Abstract
Background
Central nervous system (CNS) hemangioblastoma (HB) is one of the most common manifestations in von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL), but large-scale studies on clinical features of CNS HB in VHL are scarce.
Methods
On the basis of the results of a questionnaire, we collected data of VHL patients with CNS HB.
Results
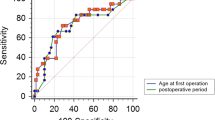
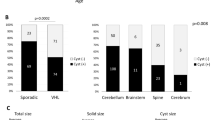
The total number of CNS HBs in 111 VHL patients (male 59, female 52) was 264 with the following distributions: cerebellar, 65.4 %; brainstem, 9.9 %; spinal cord, 23.9 %; and pituitary, 1. 1 %. The follow-up period was 0.6 to 39.2 years, with the mean 12.5 years. Patients bearing brainstem or spinal cord HB also had another HB significantly more frequently than those bearing cerebellar HBs (P < 0.05). The mean onset age of CNS HB was 29.1 years, and that of patients bearing a single HB (mean 34.4 years) was significantly greater than that of multiple HBs (mean 25.7 years). Patients with multiple HBs under 40 years are more dominant than those with a single HB. The distribution rate of brainstem HB is significantly smaller in patients below 30 years than patients above 29 years. Although ECOG PS score increased along with number of operations, the onset age decreased with increasing number of operations. The mean ECOG PS score of patients below 20 years is significantly smaller than patients above 19 years.
Conclusions
When the onset age of CNS HB is under 40 years, and CNS HB is located at the brainstem or spinal cord HB, the probability of multiple occurrence can be predicted. Since patients with an onset age under 20 years old preserve a high performance status, early detection of CNS HB would be important. In addition, since a multiple operations aggravate performance status, number of operations should be reduced.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammerman JM, Lonser RR, Dambrosia J, Butman JA, Oldfield EH (2006) Long-term natural history of hemangioblastomas in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease: implications for treatment. J Neurosurg 105:248–255
Colombo N, Kucharczyk W, Brant-Zawadzki M, Norman D, Scotti G, Newton TH (1986) Magnetic resonance imaging of spinal cord hemangioblastoma. Acta Radiol Suppl 369:734–737
Conway JE, Chou D, Clatterbuck RE, Brem H, Long DM, Rigamonti D (2001) Hemangioblastomas of the central nervous system in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome and sporadic disease. Neurosurgery 48:55–63
Filling-Katz MR, Choyke PL, Oldfield E, Charnas L, Patronas N, Glenn G, Gorin M, Morgan J, Linehan W, Seizinger B, Zbar B (1991) Central nervous system involvement in Von Hippel-Lindau disease. Neurology 41:41–46
Kanno H, Kondo K, Ito S, Yamamoto I, Fujii S, Trigoe S, Sakai N, Hosaka M, Shuin T, Yao M (1994) Somatic mutations of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene in sporadic central nervous system hemangioblastomas. Cancer Res 54:4845–4847
Kanno H, Yamamoto I, Nishikawa R, Matsutani M, Wakabayashi T, Yoshida J, Shitara N, Yamasaki I, Shuin T, Clinical VHL Research Group in Japan (2009) Spinal cord hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Spinal Cord 47
Latif F, Tory K, Gnarra J, Yao M, Duh FM, Orcutt ML, Stackouse T, Kuzmin I, Modi W, Geil L, Schmidt L, Zhou F, Li H, Wei MH, Chen F, Glenn G, Choyke P, Walther MM, Weng Y, Duan DR, Dean A, Glavac D, Richards FM, Crossey PA, Ferguson-Smith MA, Le Paslier D, Chumakov I, Cohen D, Chinault CA, Maher ER, Linehan WM, Zbar B (1993) Identification of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Science 260:1317–1320
Lonser RR, Butman JA, Kiringoda R, Song D, Oldfield EH (2009) Pituitary stalk hemangioblastomas in von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Neurosurg 110(2):350–353
Lonser R, Glenn GM, Walther M, Chew EY, Libutti SK, Linehan WM, Oldfield EH (2003) Von Hippel-Lindau disease. Lancet 361:2059–2067
Neumann HP, Eggert HR, Scheremet R, Schumacher M, Mohadjer M, Wakhloo A, Volk B, Hettmannsperger U, Riegler P, Schollmeyer P, Wiestler O (1992) Central nervous system lesions in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:898–901
Neumann HP, Lips CJ, Hsia YE, Zbar B (1995) Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome. Brain Pathol 5:181–193
Maher ER, Kaelin WG Jr (1997) von Hippel-Lindau disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 76:381–391
Maher ER, Yates JR, Harries R, Benjamin C, Harris R, Moore AT, Ferguson-Smith MA (1990) Clinical features and natural history of von Hippel-Lindau disease. Q J Med 77:1151–1163
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J, Davis TE, McFadden ET, Carbone PP (1982) Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol 5:649–655
Park DM, Zhuang Z, Chen L, Szerlip N, Maric I, Li J, Sohn T, Kim SH, Lubensky IA, Vortmeyer AO, Rodgers GP, Oldfield EH, Lonser RR (2007) von Hippel-Lindau disease-associated hemangioblastomas are derived from embryologic multipotent cells. PLoS Med 4:333–341
Shuin T, Kondo K, Torigoe S, Kishida T, Kubota Y, Hosaka M, Nagashima Y, Kitamura H, Latif F, Zbar B, Lerman M, Yao M (1994) Frequent somatic mutations and loss of heterozygosity of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene in primary human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 54:2852–2855
Wanebo JE, Lonser RR, Glenn GM, Oldfield EH (2003) The natural history of hemangioblastomas of the central nervous system in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease. J Neurosurg 98:82–94
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant-in-aid for scientific research No. 228 from the Ministry of Health and Labor of Japan.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanno, H., Kuratsu, Ji., Nishikawa, R. et al. Clinical features of patients bearing central nervous system hemangioblastoma in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Acta Neurochir 155, 1–7 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1514-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1514-y