Abstract
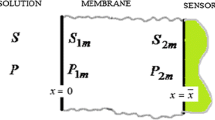
An analysis of the reaction diffusion in a carrier-mediated transport process through a membrane is presented. A simple approximate analytical expression of concentration profiles is derived in terms of all dimensionless parameters. Furthermore, in this work we employ the homotopy perturbation method to solve the nonlinear reaction–diffusion equations. Moreover, the analytical results have been compared to the numerical simulation using the Matlab program. The simulated results are comparable with the appropriate theories. The results obtained in this work are valid for the entire solution domain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anitha S, Subbiah A, Subramaniam S, Rajendran L (2011) Analytical solution of amperometric enzymatic reactions based on homotopy perturbation method. Electrochim Acta 56:3345–3352
Baker R, Blume I (1990) Coupled transport membranes. In: Porter M (ed) Handbook of industrial membrane technology. Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, pp 511–558
Barbero AJ, Manzanares JA, Mafe S (1995) A computational study of facilitated diffusion using the boundary element method. J Non-Equilib Thermodyn 20:332–341
Bartsch RA, Douglas JD (1996) Chemical separations with liquid membranes: an overview. ACS Symp Ser 642:1–10
de Gyves J, de San Miguel ER (1999) Metal ion separations by supported liquid membranes. Ind Eng Chem Res 38:2182–2202
Diederich F, Dick K (1984) A new water-soluble macrocyclic host of the cyclophane type: host–guest complexation with aromatic guests in aqueous solution and acceleration of the transport of arenes through an aqueous phase. J Am Chem Soc 106:8024–8036
Draxler J, Mar RJ (1986) Emulsion liquid membranes. Part I. Phenomenon and industrial application. Chem Eng Process 20:319–329
Fyles TM, Osa T, Atwood JL (1991) Inclusion aspects of membrane chemistry. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 59–110
Ghori QK, Ahmed M, Siddiqui AM (2007) Application of homotopy perturbation method to squeezing flow of a Newtonian fluid. Int J Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 8:179–184
Goddard JD (1977) Further applications of carrier-mediated transport theory—a survey. Chem Eng Sci 32:795–809
He JH (1999) Homotopy perturbation technique. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 178:257–262
He JH (2003a) Homotopy perturbation method: a new nonlinear analytical technique. Appl Math Comput 135:73–79
He JH (2003b) A simple perturbation approach to the Blasius equation. Appl Math Comput 140:217–222
Izatt RM, Roper DK, Bruening RL, Lamb JD (1989) Macrocycle-mediated cation transport using hollow fiber supported liquid membranes. J Membr Sci 45:73–84
Kim JS, Kim SK, Ko JW, Kim ET, Yu SH, Cho MH, Kwon SG, Lee EH (2000) Selective transport of cesium ion in polymeric CTA membrane containing calixcrown ethers. Talanta 52:1143–1148
Kim JS, Kim SK, Cho MH, Lee SH, Kim JY, Kwon SG, Lee EH (2001) Permeation of silver ion through polymeric CTA membrane containing acyclic polyether bearing amide and amine end-group. Bull Korean Chem Soc 22:1076–1080
Li SJ, Liu YX (2006) An improved approach to nonlinear dynamical system identification using PID neural networks. Int J Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 7:177–182
Loghambal S, Rajendran L (2010) Mathematical modeling of diffusion and kinetics of amperometric immobilized enzyme electrodes. Electrochim Acta 55:5230–5238
Lonsdale HK (1982) The growth of membrane technology. J Membr Sci 10:81–181
Matson SL, Herrick CS, Ward WJ (1977) Progress on the selective removal of H2S from gasified coal using an immobilized liquid membrane. Ind Eng Chem Process Des Dev 16:370–374
Meena A, Rajendran L (2010) Mathematical modeling of amperometric and potentiometric biosensors and system of non-linear equations—homotopy perturbation approach. J Electroanal Chem 644:50–59
Mousa MM, Ragab SF (2008) Application of the homotopy perturbation method to linear and nonlinear Schrödinger equations. Z Naturforsch A 63:140–144
Ozis T, Yildirim A (2007) A comparative study of He’s homotopy perturbation method for determining frequency–amplitude relation of a nonlinear oscillator with discontinuities. Int J Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 8:243–248
Sastre AM, Kumar A, Shukla JP, Singh RK (1998) Improved techniques in liquid membrane separations: an overview. Sep Purif Methods 27:213–298
Schow AJ, Peterson RT, Lamb JD (1996) Polymer inclusion membranes containing macrocyclic carriers for use in cation separations. J Membr Sci 111:291–295
Schultz JS (1977) Carrier-mediated transport in liquid–liquid membrane systems. In: Li NN (ed) Recent developments in separation science. CRC Press, Cleveland, OH, pp 243–260
Schultz JS, Goddard JD, Suchdeo SR (1974) Facilitated transport via carrier-mediated diffusion in membranes. Part I, Mechanistic aspects, experimental systems and characteristic regimes. AIChE J 20:417–445
Smith DR, Lander RJ, Quinn JA (1977) Carrier-mediated transport in synthetic membranes. In: Li NN (ed) Recent developments in separation science. CRC Press, Cleveland, OH, p 225
Thiagarajan S, Meena A, Anitha S, Rajendran L (2011) Analytical expression of the steady-state catalytic current of mediated bioelectrocatalysis and the application of He’s homotopy perturbation method. J Math Chem 49:1727–1740
Thien MP, Hatton TA (1988) Liquid emulsion membranes and their applications in biochemical processing. Sep Sci Technol 23:819–853
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (01[2442]/10/EMR-II), Government of India. The authors also thank the secretary, The Madura College Board, and the principal, The Madura College, Madurai, Tamil Nadu, India, for their constant encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1: Approximate Analytical Solution of the Concentration Species Using the Homotopy Perturbation Method
In this appendix, we derive the solution of nonlinear reaction Eqs. 8–10 using He’s HPM. To illustrate the basic concepts of this method, we consider the following nonlinear differential equation (Ghori et al. 2007; Ozis and Yildirim 2007; Li and Liu 2006; Mousa and Ragab 2008):
where L is a linear operator, N is a nonlinear operator and f(r) is a given continuous function. We construct a homotopy \(\Upomega \times [0,1] \to R\) which satisfies
Suppose the approximate solutions of Eqs. 17–19 have the form
Substituting Eq. 20 into Eqs. 17–19 and equating the terms with the identical powers of p, we obtain
and
and
The initial conditions are as follows:
and
Solving Eqs. 21, 23 and 25 and using the boundary condition Eqs. 27–29, we get
Substituting the above values of \(C_{S,0}^{*} ,\,C_{L,0}^{*}\) and \(C_{LS,\,0}^{ * }\) and solving Eqs. 22, 24 and 26 using the boundary condition Eqs. 30–32, we obtain the following results:
Adding Eqs. 34 and 37, we get Eq. 13 in the text. Similarly, we can get Eqs. 14 and 15.
Appendix 2: Matlab Program to Find the Numerical Solution of Equations 8–10
function pdex4
m = 0;
x = linspace(0,1);
t = linspace(0,1000);
sol = pdepe(m,@pdex4pde,@pdex4ic,@pdex4bc,x,t);
u1 = sol(:,:,1);
u2 = sol(:,:,2);
u3 = sol(:,:,3);
figure
plot(x,u1(end,:))
title(‘u1(x,t)’)
% ———————————————–
function (c,f,s) = pdex4pde(x,t,u,DuDx)
M = 0.1;
N = 1;
c = (1; 1; 1);
f = (1; 1; 1).* DuDx;
F1 = –M*u(1)*u(2) + N*u(3);
F2 = –M*u(1)*u(2) + N*u(3);
F3 = M*u(1)*u(2)–N*u(3);
s = (F1; F2; F3);
% ———————————————–
function u0 = pdex4ic(x);
u0 = (1; 0;0);
% ———————————————–
function (pl,ql,pr,qr) = pdex4bc(xl,ul,xr,ur,t)
pl = (ul(1)–1; ul(2);ul(3)–1);
ql = (0;0; 0);
pr = (ur(1); ur(2)–1; ur(3));
qr = (0; 0; 0);
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganesan, S., Anitha, S., Subbiah, A. et al. Mathematical Modeling of a Carrier-Mediated Transport Process in a Liquid Membrane. J Membrane Biol 246, 435–442 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-013-9555-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-013-9555-6