Abstract
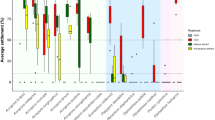
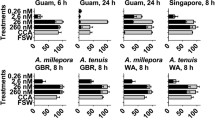
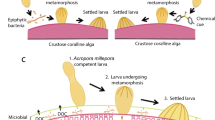
The crustose coralline alga Lithothamnium pseudosorum induces high rates of settlement and metamorphosis of larvae of the coral-eating crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster planci). In cases where crustose coralline algae (CCA) induce metamorphosis of marine invertebrate larvae it is normally assumed that the inductive molecules are produced by the alga, but an alternative is that they originate from bacteria on the plant surface. Bioassays using shards of L. pseudosorum treated with several antibiotics, whereby some shards were reinfected with bacteria from the alga, showed that if bacteria populations are depleted then settlement and metamorphosis of larvae of A. planci are inhibited. This demonstrates that bacteria are necessary for induction and suggests that morphogenic substances are produced by bacteria on the surface of the alga and not directly by the alga itself. However, surface bacteria are not inductive if they are isolated from soluble algal compounds, suggesting either that they require a substrate from the alga to produce the inductive agents or, alternatively but less likely, that compounds from both the alga and bacteria are required. There is no evidence that inductive compounds derive from the alga, since algal cell debris and soluble extracts prepared from the alga do not induce metamorphosis of A. planci. This is the first time that induction of metamorphosis in a marine invertebrate by CCA has been shown to be mediated by bacteria associated with the alga.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brancato MS, Woollacott RM (1982) Effect of microbial films on settlement of bryozoan larvae (Bugula simplex, B. stolonifera and B. turrita). Mar Biol 71:51–56
Day RW, Quinn, GP (1989) Comparison of treatments after an analysis of variance in ecology. Ecol Monogr 59:433–463
Fitt, WK, Coon SL, Walch M, Weimer RM, Colwell, R, Bonar DB (1990) Settlement behaviour and metamorphosis of oyster larvae (Crassostrea gigas) in response to bacterial supernatants. Mar Biol 106:389–394
Garland CD, Cooke, SL, Grant JF, McMeekin TA (1985) Ingestion of bacteria on and the cuticle of crustose (non-articulated) coral-line algae by post-larval and juvenile abalone (Haliotis ruber Leach) from Tasmanian waters. J. exp mar Biol Ecol 91:137–149
Gottschalk G (1986) Bacterial metabolism (2nd edn). Springer-Verlag, New York
Hahn KO (ed) (1989) Induction of settlement in competent abalone larvae. In: Hahn KO (ed.) Handbook of culture of abalone and other marine gastropods. CRC Press, Florida, pp 101–112
Hofmann DK, Brand U (1987) Induction of metamorphosis in the symbiotic scyphozoan Cassiopea andromeda: role of marine bacteria and biochemicals. Symbiosis 4:99–116
Johnson CR (1992) Settlement and recruitment of Acanthaster planci on the Great Barrier Reef: questions of process and scale. Aust J mar Freshwat Res 43:611–627
Johnson CR, Mann KH (1986) The crustose coralline alga, Phymatolithon Foslie, inhibits the overgrowth of seaweeds without relying on herbivores. J exp mar biol Ecol 96:127–146
Johnson CR, Muir DG, Reysenbach AL (1991 a) Characteristic bacteria associated with surfaces of coralline algae: a hypothesis for bacterial induction of marine invertebrate larvae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 74:281–294
Johnson CR, Sutton, DC, Olson RR, Giddins R (1991 b) Settlement of crown-of-thorns starfish: role of bacteria on surfaces of coral-line algae and a hypothesis for deepwater recruitment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 71:143–162
Kirchman D, Graham S, Reish D, Mitchell R (1982) Bacteria induce settlement and metamorphosis of Janua (Dexiospira) Brasiliensis Grube (Polychaeta: Spirorbidae). J. exp mar Biol Ecol 56: 153–163
Lewis TE, Garland CD, McMeekin TA (1985) The bacterial biota on crustose (nonarticulated) coralline algae from Tasmanian waters. Microb Ecol 11:221–230
Moriarty DW (1986) Measurement of bacterial growth rates in aquatic systems from rates of nucleic acid synthesis. Adv microb Ecol 9:245–291
Morse ANC, Froyd CA, Morse DE (1984) Molecules from cyanobacteria and red algae that induce larval settlement and metamorphosis in the mollusc Haliotis rufescens. Mar Biol 81:293–298
Morse DE, Hooker N, Duncan H, Jensen L (1979) γ-aminobutyric acid, a neurotransmitter, induces planktonic abalone larvae to settle and begin metamorphosis. Science, NY 204:407–410
Morse ANC, Morse DE (1984) Recruitment and metamorphosis of Haliotis larvae induced by molecules uniquely available at the surfaces of crustose red algae. J exp mar Biol Ecol 75:191–215
Neumann R (1979) Bacterial induction of settlement and metamorphosis in the planula larvae of Cassiopea andromeda (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa, Rhizostomeae). Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 1:21–28
Pawlik JR (1990) Natural and artificial induction of metamorphosis of Phragmatopoma lapidosa californica (Polychaeta: Sabellariidae), with a critical look at the effects of bioactive compounds on marine invertebrate larvae. Bull mar Sci 46:512–536
Steneck RS (1982) A limpet-coralline alga association: adaptations and defenses between a selective herbivore and its prey. Ecology 63:507–522
Weiner RM, Segall AM, Colwell RR (1985) Characterization of a marine bacterium associated with Crassostrea virginica (the eastern oyster). Appl envirl Microbiol 49:83–90
White A, Handler P, Smith EL (1968) Principles of biochemistry (4th edn). McGraw Hill, New York
Wolk M, Rahat M, Fitt WK, Hofmann DK (1985) Cholera toxin and thyrotropine can replace natural inducers required for the metamorphosis of larvae and buds of the scyphozoan Cassiopea andromeda. Roux's Archs devl Biol 194:487–490
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, C.R., Sutton, D.C. Bacteria on the surface of crustose coralline algae induce metamorphosis of the crown-of-thorns starfish Acanthaster planci . Marine Biology 120, 305–310 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349692
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349692