Abstract
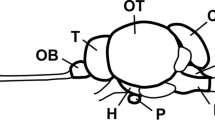
Research in mammals has established the existence of a neuronal network that lies within the hypothalamus and that regulates energy homeostasis. However, it is unknown whether this system has been evolutionarily conserved. The objective of the present study was therefore to examine the influence of the agouti-related peptide (AGRP), pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC), prepro-orexin, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) genes on energy balance in birds by quantifying the effect of a 24-h fast on their expression in the hypothalamus of the Japanese quail. In situ hybridization revealed strong signals for AGRP and POMC mRNAs in the infundibular nucleus (IN), for prepro-orexin in the lateral hypothalamic area (LHy) and periventricular hypothalamic nucleus, and for VIP in the LHy. POMC mRNA was co-localized with α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-like immunoreactivity in individual IN neurons. Compared with the ad-libitum-fed state, a 24-h fast resulted in a 2.2-fold increased expression of AGRP mRNA in the IN. However, fasting did not induce changes in POMC, prepro-orexin, or VIP mRNAs. The results suggest an involvement of the central melanocortin system in the regulation of energy balance in birds, as in mammals. In contrast, orexins in birds may be primarily involved in the control of physiological functions other than energy homeostasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam CL, Archer ZA, Findlay PA, Thomas L, Marie M (2002) Hypothalamic gene expression in sheep for cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript, pro-opiomelanocortin, neuropeptide Y, agouti-related peptide and leptin receptor and responses to negative energy balance. Neuroendocrinology 75:250–256
Archer ZA, Findlay PA, Rhind SM, Mercer JG, Adam CL (2002) Orexin gene expression and regulation by photoperiod in the sheep hypothalamus. Regul Pept 104:41–45
Aste N, Viglietti-Panzica C, Fasolo A, Panzica GC (1995). Mapping of neurochemical markers in quail central nervous system: VIP- and SP-like immunoreactivity. J Chem Neuroanat 8:87–102
Bagnol D, Lu X-Y, Kaelin CB, Day HEW, Ollmann M, Gantz I, Akil H, Barsh GS, Watson SJ (1999) Anatomy of an endogenous antagonist: relationship between agouti-related protein and proopiomelanocortin in brain. J Neurosci 19:RC26
Boswell T, Richardson RD, Seeley RJ, Ramenofsky M, Wingfield JC, Friedman MI, Woods SC (1995) Regulation of food intake by metabolic fuels in white-crowned sparrows. Am J Physiol 269:R1462-R1468
Boswell T, Lehman TL, Ramenofsky M (1997) Effect of plasma glucose manipulations on food intake in white-crowned sparrows. Comp Biochem Physiol 118A:721–726
Boswell T, Li Q, Takeuchi S (2002) Neurons expressing neuropeptide Y mRNA in the infundibular hypothalamus of Japanese quail are activated by fasting and co-express agouti-related protein mRNA. Mol Brain Res 100:31–42
Brady LS, Smith MS, Gold PW, Herkenham M (1990) Altered expression of hypothalamic neuropeptide mRNAs in food-restricted and food-deprived rats. Neuroendocrinology 52:441–447
Broberger C, Hökfelt T (2001) Hypothalamic and vagal neuropeptide circuitries regulating food intake. Physiol Behav 74:669–682
Butler AA, Kesterson RA, Khong K, Cullen MJ, Pelleymounter MA, Dekoning J, Baetscher M, Cone RD (2000) A unique metabolic syndrome causes obesity in the melanocortin-3 receptor-deficient mouse. Endocrinology 141:3518–3521
Cai XJ, Liu XH, Evans M, Clapham JC, Wilson S, Arch JRS, Morris R, Williams G (2002) Orexins and feeding: special occasions or everyday occurrence? Regul Pept 104:1–9
Chemelli RM, Willie JT, Sinton CM, Elmquist JK, Scammell T, Lee C, Richardson JA, Williams SC, Xiong Y, Kisanuki Y, Fitch TE, Nakazato M, Hammer RE, Saper CB, Yanagisawa M (1999) Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell 98:437–451
Chen AS, Marsh DJ, Trumbauer ME, Frazier EG, Guan X-M, Yu H, Rosenblum CI, Vongs A, Feng Y, Cao L, Metzger JM, Strack AM, Camacho RE, Mellin TN, Nunes CN, Min W, Fisher J, Gopal-Truter S, MacIntyre DE, Chen HY, Van der Ploeg LH (2000) Inactivation of the mouse melanocortin-3 receptor results in increased fat mass and reduced lean body mass. Nature Genet 26:97–102
Cone RD (1999) The central melanocortin system and energy homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab 10:211–216
Date Y, Ueta Y, Yamashita H, Yamaguchi H, Matsukura S, Kangawa K, Sakurai T, Yanagisawa M, Nakazato M (1999) Orexins, orexigenic hypothalamic peptides, interact with autonomic, neuroendocrine and neuroregulatory systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:748–753
De Lecea L, Kilduff TS, Peyron C, Gao X-B, Foye PE, Danielson PE, Fukuhara C, Battenberg EL, Gautvik VT, Bartlett FS II, Frankel WN, Pol AN van den, Bloom FE, Gautvik KM, Sutcliffe JG (1998) The hypocretins: hypothalamus-specific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:322-327
Elias CF, Saper CB, Maratos-Flier E, Tritos NA, Lee C, Kelly J, Tatro JB, Hoffman GE, Ollmann MM, Barsh GS, Sakurai T, Yanagisawa M, Elmquist JK (1998) Chemically defined projections linking the mediobasal hypothalamus and the lateral hypothalamic area. J Comp Neurol 402:442–459
Elmquist JK, Elias CF, Saper CB (1999) From lesions to leptin: hypothalamic control of food intake and body weight. Neuron 22:221–232
Fan W, Boston BA, Kesterson RA, Hruby VJ, Cone RD (1997) Role of melanocortinergic neurons in feeding and the agouti obesity syndrome. Nature 385:165–168
Friedman-Einat M, Boswell T, Horev G, Girishvarma G, Dunn IC, Talbot RT, Sharp PJ (1999) The chicken leptin gene: has it been cloned? Gen Comp Endocrinol 115:354–363
Furuse M, Ando R, Bungo T, Ao R, Shimojo M, Masuda Y (1999) Intracerebroventricular injection of orexins does not stimulate food intake in neonatal chicks. Br Poult Sci 40:698–700
Gerets HHJ, Peeters K, Arckens L, Vandesande F, Berghman LR (2000) Sequence and distribution of pro-opiomelanocortin in the pituitary and the brain of the chicken (Gallus gallus). J Comp Neurol 417:250–262
Graham M, Shutter JR, Sarmiento U, Sarosi I, Stark KL (1997) Overexpression of Agrt leads to obesity in transgenic mice. Nature Genet 17:273–274
Hara J, Beuckmann CT, Nambu T, Willie JT, Chemelli RM, Sinton CM, Sugiyama F, Yagami K, Goto K, Yanagisawa M, Sakurai T (2001) Genetic ablation of orexin neurons in mice results in narcolepsy, hypophagia, and obesity. Neuron 30:345–354
Horev G, Einat P, Aharoni T, Eshdat Y, Friedman-Einat M (2000) Molecular cloning and properties of the chicken leptin-receptor (CLEPR) gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol 162:95–106
Horvath TL, Diano S, Pol AN van den (1999) Synaptic interaction between hypocretin (orexin) and neuropeptide Y cells in the rodent and primate hypothalamus: a novel circuit implicated in metabolic and endocrine regulations. J Neurosci 19:1072–1087
Huszar D, Lynch CA, Fairchild-Huntress V, Dunmore JH, Fang, Q, Berkemeier LR, Gu W, Kesterson RA, Boston BA, Cone RD, Smith FJ, Campfield LA, Burn P, Lee F (1997) Targeted disruption of the melanocortin-4 receptor results in obesity in mice. Cell 88:131–141
Kawakami S-I, Bungo T, Ando R, Ohgushi A, Shimojo M, Masuda Y, Furuse M (2000) Central administration of α-melanocyte stimulating hormone inhibits fasting- and neuropeptide Y-induced feeding in neonatal chicks. Eur J Pharmacol 398:361–364
Kuenzel WJ, Masson M (1988) A stereotaxic atlas of the brain of the chick (Gallus domesticus). Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Kuenzel WJ, McCune SK, Talbot RT, Sharp PJ, Hill JM (1997) Sites of gene expression for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide throughout the brain of the chick (Gallus domesticus). J Comp Neurol 381:101–118
Mizuno TM, Mobbs CV (1999) Hypothalamic agouti-related protein messenger ribonucleic acid is inhibited by leptin and stimulated by fasting. Endocrinology 140:814–817
Morton GJ, Schwartz MW (2001) The NPY/AGRP neuron and energy homeostasis. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord Suppl 5:S56-S62
Mountjoy K, Wong J (1997) Obesity, diabetes and functions for proopiomelanocortin-derived peptides. Mol Cell Endocrinol 128:171–177
Ohkubo T, Tanaka M, Nakashima K (2000) Structure and tissue distribution of chicken leptin receptor (cOb-R) mRNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 1491:303–308
Ohkubo T, Boswell T, Lumineau S (2002) Molecular cloning of chicken propro-orexin cDNA and preferential expression in the chicken hypothalamus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1577:476–480
Ollmann MM, Wilson BD, Yang Y-K, Kerns JA, Chen Y, Gantz I, Barsh GS (1997) Antagonism of central melanocortin receptors in vitro and in vivo by agouti-related protein. Science 278:135–138
Peyron C, Tighe DK, Pol AN van den, De Lecea L, Heller HC, Sutcliffe JG, Kilduff TS (1998) Neurons containing hypocretin (orexin) project to multiple neuronal systems. J Neurosci 18:9996–10015
Poggioli R, Vergoni AV, Bertolini A (1986) ACTH-(1–24) and α-MSH antagonize feeding behavior stimulated by kappa opiate agonists. Peptides 7:843–846
Rossi M, Kim MS, Morgan DGA, Small CJ, Edwards CMB, Sunter D, Abusnana S, Goldstone AP, Russell SH, Stanley SA, Smith DM, Yagaloff K, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (1998) A C-terminal fragment of agouti-related protein increases feeding and antagonizes the effect of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone in vivo. Endocrinology 139:4428–4431
Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, Matsuzaki I, Chemelli RM, Tanaka H, Williams SC, Richardson JA, Kozlowski GP, Wilson S, Arch JR, Buckingham RE, Haynes AC, Carr SA, Annan RS, McNulty DE, Liu WS, Terrett JA, Elshourbagy NA, Bergsma DJ, Yanagisawa M (1998) Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 92:573–585
Sartori DRS, Migliorini RH, Veiga JAS, Moura JL, Kettelhut IC, Linder C (1995) Metabolic adaptations induced by long-term fasting in quails. Comp Biochem Physiol 111A:487–493
Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D Jr (2000) Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 404:661–671
Sharp PJ, Sterling RJ, Talbot RT, Huskisson NS (1989) The role of hypothalamic vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the maintenance of prolactin secretion in incubating bantam hens: observations using passive immunization, radioimmunoassay and immunohistochemistry. J Endocrinol 122:5–13
Sherry DF, Mrosovsky N, Hogan J (1980) Weight loss and anorexia during incubation in birds. J Comp Physiol Psychol 94:89–98
Strader AD, Schiöth HB, Buntin JD (2003) The role of the melanocortin system and the melanocortin-4 receptor in ring dove (Streptopelia risoria) feeding behavior. Brain Res 960:112–121
Tachibana T, Sugahara K, Ohgushi A, Ando R, Kawakami S-I, Yoshimatsu T, Furuse M (2001) Intracerebroventicular injection of agouti-related protein attenuates the anorexigenic effect of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone in neonatal chicks. Neurosci Lett 305:131–134
Tachibana T, Saito S, Tomonaga S, Takagi T, Saito E-S, Boswell T, Furuse M (2003) Intracerebroventricular injection of vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibits feeding in chicks. Neurosci Lett 339:203–206
Takeuchi S, Takahashi S (1998) Melanocortin receptor genes in the chicken tissue distributions. Gen Comp Endocrinol 112:220–231
Takeuchi S, Takahashi S (1999) A possible involvement of melanocortin 3 receptor in the regulation of adrenal gland function in the chicken. Biochim Biophys Acta 1448:512–518
Takeuchi S, Teshigawara K, Takahashi S (1999) Molecular cloning and characterization of the chicken pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1450:452–459
Takeuchi S, Teshigawara K, Takahashi S (2000) Widespread expression of agouti-related protein (AGRP) in the chicken: a possible involvement of AGRP in regulating peripheral melanocortin systems in the chicken. Biochim Biophys Acta 1496:261–269
Teruyama R, Beck MM (2001) Double immunocytochemistry of vasoactive intestinal peptide and cGnRH-I in male quail: photoperiodic effects. Cell Tissue Res 303:403–414
Willie JT, Chemelli RM, Sinton CM, Yanagisawa M (2001) To eat or to sleep? Orexin in the regulation of feeding and wakefulness. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:429–458
Zheng B, Eng J, Yalow RS (1987) Brain/gut peptides in fed and fasted rats. Endocrinology 120:714–717
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by a Commonwealth Fellowship to D.P.-S. and a BBSRC Fellowship to T.B.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phillips-Singh, D., Li, Q., Takeuchi, S. et al. Fasting differentially regulates expression of agouti-related peptide, pro-opiomelanocortin, prepro-orexin, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide mRNAs in the hypothalamus of Japanese quail. Cell Tissue Res 313, 217–225 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0755-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-003-0755-8