Abstract
Purpose
The need to treat small (<7 mm) unruptured aneurysms is still controversial, despite data collected through several large cohort studies. Such lesions typically are incidental findings, usually followed for potential growth through serial imaging. For this study, growth estimates for untreated unruptured small-sized aneurysms were generated, examining incidence and related risk factors.
Methods
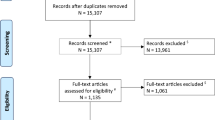
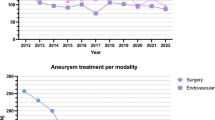
A cohort of 135 consecutive patients harboring 173 untreated unruptured small-sized aneurysms (<7 mm) was subjected to extended monitoring (mean, 73.1 ± 30.0 months). Growth was defined as a 1-mm increase at minimum in one or more aneurysmal dimensions or as a significant change in shape. Medical records and radiological data were reviewed. Cumulative growth rate and related risk factors were analyzed via Cox proportional hazards regression and Kaplan-Meier product-limit estimator.
Results
A total of 28 aneurysms (16.2%) displayed growth during continued surveillance (1054.1 aneurysm-years). The annual growth rate was 2.65% per aneurysm-year, with 15 surfacing within 60 months and 13 after 60 months. Multivariate analysis indicated that bifurcation type was the sole significant risk factor (hazard ratio HR = 7.64; p < 0.001) in terms of growth. Cumulative survival rates without growth were significantly lower in subjects with bifurcation aneurysms than with side-wall aneurysms (p < 0.001). During the follow-up period, one patient suffered a subarachnoid hemorrhage and then aneurysm growth was detected.
Conclusion
Most (83.8%) untreated unruptured small-sized aneurysms (<7 mm) remained stable and devoid of growth in long-term follow-up. Because bifurcation aneurysms were prone to eventual growth, careful long-term monitoring at regular intervals is advised if left untreated.



Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Rinkel GJ. Natural history, epidemiology and screening of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2008;164:781–6.
Brown RD. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Semin Neurol. 2010;30:537–44.
Vlak GMH, Algra A, Brandenburg R, Rinkel GJ. Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10:626–36.
Liu H, Park D, Hwang SM, Lee GY, Lim OK, Kim M, Lee DH, Park W, Koo HW, Yang K, Suh DC. Outpatient day-care Neuroangiography and Neurointervention of Unruptured Intracranial aneurysms. Neurointervention. 2016;11:37–41.
Park KY, Kim BM, Kim DJ. Comparison between balloon-assisted and stent-assisted technique for treatment of unruptured internal carotid artery aneurysms. Neurointervention. 2016;11:99–104.
Zacharia BE, Ducruet AF, Hickman ZL, Grobelny BT, Badjatia N, Mayer SA, Berman MF, Solomon RA, Connolly ES Jr. Technological advances in the management of unruptured intracranial aneurysms fail to improve outcome in New York state. Stroke. 2011;42:2844–9.
Hoh BL, Nathoo S, Chi YY, Mocco J, Barker FG 2nd. Incidence of seizures or epilepsy after clipping or coiling of ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysms in the nationwide inpatient sample database: 2002–2007. Neurosurgery. 2011;69:644–50.
Naggara ON, Lecler A, Oppenheim C, Meder JF, Raymond J. Endovascular treatment of intracranial unruptured aneurysms: A systematic review of the literature on safety with emphasis on subgroup analyses. Radiology. 2012;263:828–35.
Raaymakers TW, Rinkel GJ, Limburg M, Algra A. Mortality and morbidity of surgery for unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a meta-analysis. Stroke. 1998;29:1531–8.
Juvela S, Poussa K, Lehto H, Porras M. Natural history of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: A long-term follow-up study. Stroke. 2013;44:2414–21.
Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Huston J 3rd, Meissner I, Brown RD Jr, Piepgras DG, Forbes GS, Thielen K, Nichols D, O’Fallon WM, Peacock J, Jaeger L, Kassell NF, Kongable-Beckman GL, Torner JC; International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Investigators.. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: Natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet. 2003;362:103–10.
Korja M, Lehto H, Juvela S. Lifelong rupture risk of intracranial aneurysms depends on risk factors: A prospective Finnish cohort study. Stroke. 2014;45:1958–63.
UCAS Japan Investigators., Morita A, Kirino T, Hashi K, Aoki N, Fukuhara S, Hashimoto N, Nakayama T, Sakai M, Teramoto A, Tominari S, Yoshimoto T. The natural course of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in a Japanese cohort. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2474–82.
Chmayssani M, Rebeiz JG, Rebeiz TJ, Batjer HH, Bendok BR. Relationship of growth to aneurysm rupture in asymptomatic aneurysms ≤ 7 mm: a systematic analysis of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2011;68:1164–71.
Brinjikji W, Zhu YQ, Lanzino G, Cloft HJ, Murad MH, Wang Z, Kallmes DF. Risk factors for growth of Intracranial aneurysms: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016;37:615–20.
Backes D, Rinkel GJ, Laban KG, Algra A, Vergouwen MD. Patient- and aneurysm-specific risk factors for Intracranial aneurysm growth: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Stroke. 2016;47:951–7.
Mehan WA Jr, Romero JM, Hirsch JA, Sabbag DJ, Gonzalez RG, Heit JJ, Schaefer PW. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms conservatively followed with serial CT angiography: Could morphology and growth predict rupture? J Neurointerv Surg. 2014;6:761–6.
Gao B, Baharoglu MI, Cohen AD, Malek AM. Stent-assisted coiling of intracranial bifurcation aneurysms leads to immediate and delayed intracranial vascular angle remodeling. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33:649–54.
Baharoglu MI, Lauric A, Gao BL, Malek AM. Identification of a dichotomy in morphological predictors of rupture status between sidewall- and bifurcation-type intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2012;116:871–81.
Burns JD, Huston J 3rd, Layton KF, Piepgras DG, Brown RD Jr.. Intracranial aneurysm enlargement on serial magnetic resonance angiography: frequency and risk factors. Stroke. 2009;40:406–11.
Bor AS, Tiel Groenestege AT, terBrugge KG, Agid R, Velthuis BK, Rinkel GJ, Wermer MJ. Clinical, radiological, and flow-related risk factors for growth of untreated, unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Stroke. 2015;46:42–8.
Qureshi AI, Suri MF, Nasar A, Kirmani JF, Divani AA, He W, Hopkins LN. Trends in hospitalization and mortality for subarachnoid hemorrhage and unruptured aneurysms in the United States. Neurosurgery. 2005;57:1–8.
Nieuwkamp DJ, Setz LE, Algra A, Linn FH, de Rooij NK, Rinkel GJ. Changes in case fatality of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and region: a meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:635–42.
Brown RD Jr., Broderick JP. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: epidemiology, natural history, management options, and familial screening. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13:393–404.
Ishibashi T, Murayama Y, Urashima M, Saguchi T, Ebara M, Arakawa H, Irie K, Takao H, Abe T. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: incidence of rupture and risk factors. Stroke. 2009;40:313–6.
Villablanca JP, Duckwiler GR, Jahan R, Tateshima S, Martin NA, Frazee J, Frazee J, Gonzalez NR, Sayre J, Viñuela FV. Natural history of asymptomatic unruptured cerebral aneurysms evaluated at CT angiography: Growth and rupture incidence and correlation with epidemiologic risk factors. Radiology. 2013;269:258–65.
Teo M, George StEJ. Radiologic surveillance of untreated Unruptured Intracranial aneurysms: A single surgeon’s experience. World Neurosurg. 2016;90:20–8.
Inoue T, Shimizu H, Fujimura M, Saito A, Tominaga T. Annual rupture risk of growing unruptured cerebral aneurysms detected by magnetic resonance angiography. J Neurosurg. 2012;117:20–5.
Nahed BV, DiLuna ML, Morgan T, Ocal E, Hawkins AA, Ozduman K, Kahle KT, Chamberlain A, Amar AP, Gunel M. Hypertension, age, and location predict rupture of small intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2005;57:676–83.
Chalouhi N, Ali MS, Jabbour PM, Tjoumakaris SI, Gonzalez LF, Rosenwasser RH, Koch WJ, Dumont AS. Biology of intracranial aneurysms: role of inflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2012;32:1659–76.
Jeong W, Rhee K. Hemodynamics of cerebral aneurysms: computational analyses of aneurysm progress and treatment. Comput Math Methods Med. 2012;2012:782801.
Feng Y, Wada S, Tsubota K, Yamaguchi T. The application of computer simulation in the genesis and development of intracranial aneurysms. Technol Health Care. 2005;13:281–91.
Meng H, Wang Z, Hoi Y, Gao L, Metaxa E, Swartz DD, Kolega J. Complex hemodynamics at the apex of an arterial bifurcation induces vascular remodeling resembling cerebral aneurysm initiation. Stroke. 2007;38:1924–31.
Shojima M, Oshima M, Takagi K, Torii R, Hayakawa M, Katada K, Morita A, Kirino T. Magnitude and role of wall shear stress on cerebral aneurysm: Computational fluid dynamic study of 20 middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Stroke. 2004;35:2500–5.
Alfano JM, Kolega J, Natarajan SK, Xiang J, Paluch RA, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Meng H. Intracranial aneurysms occur more frequently at bifurcation sites that typically experience higher hemodynamic stresses. Neurosurgery. 2013;73:497–505.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
H.H. Choi, Y.D. Cho, J.P. Jeon, D.H. Yoo, J. Moon, J. Lee, H.-S. Kang, W.-S Cho, J.E. Kim, L. Zhang and M.H. Han declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
All studies on humans described in this manuscript were carried out with approval of the responsible ethics committee and in accordance with national law and the Helsinki Declaration from 1964 (in its current revised form). The requirement to obtain written informed consent for study participation was waived.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, H.H., Cho, Y.D., Jeon, J.P. et al. Growth of Untreated Unruptured Small-sized Aneurysms (≺7mm): Incidence and Related Factors. Clin Neuroradiol 28, 183–189 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-017-0559-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-017-0559-y