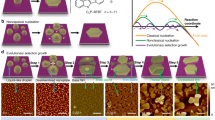
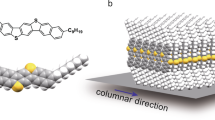
Abstract
The use of organic materials presents a tremendous opportunity to significantly impact the functionality and pervasiveness of large-area electronics. Commercialization of this technology requires reduction in manufacturing costs by exploiting inexpensive low-temperature deposition and patterning techniques, which typically lead to lower device performance. We report a low-cost approach to control the microstructure of solution-cast acene-based organic thin films through modification of interfacial chemistry. Chemically and selectively tailoring the source/drain contact interface is a novel route to initiating the crystallization of soluble organic semiconductors, leading to the growth on opposing contacts of crystalline films that extend into the transistor channel. This selective crystallization enables us to fabricate high-performance organic thin-film transistors and circuits, and to deterministically study the influence of the microstructure on the device characteristics. By connecting device fabrication to molecular design, we demonstrate that rapid film processing under ambient room conditions and high performance are not mutually exclusive.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horowitz, G. Organic field-effect transistors. Adv. Mater. 10, 365–377 (1998).
Dimitrakopoulos, C. D. & Malenfant, P. R. L. Organic thin film transistors for large area electronics. Adv. Mater. 14, 99–117 (2002).
Sirringhaus, H. Device physics of solution-processed organic field-effect transistors. Adv. Mater. 17, 2411–2425 (2005).
Sheraw, C. D. et al. Organic thin-film transistor-driven polymer-dispersed liquid crystal displays on flexible polymeric substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 1088–1090 (2002).
Gelinck, G. H. et al. Flexible active-matrix displays and shift registers based on solution-processed organic transistors. Nature Mater. 3, 106–110 (2004).
Baude, P. F. et al. Pentacene-based radio-frequency identification circuitry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3964 (2003).
Noguchi, Y., Sekitani, T. & Someya, T. Organic-transistor-based flexible pressure sensors using ink-jet-printed electrodes and gate dielectric layers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 253507 (2006).
McCulloch, I. et al. Liquid-crystalline semiconducting polymers with high charge-carrier mobility. Nature Mater. 5, 328–333 (2006).
Klauk, H., Zschieschang, U., Pflaum, J. & Halik, M. Ultralow-power organic complementary circuits. Nature 445, 745–748 (2007).
Jackson, T. N. Organic semiconductors: Beyond Moore’s law. Nature Mater. 4, 581–582 (2005).
Gundlach, D. J. Low-power, big impact. Nature Mater. 6, 173–174 (2007).
Berggren, M., Nilsson, D. & Robinson, N. D. Organic materials for printed electronics. Nature Mater. 6, 3–5 (2007).
Kane, M. G. et al. Analog and digital circuits using organic thin-film transistors on polyester substrates. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 21, 534–536 (2000).
Steudel, S., Myny, K., De Vusser, S., Genoe, J & Heremans, P. Patterning of organic thin film transistors by oxygen plasma etch. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 183503 (2006).
Kymissis, I., Dimitrakopoulos, C. D. & Purushothaman, S. Patterning pentacene organic thin film transistors. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 20, 956–959 (2002).
Loo, Y. L., Willet, R. L., Baldwin, K. W. & Rogers, J. A. Interfacial chemistries for nanoscale transfer printing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 7654–7655 (2002).
Hines, D. R. et al. Nanotransfer printing of organic and carbon nanotube thin-film transistors on plastic substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 163101 (2005).
Blanchet, G. B., Loo, Y. L., Rogers, J. A., Gao, F. & Fincher, C. R. Large area, high resolution, dry printing of conducting polymers for organic electronics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 463–465 (2003).
Choi, H. Y., Kim, S. H. & Jang, J. Self-organized organic thin-film transistors on plastic. Adv. Mater. 16, 732–736 (2004).
Steudel, S., Janssen, D., Verlaak, S., Genoe, J & Heremans, P. Patterned growth of pentacene. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 5550–5552 (2004).
Briseno, A. et al. Patterned growth of large oriented organic semiconductor single crystals on self-assembled monolayer templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 12164–12165 (2005).
Briseno, A. et al. Patterning organic crystal transistor arrays. Nature 444, 913–917 (2006).
Park, S. K., Kuo, C.-C., Anthony, J. E. & Jackson, T. N. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2005, IEDM Technical Digest 113–116 (The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Piscataway, 2005).
Kuo, C.-C., Payne, M. M., Anthony, J. E. & Jackson, T. N. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2004 IEDM Technical Digest 373–376 (The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Piscataway, 2004).
Payne, M. M., Parkin, S. R., Anthony, J. E., Kuo, C.-C. & Jackson, T. N. Organic field-effect transistors from solution-deposited functionalized acenes with mobilities as high as 1 cm2 V−1 s−1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 4986–4987 (2005).
Anthony, J. E., Brooks, J. S., Eaton, D. L. & Parkin, S. R. Functionalized pentacene: Improved electronic properties from control of solid-state order. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 9486–9483 (2001).
Anthony, J. E., Eaton, D. L. & Parkin, S. R. A road map to stable, soluble, easily crystallized pentacene derivatives. Org. Lett. 4, 15–18 (2002).
Gundlach, D. J., Jia, L. L. & Jackson, T. N. Pentacene TFT with improved linear region characteristics using chemically modified source and drain electrodes. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 22, 571–573 (2001).
Kymissis, I., Dimitrakopoulos, C. D. & Purushothaman, S. High-performance bottom electrode organic thin-film transistors. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 48, 1060–1064 (2001).
Bock, C. et al. Improved morphology and charge carrier injection in pentacene field-effect transistors with thiol-treated electrodes. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 114517 (2006).
Gundlach, D. J. et al. An experimental study of contact effects in organic thin film transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 024509 (2006).
Dickey, K. C., Anthony, J. E. & Loo, Y.-L. Improving organic thin-film transistor performance through solvent vapor annealing of solution-processable triethysilylethynyl anthradithiophene. Adv. Mater. 18, 1721–1726 (2006).
Reichenbächer, K., Süss, H. I. & Hulliger, J. Fluorine in crystal engineering—the little atom that could. Chem. Soc. Rev. 34, 22–30 (2005).
Minari, T., Nemoto, T. & Isoda, S. Temperature and electric-field dependence of the mobility of a single-grain pentacene field-effect transistor. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 034506 (2006).
Nelson, S. F., Lin, Y.-Y., Gundlach, D. J. & Jackson, T. N. Temperature-independent transport in high-mobility pentacene transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 1854–1856 (1998).
Park, S. K. et al. 65th Device Research Conference Digest 23–24 (The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Piscataway, 2007).
Subramanian, S. et al. Chromophore fluorination enhances crystallization and stability of soluble anthradithiophene semiconductors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (in the press).
Acknowledgements
Financial support under the Summer Undergraduate Research Fellowship (SURF) by the National Science Foundation is gratefully acknowledged by J.E.R. L.C.T., A.J.M. and B.H.H. acknowledge financial support from the National Research Council postdoctoral fellowship program. J.E.A. acknowledges the Office of Naval Research for financial support of synthesis efforts. D.J.G. acknowledges L. Loo, Princeton U., for many helpful discussions concerning nucleation and film microstructure, and B. Vogel, visiting assistant professor at Bucknell University, for assistance with preliminary differential scanning calorimetry measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary figures S1–S6 (PDF 484 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gundlach, D., Royer, J., Park, S. et al. Contact-induced crystallinity for high-performance soluble acene-based transistors and circuits. Nature Mater 7, 216–221 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2122
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2122
This article is cited by
-
Retina-inspired organic neuromorphic vision sensor with polarity modulation for decoding light information
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
Effect of crystallinity on capacity and cyclic stability of Na1.1V3O7.9 nanoplates as lithium-ion cathode materials
Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry (2020)
-
Organic molecular crystal-based photosynaptic devices for an artificial visual-perception system
NPG Asia Materials (2019)
-
Small contact resistance and high-frequency operation of flexible low-voltage inverted coplanar organic transistors
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Contact patterning by laser printing for flexible electronics on paper
npj Flexible Electronics (2019)