Abstract
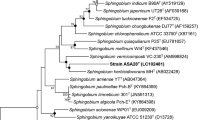
A yellow-pigmented novel bacterial strain, MAH-12T, was isolated from a soil sample of Korean radish garden and was characterized using a polyphasic approach. Cells were Gram-staining negative, non-motile and rod-shaped. The strain was aerobic, catalase positive, optimum growth temperature and pH were 28–30 °C and 6.0, respectively. The novel strain is able to hydrolyze l-tyrosine, starch, esculin and 4-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside. On the basis of 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, strain MAH-12T belongs to the genus Sphingobium and is most closely related to several Sphingobium type strains (97.2–97.8%). In DNA–DNA hybridization tests, the DNA relatedness between strain MAH-12T and its closest phylogenetic neighbors was below 45.0%. The DNA G + C content was 64.0 mol% and the predominant respiratory quinone was ubiquinone-10. The major cellular fatty acids were summed feature 8 (C18:1 ω7c and/or C18:1 ω6c) and C16:0. The DNA–DNA hybridization results and results of the genotypic analysis in combination with chemotaxonomic and physiological data demonstrated that strain MAH-12T represented a novel species within the genus Sphingobium, for which the name Sphingobium tyrosinilyticum is proposed. The type strain is MAH-12T (= KACC 19297T = CGMCC 1.16225T). The NCBI GenBank accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain MAH-12T is KY964278 and the digital protologue database taxon number of strain MAH-12T is TA00463.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bala K, Sharma P, Lal R (2010) Sphingobium quisquiliarum sp. nov., a hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH)-degrading bacterium isolated from an HCH-contaminated soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60(2):429–433
Christensen WB (1946) Urea decomposition as a means of differentiating proteus and paracolon cultures from each other and from Salmonella and Shigella types. J Bacteriol 52:461–466
Collins MD (1985) Isoprenoid quinone analyses in bacterial classification and identification. In: Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (eds) Chemical methods in bacterial systematics. Academic Press, London, pp 267–287
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Fautz E, Reichenbach H (1980) A simple test for flexirubin-type pigments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 8:87–91
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Francis IM, Jochimsen KN, De Vos P, van Bruggen AH (2014) Reclassification of rhizosphere bacteria including strains causing corky root of lettuce and proposal of Rhizorhapis suberifaciens gen. nov., comb. nov., Sphingobium mellinum sp. nov., Sphingobium xanthum sp. nov. and Rhizorhabdus argentea gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64(4):1340–1350
Gillis M, De Ley J, De Cleene M (1970) The determination of molecular weight of bacterial genome DNA from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:143–153
Gomori G (1955) Preparation of buffers for use in enzyme studies. In: Colowick SP, Kaplan NO (eds) Methods in enzymology. Academic Press, New York, pp 138–146
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Huq MA (2018) Caenispirillum humi sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from the soil of Korean pine garden. Arch Microbiol 200:343–348
Kaur J, Moskalikova H, Niharika N, Sedlackova M, Hampl A, Damborsky J, Prokop Z, Lal R (2013) Sphingobium baderi sp. nov., isolated from a hexachlorocyclohexane dump site. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(2):673–678
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematic. Wiley, New York, pp 115–175
Maeda AH, Kunihiro M, Ozeki Y, Nogi Y, Kanaly RA (2015) Sphingobium barthaii sp. nov., a high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium isolated from cattle pasture soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65(9):2919–2924
McConaughy BL, Laird CD, McCarthy BJ (1969) Nucleic acid reassociation in formamide. Biochemistry 8:3289–3295
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G + C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Moore DD, Dowhan D (1995) Preparation and analysis of DNA. In: Ausubel FW, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (eds) Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, New York, pp 2–11
Prakash O, Lal R (2006) Description of Sphingobium fuliginis sp. nov., a phenanthrene-degrading bacterium from a fly ash dumping site, and reclassification of Sphingomonas cloacae as Sphingobium cloacae comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56(9):2147–2152
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Bio Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids, MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc, Newark
Skerman VBD (1967) A guide to the identification of the genera of bacteria, 2nd edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Stabili L, Gravili C, Tredici SM, Piraino S, Talà A, Boero F, Alifano P (2008) Epibiotic Vibrio luminous bacteria isolated from some hydrozoa and bryozoa species. Microb Ecol 56:625–636
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: A place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Takeuchi M, Hamana K, Hiraishi A (2001) Proposal of the genus Sphingomonas sensu stricto and three new genera, Sphingobium, Novosphingobium and Sphingopyxis, on the basis of phylogenetic and chemotaxonomic analyses. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51(4):1405–1417
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Vaz-Moreira I, Faria C, Lopes AR, Svensson L, Falsen E, Moore ER, Ferreira AC, Nunes OC, Manaia CM (2009) Sphingobium vermicomposti sp. nov., isolated from vermicompost. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59(12):3145–3149
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR et al (1987) International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Acknowledgements
This study was performed with the support of the Cooperative Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea Grant (Project No. NRF-2016R1A2B4014591) funded by the Korea government (MISP), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
The NCBI GenBank accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strains MAH-12T is KY964278.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
203_2018_1531_MOESM1_ESM.pptx
Supplementary Table 1. Negative properties of strain MAH-12T carried out by commercial test kits (API 20NE and API ZYM) (PPTX 50 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huq, M.A., Akter, S., Siddiqi, M.Z. et al. Sphingobium tyrosinilyticum sp. nov., a tyrosine hydrolyzing bacterium isolated from Korean radish garden. Arch Microbiol 200, 1143–1149 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1531-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1531-1