Summary
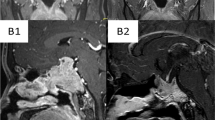
Patients with large prolactin (PRL)-secreting pituitary adenoma often have symptoms due to varying degree of hypopituitarism and/or mass effect on visual structures, while presentation with hydrocephalus is extremely uncommon. Even more exceptional is the development of the syndrome of intracranial hypertension as a consequence of tumor obstruction of the cerebrospinal fluid circulation. In this report, we describe a 26-year-old man who was referred to the emergency department of our hospital because of headache, nausea, and vomiting. Clinical and radiological assessment led to the diagnosis of obstructive hydrocephalus caused by a giant macroprolactinoma. The patient received a temporary external ventricular drainage to relieve the symptoms of intracranial hypertension. The same day, after we received the result of the basal PRL level, medical treatment with cabergoline was initiated. A prompt response to the drug ensued with resolution of the obstructive hydrocephalus, which allowed removal of the external ventricular drainage. Initial shrinkage of the mass was already noted on a magnetic resonance imaging performed 12 days thereafter. Subsequent medical treatment led to progressive and marked shrinkage of the tumor. Eighteen months after presentation the patient was well while on cabergoline treatment and showed no symptom attributable to compression of the surrounding nervous structures. Our report confirms that, even in cases of giant sellar mass with neurological symptoms, a rapid hormonal evaluation is mandatory. If a macroprolactinoma is diagnosed, treatment with dopamine agonists can lead to prompt clinical amelioration and shrinkage of the tumor, with eventual resolution of neurological symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
JA Schlechte (2003) ArticleTitleClinical practice: prolactinoma N Engl J Med 349 2035–2041 Occurrence Handle14627789 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJMcp025334 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXptFKmu7w%3D
JS Bevan J Webster CW Burke MF Scanlon (1992) ArticleTitleDopamine agonists and pituitary shrinkage Endocr Rev 2 220–240
PU Freda SL Wardlaw (1999) ArticleTitleClinical review 110: diagnosis and treatment of pituitary tumors J Clin Endocrinol Metab 11 3859–3866
ME Molitch (1999) ArticleTitleMedical treatment of prolactinomas Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 28 143–169 Occurrence Handle10207689 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0889-8529(05)70061-X Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3isVSqtA%3D%3D
JK Liu WT Couldwell (2004) ArticleTitleContemporary management of prolactinomas Neurosurg Focus 16 1–11 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXhtFWitrk%3D
Molitch ME, Elton RJ, Blackwell RE, Caldwell B, Chang RJ, Jaffe R, Joplin G, Robbins RJ, Tyson J, Thorner MO and the bromocriptine study group: Bromocriptine as primary therapy for prolactin-secreting macroadenomas: results of a prospective multicenter study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 60:698–705, 1985
A Colao A Sarno ParticleDi ML Landi F Scavuzzo P Cappabianca R Pivonello R Volpe F Salle ParticleDi S Cirillo L Annunziato G Lombardi (2000) ArticleTitleMacroprolactinoma shrinkage during cabergoline treatment is greater in naïve patients than in patients pretreated with other dopamine agonists: a prospective study in 110 patients J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85 2247–2252 Occurrence Handle10852458 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlsVCjsrw%3D
SN Aleksic AE George (1973) ArticleTitleDementia and low-pressure hydrocephalus in patients with pituitary adenoma J Neurol Sci 19 341–349 Occurrence Handle4541480 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE3s3htlCquw%3D%3D
P Iglesias L Pérez Macho JJ Dìez (2004) ArticleTitleResolution of macroprolactinoma-induced symptomatic hydrocephalus following cabergoline therapy Age Ageing 33 410–412 Occurrence Handle15136289 Occurrence Handle10.1093/ageing/afh108
D Perani N Colombo G Scotti C Tonon (1984) ArticleTitleRapid size reduction of giant prolactinoma following medical treatment J Comput Assist Tomogr 8 131–133 Occurrence Handle6690496 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2c%2FovVeqsQ%3D%3D
PK Sarkar R Manapuzha S Ahmad AE Ritch (2001) ArticleTitleFluctuating confusional state due to massive macro-prolactinoma resulting in obstructive hydrocephalus Age Ageing 30 426–428 Occurrence Handle11709386 Occurrence Handle10.1093/ageing/30.5.426 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MnmtleltQ%3D%3D
HA Shenkin JN Crowley (1973) ArticleTitleHydrocephalus complicating pituitary adenoma J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 36 1063–1068 Occurrence Handle4772720 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE2c%2Fot1Krtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1136/jnnp.36.6.1063
J Verhelst J Berwaerts R Abs G Dua D Weyngaert Particlevan den C Mahler (1998) ArticleTitleObstructive hydrocephalus as complication of a giant nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma: therapeutical approach Acta Clin Belg 53 47–52 Occurrence Handle9562706 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3itlOquw%3D%3D
OM Zikel JLD Atkinson DL Hurley (1999) ArticleTitleProlactinoma manifesting with symptomatic hydrocephalus Mayo Clin Proc 74 475–477 Occurrence Handle10319078 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3lt1KgtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.4065/74.5.475
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scarone, P., Losa, M., Mortini, P. et al. Obstructive Hydrocephalus and Intracranial Hypertension Caused by a Giant Macroprolactinoma. Prompt Response to Medical Treatment. J Neurooncol 76, 51–54 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-2319-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-2319-0