of fishermen/fishmongers. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 84:439–444. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62278-8
Rodriguez-Mahillo AI, Gonzalez-Munoz M, de las Heras C, Tejada M, Moneo I (2010) Quantification of Anisakis simplex allergens in fresh, long-term frozen, and cooked fish muscle. Foodborne Pathog Dis 7:967–973. doi:10.1089/fpd.2009.0517
Sun Y, Tang XM, Half E, Kuo MT, Sinicrope FA (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression reduces apoptotic susceptibility by inhibiting the cytochrome c-dependent apoptotic pathway in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 62:6323–6328
Talavera MM, Kralik N, Jin Y, Chen B, Liu Y, Nelin LD (2015) Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis in immature rat intestinal epithelial cells. Pediatr Res 78:128–136. doi:10.1038/pr.2015.88
Tejada M, Olivares F, de las Heras C, Careche M, Solas MT, García ML, Fernandez A, Mendizábal A, Navas A, Rodríguez-Mahillo AI, González-Muñoz M (2015) Antigenicity of Anisakis simplex s.s. L3 in parasitized fish after heating conditions used in the canning processing. J Sci Food Agric 95:922–927. doi:10.1002/jsfa.6763
Tsutsumi Y, Fujimoto Y (1983) Early gastric cancer superimposed on infestation of an Anisakis-like larva: a case report Tokai. J Exp Clin Med 8:265–273
Ubeira FM, Anadón AM, Salgado A, Carvajal A, Ortega S, Aguirre C, López-Goikoetxea MJ, Ibanez L, Figueiras A (2011) Synergism between prior Anisakis simplex infections and intake of NSAIDs, on the risk of upper digestive bleeding: a case-control study. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 5:e1214. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0001214
Zhang H, Li X, Ding J, Xu H, Dai X, Hou Z, Zhang K, Sun K, Sun W (2013) Delivery of ursolic acid (UA) in polymeric nanoparticles effectively promotes the apoptosis of gastric cancer cells through enhanced inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2). Int J Pharm 441:261–268. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.11.034
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Speciale, A., Trombetta, D., Saija, A. et al. Exposure to Anisakis extracts can induce inflammation on in vitro cultured human colonic cells. Parasitol Res 116, 2471–2477 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5551-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5551-6