Abstract
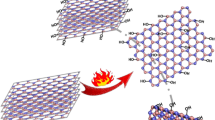
The formation and control of a room-temperature magnetic order in two-dimensional (2D) materials is a challenging quest for the advent of innovative magnetic- and spintronic-based technologies. To date, edge magnetism in 2D materials has been experimentally observed in hydrogen (H)-terminated graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) and graphene nanomeshes (GNMs), but the measured magnetization remains far too small to allow envisioning practical applications. Herein, we report experimental evidences of large room-temperature edge ferromagnetism (FM) obtained from oxygen (O)-terminated zigzag pore edges of few-layer black phosphorus (P) nanomeshes (BPNMs). The magnetization values per unit area are ~100 times larger than those reported for H-terminated GNMs, while the magnetism is absent for H-terminated BPNMs. The magnetization measurements and the first-principles simulations suggest that the origin of such a magnetic order could stem from ferromagnetic spin coupling between edge P with O atoms, resulting in a strong spin localization at the edge valence band, and from uniform oxidation of full pore edges over a large area and interlayer spin interaction. Our findings pave the way for realizing high-efficiency 2D flexible magnetic and spintronic devices without the use of rare magnetic elements.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrari, A. C.; Bonaccorso, F.; Fal’ko, V.; Novoselov, K. S.; Roche, S.; Bøggild, P.; Borini, S.; Koppens, F. H. L.; Palermo, V.; Pugno, N. et al. Science and technology roadmap for graphene, related two-dimensional crystals, and hybrid systems. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 4598–4810.
Roche, S.; Åkerman, J.; Beschoten, B.; Charlier, J. C.; Chshiev, M.; Dash, S. P.; Dlubak, B.; Fabian, J.; Fert, A.; Guimarães, M. et al. Graphene spintronics: The European Flagship perspective. 2D Mater. 2015, 2, 030202.
Yang, H. X.; Hallal, A.; Terrade, D.; Waintal, X.; Roche, S.; Chshiev, M. Proximity effects induced in graphene by magnetic insulators: First-principles calculations on spin filtering and exchange-splitting gaps. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 046603.
Leutenantsmeyer, J. C.; Kaverzin, A. A.; Wojtaszek, M.; van Wees, B. J. Proximity induced room temperature ferromagnetism in graphene probed with spin currents. 2D Mater. 2017, 4, 014001.
Avsar, A.; Tan, J. Y.; Taychatanapat, T.; Balakrishnan, J.; Koon, G. K. W.; Yeo, Y.; Lahiri, J.; Carvalho, A.; Rodin, A. S.; O’Farrell, E. C. T. et al. Spin–orbit proximity effect in graphene. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4875.
Lin, C. F.; Feng, Y. X.; Xiao, Y. D.; Dürr, M.; Huang, X. Q.; Xu, X. Z.; Zhao, R. G.; Wang, E. G.; Li, X.-Z.; Hu, Z. H. Direct observation of ordered configurations of hydrogen adatoms on graphene. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 903–908.
Magda, G. Z.; Jin, X. Z.; Hagymási, I.; Vancsó, P.; Osváth, Z.; Nemes-Incze, P.; Hwang, C.; Biró, L. P.; Tapasztó, L. Room-temperature magnetic order on zigzag edges of narrow graphene nanoribbons. Nature 2014, 514, 608–611.
Nakada, K.; Fujita, M.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M. S. Edge state in graphene ribbons: Nanometer size effect and edge shape dependence. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 17954–17961.
Soriano, D.; Leconte, N.; Ordejón, P.; Charlier, J. C.; Palacios, J. J.; Roche, S. Magnetoresistance and magnetic ordering fingerprints in hydrogenated graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 016602.
Lee, H.; Park, N.; Son, Y. W.; Han, S.; Yu, J. Ferromagnetism at the edges of the stacked graphitic fragments: An ab initio study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 398, 207–211.
Kusakabe, K.; Maruyama, M. Magnetic nanographite. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 092406.
Shimizu, T.; Haruyama, J.; Marcano, D. C.; Kosinkin, D. V.; Tour, J. M.; Hirose, K.; Suenaga, K. Large intrinsic energy bandgaps in annealed nanotube-derived graphene nanoribbons. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 45–50.
Tada, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Haruyama, J.; Yang, H.; Chshiev, M. Spontaneous spin polarization and spin pumping effect on edges of graphene antidot lattices. Phys. Status Solidi B 2012, 249, 2491–2496.
Kato, T.; Nakamura, T.; Kamijyo, J.; Kobayashi, T; Yagi, Y.; Haruyama, J. High-efficiency graphene nanomesh magnets realized by controlling mono-hydrogenation of pore edges. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 252410.
Hashimoto, T.; Kamikawa, S.; Soriano, D.; Pedersen, J. G.; Roche, S.; Haruyama, J. Tunneling magnetoresistance phenomenon utilizing graphene magnet electrode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 183111.
Hashimoto, T.; Kamikwa, S.; Yagi, Y.; Haruyama, J. Electronic properties of nanopore edges of ferromagnetic graphene nanomeshes at high carrier densities under ionic-liquid gating. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2014, 5, 1–9.
Jia, X. T.; Hofmann, M.; Meunier, V.; Sumpter, B. G.; Campos-Delgado, J.; Romo-Herrera, J. M.; Son, H.; Hsieh, Y.-P.; Reina, A.; Kong, J. et al. Controlled formation of sharp zigzag and armchair edges in graphitic nanoribbons. Science 2009, 323, 1701–1705.
Girit, Ç. Ö.; Meyer, J. C.; Erni, R.; Rossell, M. D.; Kisielowski, C.; Yang, L.; Park, C.-H.; Crommie, M. F.; Cohen, M. L.; Louie, S. G. et al. Graphene at the edge: Stability and dynamics. Science 2009, 323, 1705–1708.
You, Y. M.; Ni, Z. H.; Yu, T.; Shen, Z. X. Edge chirality determination of graphene by Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 163112.
Haruyama, J. Graphene and graphene nanomesh spintronics. Electronics 2013, 2, 368–386.
Li, L. K.; Yu, Y. J.; Ye, G. J.; Ge, Q. Q.; Ou, X. D.; Wu, H.; Feng, D. L.; Chen, X. H.; Zhang, Y. B. Black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 372–377.
Churchill, H. O. H.; Jarillo-Herrero, R. Two-dimensional crystals: Phosphorus joins the family. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 330–331.
Koenig, S. P.; Doganov, R. A.; Schmidt, H.; Castro Neto, A. H.; Özyilmaz, B. Electric field effect in ultrathin black phosphorus. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 103106.
Castellanos-Gomez, A.; Vicarelli, L.; Prada, E.; Island, J. O.; Narasimha-Acharya, K. L.; Blanter, S. I.; Groenendijk, D. J.; Buscema, M.; Steele, G. A.; Alvarez, J. V. et al. Isolation and characterization of few-layer black phosphorus. 2D Mater. 2014, 1, 025001.
Zhu, Z. L.; Li, C.; Yu, W. Y.; Chang, D. H.; Sun, Q.; Jia, Y. Magnetism of zigzag edge phosphorene nanoribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 113105.
Peng, X. H.; Copple, A.; Wei, Q. Edge effects on the electronic properties of phosphorene nanoribbons. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 144301.
Carvalho, A.; Rodin, A. S.; Castro Neto, A. H. Phosphorene nanoribbons. EPL 2014, 108, 47005.
Ong, Z. Y.; Cai, Y. Q.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.-W. Strong thermal transport anisotropy and strain modulation in singlelayer phosphorene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 25272–25277.
Du, Y. P.; Liu, H. M., Xu, B.; Sheng, L.; Yin, J.; Duan, C. G.; Wan, X. G. Unexpected magnetic semiconductor behavior in zigzag phosphorene nanoribbons driven by half-filled one dimensional band. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8921.
Zhu, W. N.; Yogeesh, M. N.; Yang, S. X.; Aldave, S. H.; Kim, J.-S.; Sonde, S.; Tao, L.; Lu, N. S.; Akinwande, D. Flexible black phosphorus ambipolar transistors, circuits and AM demodulator. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 1883–1890.
Dai, J.; Zeng, X. C. Bilayer phosphorene: Effect of stacking order on bandgap and its potential applications in thin-film solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1289–1293.
Luo, X.; Lu, X.; Koon, G. K. W.; Castro Neto, A. H.; Özyilmaz, B.; Xiong, Q. H.; Quek, S. Y. Large frequency change with thickness in interlayer breathing mode—Significant interlayer interactions in few layer black phosphorus. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3931–3938.
Ziletti, A.; Carvalho, A; Trevisanutto, P. E.; Campbell, D. K.; Coker, D. F.; Castro Neto, A. H. Phosphorene oxides: Bandgap engineering of phosphorene by oxidation. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 085407.
Liu, H.; Neal, A. T.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Xu, X. F.; Tománek, D.; Ye, P. D. Phosphorene: An unexplored 2D semiconductor with a high hole mobility. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4033–4041.
Gillgren, N.; Wickramaratne, D.; Shi, Y. M.; Espiritu, T.; Yang, J. W.; Hu, J.; Wei, J.; Liu, X.; Mao, Z. Q.; Watanabe, K. et al. Gate tunable quantum oscillations in air-stable and high mobility few-layer phosphorene heterostructures. 2D Mater. 2015, 2, 011001.
Zhu, Z.; Tománek, D. Semiconducting layered blue phosphorus: A computational study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 176802.
Tongay, S.; Varnoosfaderani, S. S.; Appleton, B. R.; Wu, J. Q.; Hebard, A. F. Magnetic properties of MoS2: Existence of ferromagnetism. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 123105.
Ohata, C.; Tagami, R.; Nakanishi, Y.; Iwaki, R.; Nomura, K.; Haruyama, J. Hexagonal boron-nitride nanomesh magnets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 133110.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank J. Akimitsu, K. Horigane, T. Muranaka, Y. K. Fukai, T. Enoki, Y. Otani, S. Murakami, M. Yamamoto, S. Tarucha, T. Ando, A. H. Macdonald, P. Seneor, R. Wiesendanger, M. S. Dresselhaus, P. Herrero, and P. Kim for their technical contributions, fruitful discussions, and encouragements. This work at Aoyama Gakuin was partly supported by a Grantin-aid for Scientific Research (Basic research A: 24241046 and Challenging Exploratory Research: 15K13277) and grant for private University in MEXT and AOARD grant (No. 135049) in U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research. The work in the University of Tokyo was also supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Area, “Nano Spin Conversion Science” (No. 26103003), and by Grants (Nos. 25247051 and 15K17676). S. R. acknowledges Funding from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness and the European Regional Development Fund (No. FIS2015-67767-P (MINECO/FEDER)), the Secretaria de Universidades e Investigación del Departamento de Economía y Conocimiento de la Generalidad de Cataluña, and the Severo Ochoa Program (MINECO, No. SEV-2013-0295).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakanishi, Y., Ishi, A., Ohata, C. et al. Large edge magnetism in oxidized few-layer black phosphorus nanomeshes. Nano Res. 10, 718–728 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1355-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1355-8