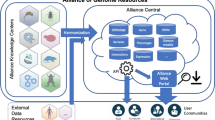
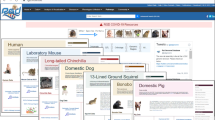
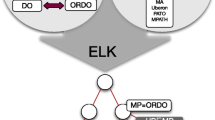
Abstract
A major aim of the biological sciences is to gain an understanding of human physiology and disease. One important step towards such a goal is the discovery of the function of genes that will lead to a better understanding of the physiology and pathophysiology of organisms, which will ultimately lead to better diagnosis and therapy. Our increasing ability to phenotypically characterise genetic variants of model organisms coupled with systematic and hypothesis-driven mutagenesis is resulting in a wealth of information that could potentially provide insight into the functions of all genes in an organism. The challenge we are now facing is to develop computational methods that can integrate and analyse such data. The introduction of formal ontologies that make their semantics explicit and accessible to automated reasoning provides the tantalizing possibility of standardizing biomedical knowledge allowing for novel, powerful queries that bridge multiple domains, disciplines, species, and levels of granularity. We review recent computational approaches that facilitate the integration of experimental data from model organisms with clinical observations in humans. These methods foster novel cross-species analysis approaches, thereby enabling comparative phenomics and leading to the potential of translating basic discoveries from the model systems into diagnostic and therapeutic advances at the clinical level.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
No Author (2010) Mouse megascience. Nature 465(7298):526
Abbott A (2010b) Mouse project to find each gene’s role. Nature 465(7297):410
Al-Hasani K, Vadolas J, Knaupp A, Wardan H, Voullaire L, Williamson R, Ioannou P (2005) A 191-kb genomic fragment containing the human α-globin locus can rescue α-thalassemic mice. Mamm Genome 16:847–853
Amberger J, Bocchini C, Hamosh A (2011) A new face and new challenges for Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®). Hum Mutat 32:564–567
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry MJ, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Tarver LI, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 25(1):25–29
Baader F, Lutz C, Suntisrivaraporn B (2005) Is tractable reasoning in extensions of the description logic EL useful in practice? In: Proceedings of the Methods for Modalities Workshop (M4M-05), Berlin, Germany
Baader F, Lutz C, Suntisrivaraporn B (2006) CEL: a polynomial-time reasoner for life science ontologies. In: Furbach U, Shankar N (eds), Proceedings of the 3rd International Joint Conference on Automated Reasoning (IJCAR ’06), Seattle, WA, August 17–20, 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 4130:287–291
Bada M, Stevens R, Goble C, Gil Y, Ashburner M, Blake JA, Cherry MJ, Harris M, Lewis S (2004) A short study on the success of the gene ontology. Web Semant 1(2):235–240
Barwise J (1989) The situation in logic. CSLI Publications, Stanford
Barwise J, Etchemendy J (2002) Language, proof and logic. CSLI Publications, Stanford
Blake JA, Bult CJ, Kadin JA, Richardson JE, Eppig JT, Mouse Genome DatabaseGroup (2011) The Mouse Genome Database (MGD): premier model organism resource for mammalian genomics and genetics. Nucleic Acids Res 39(suppl 1):D842–D848
Bodenreider O, Hayamizu TF, Ringwald M, DeCoronado S, Zhang S (2005) Of mice and men: aligning mouse and human anatomies. AMIA Annu Symp Proc 2005:61–65
Bradford Y, Conlin T, Dunn N, Fashena D, Frazer K, Howe DG, Knight J, Mani P, Martin R, Moxon SA, Paddock H, Pich C, Ramachandran S, Ruef BJ, Ruzicka L, Schaper HB, Schaper K, Shao X, Singer A, Sprague J, Sprunger B, VanSlyke C, Westerfield M (2011) ZFIN: enhancements and updates to the zebrafish model organism database. Nucleic Acids Res 39(Database issue): D822–D829
Brown S, Moore M (2012) Towards an encyclopaedia of gene function: the International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium. Dis Model Mech 5(3):289–292
Burgun A, Mougin F, Bodenreider O (2009) Two approaches to integrating phenotype and clinical information. AMIA Annu Symp Proc 2009:75–79
Ceusters W, Elkin P, Smith B (2006) Referent tracking: the problem of negative findings. Stud Health Technol Inform 124:741–746
Chen J, Xu H, Aronow B, Jegga A (2007) Improved human disease candidate gene prioritization using mouse phenotype. BMC Bioinform 8(1):392
Chen J, Bardes EE, Aronow BJ, Jegga AG (2009) ToppGene suite for gene list enrichment analysis and candidate gene prioritization. Nucl Acids Res 37(Web Server issue):W305–W311
Collins FS, Finnell RH, Rossant J, Wurst W (2007) A new partner for the international knockout mouse consortium. Cell 129(2):235
Cook DL, Bookstein FL, Gennari JH (2011) Physical properties of biological entities: an introduction to the ontology of physics for biology. PLoS One 6(12):e28708
Drysdale R, FlyBase Consortium (2008) FlyBase: a database for the Drosophila research community. Methods Mol Biol 420:45–59
Engel SR, Balakrishnan R, Binkley G, Christie KR, Costanzo MC, Dwight SS, Fisk DG, Hirschman JE, Hitz BC, Hong EL, Krieger CJ, Livstone MS, Miyasato SR, Nash R, Oughtred R, Park J, Skrzypek MS, Weng S, Wong ED, Dolinski K, Botstein D, Cherry JM (2010) Saccharomyces genome database provides mutant phenotype data. Nucl Acids Res 38(Database issue):D433–D436
Espinosa O, Hancock JM (2011) A gene-phenotype network for the laboratory mouse and its implications for systematic phenotyping. PLoS One 6(5):e19693
Fawcett T (2006) An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit Lett 27(8):861–874
Gkoutos GV (2006) Towards a phenotypic semantic web. Curr Bioinform 1(2):235–246
Gkoutos GV, Green EC, Mallon AM, Hancock JM, Davidson D (2004) Building mouse phenotype ontologies. Pac Symp Biocomput 2004:178–189
Gkoutos GV, Green EC, Mallon AM, Hancock JM, Davidson D (2005) Using ontologies to describe mouse phenotypes. Genome Biol 6(1):R8
Goble C, Stevens R (2008) State of the nation in data integration for bioinformatics. J Biomed Inform 41(5):687–693
Golbreich C, Horrocks I (2007) The obo to owl mapping, go to owl 1.1! In: Golbreich C, Kalyanpur A, Parsia B (eds), Proceedings of OWL: Experiences and Directions(OWLED-2007), Innsbruck, Austria, 6–7 June 2007.CEUR Workshop Proceedings 258, CEUR-WS.org
Grau B, Horrocks I, Motik B, Parsia B, Patelschneider P, Sattler U (2008) OWL 2: the next step for OWL. Web Semant 6(4):309–322
Groth P, Weiss B (2006) Phenotype data: a neglected resource in biomedical research? Curr Bioinform 1(3):347–358
Groth P, Pavlova N, Kalev I, Tonov S, Georgiev G, Pohlenz HD, Weiss B (2007) PhenomicDB: a new cross-species genotype/phenotype resource. Nucl Acids Res 35(Database issue):D696–D699
Gruber TR (1993) Toward principles for the design of ontologies used for knowledge sharing. In: Guarino N, Poli R (eds) Formal ontology in conceptual analysis and knowledge representation. Kluwer Academic, Deventer
Gruber TR (1995) Toward principles for the design of ontologies used for knowledge sharing. Int J Hum Comput Stud 43(5–6):909–928
Guarino N (1998) Formal ontology and information systems. In: Guarino N (ed), Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Formal Ontologies in Information Systems. IOS Press, Amsterdam, pp 3–15
Harris TW, Antoshechkin I, Bieri T, Blasiar D, Chan J, Chen WJ, De La Cruz N, Davis P, Duesbury M, Fang R, Fernandes J, Han M, Kishore R, Lee R, Müller HM, Nakamura C, Ozersky P, Petcherski A, Rangarajan A, Rogers A, Schindelman G, Schwarz EM, Tuli MA, Van Auken K, Wang D, Wang X, Williams G, Yook K, Durbin R, Stein LD, Sternberg PW, Spieth J (2010) WormBase: a comprehensive resource for nematode research. Nucl Acids Res 38(suppl 1):D463–D467
Hernandez-Boussard T, Whirl-Carrillo M, Hebert JM, Gong L, Owen R, Gong M, Gor W, Liu F, Truong C, Whaley R, Woon M, Zhou T, Altman RB, Klein TE (2008) The pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics knowledge base: accentuating the knowledge. Nucl Acids Res 36(Database issue):D913–D918
Herre H, Heller B, Burek P, Hoehndorf R, Loebe F, Michalek H (2006) General Formal Ontology (GFO): A foundational ontology integrating objects and processes version 1.0, Onto-Med Report8, IMISE, University of Leipzig, Leipzig, Germany
Hilbert D (1918) Axiomatisches Denken. Math Ann 78:405–415
Hoehndorf R, Loebe F, Kelso J, Herre H (2007) Representing default knowledge in biomedical ontologies: application to the integration of anatomy and phenotype ontologies. BMC Bioinform 8(1):377
Hoehndorf R, Kelso J, Herre H (2009) The ontology of biological sequences. BMC Bioinform 10(1):377
Hoehndorf R, Oellrich A, Dumontier M, Kelso J, Rebholz-Schuhmann D, Herre H (2010a) Relations as patterns: bridging the gap between OBO and OWL. BMC Bioinform 11(1):441
Hoehndorf R, Oellrich A, Rebholz-Schuhmann D (2010b) Interoperability between phenotype and anatomy ontologies. Bioinformatics 26(24):3112–3118
Hoehndorf R, Batchelor C, Bittner T, Dumontier M, Eilbeck K, Knight R, Mungall CJ, Richardson JS, Stombaugh J, Westhof E, Zirbel CL, Leontis NB (2011a) The RNA ontology (RNAO): an ontology for integrating RNA sequence and structure data. Appl Ontol 6(1):53–89
Hoehndorf R, Dumontier M, Gennari JH, Wimalaratne S, de Bono B, Cook DL, Gkoutos GV (2011b) Integrating systems biology models and biomedical ontologies. BMC Syst Biol 5(1):124
Hoehndorf R, Dumontier M, Oellrich A, Rebholz-Schuhmann D, Schofield PN, Gkoutos GV (2011c) Interoperability between biomedical ontologies through relation expansion, upper-level ontologies and automatic reasoning. PLoS One 6(7):e22006
Hoehndorf R, Dumontier M, Oellrich A, Wimalaratne S, Rebholz-Schuhmann D, Schofield P, Gkoutos GV (2011d) A common layer of interoperability for biomedical ontologies based on OWL EL. Bioinformatics 27(7):1001–1008
Hoehndorf R, Schofield PN, Gkoutos GV (2011) Phenomebrowser. Available at http://phenomebrowser.net. Accessed 5 Mar 2012
Hoehndorf R, Schofield PN, Gkoutos GV (2011f) Phenomenet: a whole-phenome approach to disease gene discovery. Nucl Acids Res 39(18):e119
Hoehndorf R, Oellrich A, Rebholz-Schuhmann D, Schofield PN, Gkoutos GV (2012) Linking pharmgkb to phenotype studies and animal models of disease for drug repurposing. Pac Symp Biocomput 2012:388–399
Horrocks I (2007) OBO flat file format syntax and semantics and mapping to OWL Web Ontology Language. Technical report, University of Manchester, March 2007. Available at http://www.cs.man.ac.uk/~horrocks/obo/. Accessed 5 Mar 2012
ISO (2007) Information technology: common logic (cl): a framework for a family of logic-based languages. Technical report
Kazakov Y (2009) Consequence-driven reasoning for Horn SHIQ ontologies. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 09), Pasadena, CA, July 11–17, 2009, pp 2040–2045
Kazakov Y, Krötzsch M, Simančík F (2011) Unchain my EL reasoner. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Workshop on Description Logics (DL10), CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol 573, CEUR-WS.org
Kitsios GD, Tangri N, Castaldi PJ, Ioannidis JP (2010) Laboratory mouse models for the human genome-wide associations. PLoS One 5(11):e13782
Kutz O, Mossakowski T (2011) A modular consistency proof for dolce. In AAAI
Lander ES (2011) Initial impact of the sequencing of the human genome. Nature 470(7333):187–197
Lee D, Redfern O, Orengo C (2007) Predicting protein function from sequence and structure. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(12):995–1005
Loewenstein Y, Raimondo D, Redfern O, Watson J, Frishman D, Linial M, Orengo C, Thornton J, Tramontano A (2009) Protein function annotation by homology-based inference. Genome Biol 10(2):207
Masuya H, Makita Y, Kobayashi N, Nishikata K, Yoshida Y, Mochizuki Y, Doi K, Takatsuki T, Waki K, Tanaka N, Ishii M, Matsushima A, Takahashi S, Hijikata A, Kozaki K, Furuichi T, Kawaji H, Wakana S, Nakamura Y, Yoshiki A, Murata T, Fukami-Kobayashi K, Mohan S, Ohara O, Hayashizaki Y, Mizoguchi R, Obata Y, Toyoda T (2011) The RIKEN integrated database of mammals. Nucl Acids Res 39(suppl 1):D861–D870
McGary KL, Park TJ, Woods JO, Cha HJ, Wallingford JB, Marcotte EM (2010) Systematic discovery of nonobvious human disease models through orthologous phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(14):6544–6549
Motik B, Grau BC, Horrocks I, Wu Z, Fokoue A, Lutz C (2009) Owl 2 web ontology language: Profiles. W3C Recommendation, 27 October 2009. Available at http://www.w3.org/TR/owl-profiles/. Accessed 5 Mar 2012
Motik B, Shearer R, Horrocks I (2009b) Hypertableau reasoning for description logics. J Artif Intell Res 36:165–228
Mungall CJ (2011) OBO flat file format 1.4 syntax and semantics draft. Technical report, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. Available at http://berkeleybop.org/~cjm/obo2owl/obo-syntax.html. Accessed 5 Mar 2012
Mungall C, Gkoutos G, Smith C, Haendel M, Lewis S, Ashburner M (2010) Integrating phenotype ontologies across multiple species. Genome Biol 11(1):R2
Mungall CJ, Bada M, Berardini TZ, Deegan J, Ireland A, Harris MA, Hill DP, Lomax J (2011a) Cross-product extensions of the gene ontology. J Biomed Inform 44(1):80–86
Mungall CJ, Batchelor C, Eilbeck K (2011b) Evolution of the sequence ontology terms and relationships. J Biomed Inform 44(1):87–93
Oti M, Brunner HG (2007) The modular nature of genetic diseases. Clin Genet 71:1–11
Oti M, Huynen MA, Brunner HG (2009) The biological coherence of human phenome databases. Am J Hum Genet 85(6):801–808
Rector AL (2003) Modularisation of domain ontologies implemented in description logics and related formalisms including owl. In: K-CAP ’03: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Knowledge Capture, Sanibel Island, FL, October 23–25, 2003, ACM Press, New York, pp 121–128
Robinson PN, Koehler S, Bauer S, Seelow D, Horn D, Mundlos S (2008) The human phenotype ontology: a tool for annotating and analyzing human hereditary disease. Am J Hum Genet 83(5):610–615
Ruttenberg A, Clark T, Bug W, Samwald M, Bodenreider O, Chen H, Doherty D, Forsberg K, Gao Y, Kashyap V, Kinoshita J, Luciano J, Marshall MS, Ogbuji C, Rees J, Stephens S, Wong G, Wu E, Zaccagnini D, Hongsermeier T, Neumann E, Herman I, Cheung KH (2007) Advancing translational research with the Semantic Web. BMC Bioinform 8(Suppl 3):S2
Sardana D, Vasa S, Vepachedu N, Chen J, Gudivada RC, Aronow BJ, Jegga AG (2010) PhenoHM: human-mouse comparative phenome-genome server. Nucl Acids Res 38(Web Server issue):W165–W174
Schindelman G, Fernandes J, Bastiani C, Yook K, Sternberg P (2011) Worm phenotype ontology: integrating phenotype data within and beyond the C. elegans community. BMC Bioinform 12(1):32
Schofield PN, Hoehndorf R, Gkoutos GV (2012) Mouse genetic and phenotypic resources for human genetics. Hum Mutat 33(5):826–836
Schulz S, Suntisrivaraporn B, Baader F, Boeker M (2009) SNOMED reaching its adolescence: ontologists’ and logicians’ health check. Int J Med Inform 78(Suppl 1):S86–S94
Sirin E, Parsia B (2004) Pellet: An OWL DL reasoner. In: Haarslev V, Möller R(eds), Proceedings of the 2004 International Workshop on Description Logics, DL2004, Whistler, British Columbia, Canada, June 6–8, 2004, CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol 104. Aachen, Germany:CEUR-WS.org
Skarnes WC, Rosen B, West AP, Koutsourakis M, Bushell W, Iyer V, Mujica AO, Thomas M, Harrow J, Cox T, Jackson D, Severin J, Biggs P, Fu J, Nefedov M, de Jong PJ, Stewart AF, Bradley A (2011) A conditional knockout resource for the genome-wide study of mouse gene function. Nature 474(7351):337–342
Smedley D, Swertz MA, Wolstencroft K, Proctor G, Zouberakis M, Bard J, Hancock JM, Schofield P (2008) Solutions for data integration in functional genomics: a critical assessment and case study. Brief Bioinform 9(6):532–544
Smith CL, Goldsmith CAW, Eppig JT (2004) The mammalian phenotype ontology as a tool for annotating, analyzing and comparing phenotypic information. Genome Biol 6(1):R7
Smith B, Ceusters W, Klagges B, Köhler J, Kumar A, Lomax J, Mungall C, Neuhaus F, Rector AL, Rosse C (2005) Relations in biomedical ontologies. Genome Biol 6(5):R46
Smith B, Ashburner M, Rosse C, Bard J, Bug W, Ceusters W, Goldberg LJ, Eilbeck K, Ireland A, Mungall CJ, Leontis N, Serra PR, Ruttenberg A, Sansone SA, Shah N, Scheuermann RH, Whetzel PL, Lewis S (2007) The OBO Foundry: coordinated evolution of ontologies to support biomedical data integration. Nat Biotech 25(11):1251–1255
Sowa JF (2000) Knowledge representation: logical, philosophical and computational foundations. Brooks/Cole, Pacific Grove
Sprague J, Bayraktaroglu L, Bradford Y, Conlin T, Dunn N, Fashena D, Frazer K, Haendel M, Howe DG, Knight J, Mani P, Moxon SA, Pich C, Ramachandran S, Schaper K, Segerdell E, Shao X, Singer A, Song P, Sprunger B, Van Slyke CE, Westerfield M (2007) The Zebrafish Information Network: the zebrafish model organism database provides expanded support for genotypes and phenotypes. Nucleic Acids Res 36(Database Issue):D768–D772
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, Mesirov JP (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(43):15545–15550
Suntisrivaraporn B (2008) Empirical evaluation of reasoning in lightweight DLs on life science ontologies. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Mahasarakham International Workshop on AI (MIWAI’08). Mahasarakham University, Mahasarakham, Thailand
Thorisson GA, Muilu J, Brookes AJ (2009) Genotype-phenotype databases: challenges and solutions for the post-genomic era. Nat Rev Genet 10(1):9–18
Tsarkov D, Horrocks I (2006) FaCT++ description logic reasoner: System description. In: Furbach U, Shankar N (eds), Proceedings of the 3rd International Joint Conference on Automated Reasoning (IJCAR ’06), Seattle, WA, August 17–20, 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 4130:292–297
van Driel MA, Bruggeman J, Vriend G, Brunner HG, Leunissen JAM (2006) A text-mining analysis of the human phenome. Eur J Hum Genet 14(5):535–542
Wallace HA, Marques-Kranc F, Richardson M, Luna-Crespo F, Sharpe JA, Hughes J, Wood WG, Higgs DR, Smith AJ (2007) Manipulating the mouse genome to engineer precise functional syntenic replacements with human sequence. Cell 128(1):197–209
Washington NL, Haendel MA, Mungall CJ, Ashburner M, Westerfield M, Lewis SE (2009) Linking human diseases to animal models using ontology-based phenotype annotation. PLoS Biol 7(11):e1000247
Weinreich SS, Mangon R, Sikkens JJ, Teeuw ME, Cornel MC (2008) Orphanet: a European database for rare diseases. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 9(152):518–519
Wolstencroft K, Lord P, Tabernero L, Brass A, Stevens R (2006) Protein classification using ontology classification. Bioinformatics 22(14):e530–e538
Xu T, Du LF, Zhou Y (2008) Evaluation of GO-based functional similarity measures using S. cerevisiae protein interaction and expression profile data. BMC Bioinform 9(1):472
Yamazaki Y, Jaiswal P (2005) Biological ontologies in rice databases. An introduction to the activities in Gramene and Oryzabase. Plant Cell Physiol 46(1):63–68
Zheng-Bradley X, Rung J, Parkinson H, Brazma A (2010) Large scale comparison of global gene expression patterns in human and mouse. Genome Biol 11(12):R124
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gkoutos, G.V., Schofield, P.N. & Hoehndorf, R. Computational tools for comparative phenomics: the role and promise of ontologies. Mamm Genome 23, 669–679 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-012-9404-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-012-9404-4