Abstract
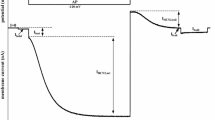
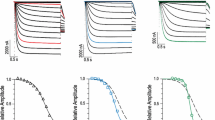
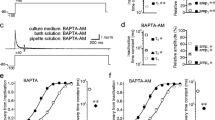
The sensitivity of Cx45 channels to CO2, transjunctional voltage (V j) and inhibition of calmodulin (CaM) expression was tested in oocytes by dual voltage clamp. Cx45 channels are very sensitive to V j and close with V j preferentially by the slow gate, likely to be the same as the chemical gate. With a CO2-induced drop in junctional conductance (G j), both the speed of V j-dependent inactivation of junctional current (I j) and V j sensitivity increased. With 40-mV V j-pulses, the τ of single exponential I j decay reversibly decreased by ˜40% during CO2 application, and Gj steady state/Gj peak decreased multiphasically, indicating that both kinetics and V j sensitivity of chemical/slow V j gating are altered by changes in [H+]i and/or [Ca2+]i. CaM expression was inhibited with oligonucleotides antisense to CaM mRNA. With 15 min CO2, relative junctional conductance (G jt/G jt0) dropped to 0% in controls, but only by ˜17% in CaM-antisense oocytes. Similarly, V j sensitivity was significantly lessened in CaM-antisense oocytes. The data indicate that both the speed and sensitivity of V j-dependent inactivation of the junctional current of Cx45 channels are affected by CO2 application, and that CaM plays a key role in channel gating.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Ahmad P.E. Martin W.H. Evans (2001) ArticleTitleAssembly of gap junction channels: mechanism, effects of calmodulin antagonists and identification of connexin oligomerization determinants. Eur. J. Biochem. 268 4544–4552 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmtlGjsrY%3D Occurrence Handle11502216
L.C. Barrio J. Capel J.A. Jarillo C. Castro A. Revilla (1997) ArticleTitleSpecies-specific voltage-gating properties of connexin-45 junctions expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Biophys. J. 73 757–769 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXkvFCmurc%3D Occurrence Handle9251792
L.C. Barrio T. Suchyna T. Bargiello L.X. Xu R.S. Roginski M.V.L. Bennett B.J. Nicholson (1991) ArticleTitleGap junctions formed by connexins 26 and 32 alone and in combination are differently affected by applied voltage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88 8410–8414 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXmt12htr4%3D Occurrence Handle1717979
F.F. Bukauskas A. Bukauskiene V.K. Verselis M.V.L. Bennett (2002) ArticleTitleCoupling asymmetry of heterotypic connexin 45/connexin 43-EGFP gap junctions: Properties of fast and slow gating mechanisms. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99 7113–7118 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjvFCqtbc%3D Occurrence Handle12011467
F.F. Bukauskas C. Peracchia (1997) ArticleTitleTwo distinct gating mechanisms in gap junction channels: CO2-sensitive and voltage-sensitive. Biophys. J. 72 2137–2142 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXivVOqs7o%3D Occurrence Handle9129815
J.M. Crow M.M. Atkinson R.G. Johnson (1994) ArticleTitleMicromolar levels of intracellular calcium reduce gap junctional permeability in lens cultures. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 35 3332–3341 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuA387hsVA%3D Occurrence Handle8045723
B. Délage J. Délèze (1998) Increase in gap junction conductance of adult mammalian heart myocytes by intracellular calcium ions. R. Werner (Eds) Gap Junctions. IOS Press Amsterdam 72–75
M. Delmar K. Stergiopoulos N. Homma G. Calero G. Morley J.F. Ek-Vitorin S.M. Taffet (2000) A molecular model for the chemical regulation of connexin43 channels: the “ball-and-chain” hypothesis. C. Peracchia (Eds) Gap Junctions. Molecular Basis of Cell Communication in Health and Disease Academic Press San Diego, CA 223–248
J.A. Diez M. Elvira A. Villalobo (1998) ArticleTitleThe epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates connexin32. Molec. Cell. Biochem. 187 201–210 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmsFKku7c%3D Occurrence Handle9788758
H.S. Duffy P.L. Sorgen M.E. Girvin P. O'Donnell W. Coombs S.M. Taffet M. Delmar D.C. Spray (2002) ArticleTitlepH-dependent intramolecular binding and structure involving Cx43 cytoplasmic domains. J. Biol. Chem. 277 36706–36714 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnsVCisbY%3D Occurrence Handle12151412
S. Elenes A.D. Martinez M. Delmar E.C. Beyer A.P. Moreno (2001) ArticleTitleHeterotypic docking of Cx43 and Cx45 connexons blocks fast voltage gating of Cx43. Biophys. J. 81 1406–1418 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmtlCktrg%3D Occurrence Handle11509355
M. Elvira A. Villalobo (1997) ArticleTitleCalmodulin prevents the proteolysis of connexin32 by m-calpain. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 42 207–211 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXktVWqtrk%3D
M.O.K. Enkvist K.D. McCarthy (1994) ArticleTitleAstroglial gap junction communication is increased by treatment with either glutamate or high K+ concentration. J. Neurochem. 62 489–495 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXht1Grtbo%3D Occurrence Handle7905024
C. Giaume L. Venance (1996) Characterization and regulation of gap junction channels in cultured astrocytes. D.C. Spray R. Dermietzel (Eds) Gap Junctions in the Nervous System. R.G. Landes Medical Pub. Co. Austin TX 135–157
S.J. Girsch C. Peracchia (1992) ArticleTitleCalmodulin binding sites in connexins. Biophys. J. 61 A506
A.L. Harris (2001) ArticleTitleEmerging issues of connexin channels: Biophysics fills the gap. Quart. Rev. Biophys. 34 325–472 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XitVCnt70%3D
M.M.P. Hermans P. Kortekaas H.J. Jongsma M.B. Rook (1995) ArticleTitlepH sensitivity of the cardiac gap junction proteins, connexin 45 and 43. Pfluegers Arch. 431 138–140 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xht1Srtbs%3D
E.L. Hertzberg N.B. Gilula (1981) ArticleTitleLiver gap junctions and lens fiber junctions: comparative analysis and calmodulin interaction. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 46 639–645 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38XksFWntr0%3D
A. Lazrak C. Peracchia (1993) ArticleTitleGap junction gating sensitivity to physiological internal calcium regardless of pH in Novikoff hepatoma cells. Biophys. J. 65 2002–2012 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXltVyltg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8298030
A. Lazrak A. Peres S. Giovannardi C. Peracchia (1994) ArticleTitleCa-mediated and independent effects of arachidonic acid on gap junctions and Ca-independent effects of oleic acid and halothane. Biophys. J. 67 1052–1059 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmtVWksrY%3D Occurrence Handle7811915
W.R. Loewenstein (1966) ArticleTitlePermeability of membrane junctions. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 137 441–472 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF28XkslGqs70%3D Occurrence Handle5229810
D. Mears N.F. Sheppard Jr. I. Atwater E. Rojas (1995) ArticleTitleMagnitude and modulation of pancreatic β-cell gap junction electrical conductance in situ. J. Membrane Biol. 146 163–176 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnt1ygu70%3D
A.P. Moreno J.G. Laing E.C. Beyer D.C. Spray (1995) ArticleTitleProperties of gap junction channels formed of connexin 45 endogenously expressed in human hepatoma (SKHep1) cells. Am. J. Physiol. 268 C356–C365 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXktFGnsrw%3D Occurrence Handle7532358
C. Peracchia (1984) ArticleTitleCommunicating junctions and calmodulin: inhibition of electrical uncoupling in Xenopus embryo by calmidazolium. J. Membrane Biol. 81 49–58 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXls1yhsLc%3D
C. Peracchia (1987) ArticleTitleCalmodulin-like proteins and communicating junctions. Electrical uncoupling of crayfish septate axons is inhibited by the calmodulin inhibitor W7 and is not affected by cyclic nucleotides. Pfluegers Arch. 408 379–385 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXltlWls70%3D
C. Peracchia (1988) The Calmodulin hypothesis for gap junction regulation six years later. E.L. Hertzberg R.G. Johnson (Eds) Gap Junctions. Modern Cell Biology Series. Vol. VII. Alan R. Liss, Inc. New York 267–282
C. Peracchia (1990a) ArticleTitleIncrease in gap junction resistance with acidification in crayfish septate axons is closely related to changes in intracellular calcium but not hydrogen ion concentration. J. Membrane Biol. 113 75–92 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXhtFKnsr8%3D
C. Peracchia (1990b) ArticleTitleEffects of caffeine and ryanodine on low pHi-induced changes in gap junction conductance and calcium concentration in crayfish septate axons. J. Membrane Biol. 117 79–89 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXlt12ru7o%3D
C. Peracchia G. Bernardini L.L. Peracchia (1981) ArticleTitleA calmodulin inhibitor prevents gap junction crystallization and electrical uncoupling. J. Cell Biol. 9 124a
C. Peracchia G. Bernardini L.L. Peracchia (1983) ArticleTitleIs calmodulin involved in the regulation of gap junction permeability? Pfluegers Arch. 399 152–154 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXmtFSisLY%3D
C. Peracchia A. Lazrak L.L. Peracchia (1994) Molecular models of channel interaction and gating in gap junctions. C. Peracchia (Eds) Handbook of Membrane Channels-Molecular and Cellular Physiology. Academic Press San Diego 361–377
Peracchia, C., Shen, L. 1993. Gap junction channel reconstitution in artificial bilayers and evidence for calmodulin binding sites in MIP26 and connexins from heart, liver and Xenopus embryo. In: Gap Junctions, J.E. Hall, G.A. Zampighi, and R.M. Davis, editors. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Prog. Cell Res. 3:163–170
C. Peracchia A. Sotkis X.G. Wang L.L. Peracchia A. Persechini (2000a) ArticleTitleCalmodulin directly gates gap junction channels. J. Biol. Chem. 275 26220–26224 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmt1Oksbo%3D
C. Peracchia X.G. Wang (1997) ArticleTitleConnexin domains relevant to the chemical gating of gap junction channels. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 30 577–590 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjvVCnu7Y%3D Occurrence Handle9283624
C. Peracchia X. Wang L. Li L.L. Peracchia (1996) ArticleTitleInhibition of calmodulin expression prevents low-pH-induced gap junction uncoupling in Xenopus oocytes. Pfluegers Arch. 431 379–387 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjtFagtb4%3D
C. Peracchia X.G. Wang L.L. Peracchia (1999) ArticleTitleIs the chemical gate of connexins voltage sensitive? Behavior of Cx32 wild-type and mutant channels. Am. J. Physiol. 276 C1361–C1373 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXktlSqs7Y%3D Occurrence Handle10362599
C. Peracchia X.G. Wang L.L. Peracchia (2000b) Behavior of chemical- and slow voltage-sensitive gating of connexin channels: the “Cork” gating hypothesis. C. Peracchia (Eds) Gap Junctions- Molecular Basis of Cell Communication in Health and Disease Academic Press San Diego, CA 271–295
C. Peracchia X.G. Wang L.L. Peracchia (2000c) ArticleTitleSlow gating of gap junction channels and calmodulin. J. Membrane Biol. 78 55–70
A.E. Pereda T.D. Bell B.H. Chang A.J. Czernik A.C. Nairn T.R. Soderling D.S. Faber (1998) ArticleTitleCa2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II mediates simultaneous enhancement of gap-junctional conductance and glutamatergic transmission. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95 13272–13277 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXntFWrsL8%3D Occurrence Handle9789078
A. Persechini K.J. Gansz R.J. Paresi (1996) ArticleTitleActivation of myosin light chain kinase and nitric oxide synthase activities by engineered calmodulins with duplicated or exchanged EF hand pairs. Biochemistry 35 224–228 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXpvFWhtr8%3D Occurrence Handle8555178
M.H. Pina-Benabou M. Srinivas D.C. Spray E. Scemes (2001) ArticleTitleCalmodulin kinase pathway mediates the K+-induced increase in gap junctional communication between mouse spinal cord astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 21 6635–6643 Occurrence Handle11517253
P.E.M. Purnick S.H. Oh C.K. Abrams V.K. Verselis T.A. Bargiello (2000) ArticleTitleReversal of the gating polarity of gap junctions by negative charge substitutions in the N-terminus of connexin 32. Biophys. J. 79 2403–2415 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXotFegtro%3D Occurrence Handle11053119
B. Rose W.R. Loewenstein (1975) ArticleTitlePermeability of cell junction depends on local cytoplasmic calcium activity. Nature 254 250–252 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2MXlsleitLs%3D Occurrence Handle234601
Y. Saimi C. Kung (2002) ArticleTitleCalmodulin as an ion channel subunit. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 64 289–311 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XisFGmsLs%3D
D.C. Spray A.L. Harris M.V.L. Bennett (1981a) ArticleTitleEquilibrium properties of a voltage-dependent junctional conductance. J. Gen. Physiol. 77 77–93 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi6C2czptlA%3D
D.C. Spray A.L. Harris M.V. Bennett (1981b) ArticleTitleGap junctional conductance is a simple and sensitive function of intracellular pH. Science 211 712–715 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXotVKhsg%3D%3D
E. Steiner L. Ebihara (1996) ArticleTitleFunctional characterization of canine connexin45. J. Membrane Biol. 150 153–161 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002329900040 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XitVKlt70%3D
K. Stergiopoulos J.L. Alvarado M. Mastroianni J.F. Ek-Vitorin S.M. Taffet M. Delmar (1999) ArticleTitleHetero-domain interactions as a mechanism for the regulation of connexin channels. Circ. Res. 84 1144–1155 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjsVygsrg%3D Occurrence Handle10347089
T.M. Suchyna L.X. Xu F. Gao C.R. Fourtner B.J. Nicholson (1993) ArticleTitleIdentification of a proline residue as a transduction element involved in voltage gating of gap junctions. Nature 365 847–849 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXivFWn Occurrence Handle8413670
K. Török K. Stauffer W.H. Evans (1997) ArticleTitleConnexin 32 of gap junctions contains two cytoplasmic calmodulin-binding domains. Biochem. J. 326 479–483 Occurrence Handle9291121
L. Turin A.E. Warner (1977) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide reversibly abolishes ionic communication between cells of early amphibian embryo. Nature 270 56–57
V. Valiunas (2002) ArticleTitleBiophysical properties of connexin-45 gap junction hemichannels studied in vertebrate cells. J. Gen. Physiol. 119 147–164 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XhsVGqsL4%3D Occurrence Handle11815665
L.J. Van Eldik E.L. Hertzberg R.C. Berdan N.B. Gilula (1985) ArticleTitleInteraction of calmodulin and other calcium-modulated proteins with mammalian and arthropod junctional membrane proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 126 825–832 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXhtVyns70%3D Occurrence Handle2983692
R.D. Veenstra H.-Z. Wang E.M. Westphale E.C. Beyer (1992) ArticleTitleMultiple connexins confer distinct regulatory and conductance properties of gap junctions in developing heart. Circ. Res. 71 1277–1283 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XmsVyrurk%3D Occurrence Handle1382884
X.G. Wang C. Peracchia (1997) ArticleTitlePositive charges of the initial C-terminus domain of Cx32 inhibit gap junction gating sensitivity to CO2. Biophys. J. 73 798–806 Occurrence Handle9251796
R. Werner E. Levine C. Rabadan-Diehl G. Dahl (1991) ArticleTitleGating properties of connexin32 cell-cell channels and their mutant expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 243 5–11
K.C. Young C. Peracchia (2002) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide sensitive voltage gating of connexin32 and connexin 32/45 chimeric channels. Mol. Biol. Cell 13 351a
D.B. Zimmer C.R. Green W.E. Evans N.B. Gilula (1987) ArticleTitleTopological analysis of the major protein in isolated intact rat liver gap junctions and gap junction-derived single membrane structures. J. Biol. Chem. 262 7751–7763 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXktlGgtr0%3D Occurrence Handle3034905
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, grant GM20113.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peracchia, C., Young, K., Wang, X. et al. Is the Voltage Gate of Connexins CO2-sensitive? Cx45 Channels and Inhibition of Calmodulin Expression . J. Membrane Biol. 195, 53–62 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-003-2044-6
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-003-2044-6