Abstract
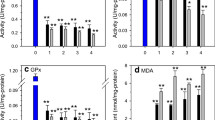
The response of the copepod (Tigriopus japonicus Mori) to cadmium (Cd) additions was investigated under laboratory-controlled conditions in a 12-day exposure. Superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), acetylcholinesterase (AchE), reduced glutathione (GSH), the ratio of reduced to oxidized glutathione (GSH/GSSG), and metallothionein (MT) were analyzed for Cd treatments (0, 10, 20, 40, and 100 μg/L) after exposure for 1, 4, 7, and 12 days. Additionally, thiobarbituric reactive species assay was used to evaluate lipid peroxidation (LPO) of the copepod after the 12-day exposure. The results indicated that Cd treatments significantly influenced the biochemical indexes (SOD, GPx, GST, AchE, GSH, and GSH/GSSG) after certain exposure times. Exposure to Cd induced LPO in the treated copepods, hinting that the copepods had suffered from oxidative damage. During exposure, the Cd initiated an induced MT synthesis in the copepods by day 7, which peaked at day 12 and which was probably responsible for Cd detoxification. Thus, Cd exposure significantly affected the detoxification process and antioxidant system of this copepod, and T. japonicus could be used as a suitable bioindicator of exposure to Cd using SOD, GPx, GST, LPO, and GSH/GSSG as biomarkers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida JA, Diniz YS, Marques SFG et al (2002) The use of the oxidative stress responses as biomarkers in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to in vivo cadmium contamination. Environ Int 27:673–679. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(01)00127-1
Amiard JC, Cosson RP (1997) Lés métallothionéines. In: Lagadic L, Caquet T, Amiard JC, Ramade F (eds) Biomarqueurs en écotoxicologie: aspects Fondamentaux, Masson. Masson, Paris, pp 53–63
Amiard JC, Amiard-Triquet C, Barka S, Pellerin J, Rainbow PS (2006) Metallothioneins in aquatic invertebrates: their role in metal detoxification and their use as biomarkers. Aquat Toxicol 76(2):160–202. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.08.015
Amiard-Triquet C, Altmann S, Amiard JC et al (1998) Fate and effects of micropollutants in the Gironde estuary, France: a multidisciplinary approach. Hydrobiologia 373/374:259–279. doi:10.1023/A:1017055118218
Ara K, Nojima K, Hiromi J (2002) Acute toxicity of Bunker A and C refined oils to the marine harpacticoid copepod Tigriopus japonicus Mori. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 69:104–110. doi:10.1007/s00128-002-0015-8
Barata C, Lekumberri I, Vila-Escalé M, Prat N, Porte C (2005a) Trace metal concentration, antioxidant enzyme activities and susceptibility to oxidative stress in the tricoptera larvae Hydropsyche exocellata from Llobregat river basin (NE Spain). Aquat Toxicol 74:3–19. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.04.002
Barata C, Varo I, Navarro JC, Arun S, Porte C (2005b) Antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in the freshwater cladoceran Daphnia magna exposed to redox cycling compounds. Comp Biochem Physiol 140C:175–186
Barka S, Pavillon JF, Amiard JC (2001) Influence of different essential and non-essential metals on MTLP levels in the copepod Tigriopus brevicornis. Comp Biochem Physiol 128C:479–493
Bem EM, Mailer K, Elson CM (1985) Influence of mercury (II), cadmium (II), methylmercury (II), and phenylmercury on the kinetic properties of rat liver glutathione peroxidase. Can J Biochem Cell Biol 63:1212–1216
Benavides MP, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2005) Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:21–34. doi:10.1590/S1677-04202005000100003
Bodar CMW, Kluytmans JH, Van Montfort JCP, Voogt PA, Zandee DI (1998) Cadmium resistance and the synthesis of metallothionein-like proteins in Daphnia magna. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international conference of environmental contamination, CEP, Edinburgh, pp 79–81
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive assay of protein utilizing the principle of dye binding. Analyt Biochem 772:248–264. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chandran R, Sivakumar AA, Mohandass S, Aruchami M (2005) Effect of cadmium and zinc on antioxidant enzyme activity in the gastropod, Achatina fulica. Comp Biochem Physiol 140C:422–426
Cheeseman KM (1982) Effects of scavengers and inhibitors on lipid peroxidation in rat liver microsomes. In: MacBrien DC, Slater TF (eds) Free radicals, lipid peroxidation and cancer. Academic Press, New York, pp 196–211
Company R, Serafim A, Bebianno MJ et al (2004) Effect of cadmium, copper and mercury on antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in the gills of the hydrothermal vent mussels Bathymodiolus azoricus. Marine Environ Res 58:337–381. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2004.03.083
Correia AD, Lima G, Costa MH, Livingstone DR (2002a) Studies on biomarkers of copper exposure and toxicity in the marine amphipod Gammarus locusta (Crustacea). I: induction of metallothionein and lipid peroxidation. Biomarkers 7:422–437. doi:10.1080/135475002760413516
Correia AD, Livingstone DR, Costa MH (2002b) Effects of water-borne copper on metallothionein and lipid peroxidation in the marine amphipod Gammarus locusta. Marine Environ Res 54:357–360. doi:10.1016/S0141-1136(02)00114-9
Couillard Y, Campbell PGC, Tessier A, Pellerinmassicotte J, Auclair A (1995) Field transplantation of a fresh-water bivalve Pyganodon grandis, across a metal contamination gradient. Temporal changes in metallothionein and metal (Cd, Cu and Zn) concentrations in soft tissues. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 52:690–702
De Luca G, Gugliotta T, Parisi G et al (2007) Effects of nickel on human and fish blood cells. Biosci Rep 27:265–273. doi:10.1007/s10540-007-9053-0
Di Giulio R, Benson W, Sanders B, Van Veld P (1995) Biochemical mechanisms: metabolism, adaptation and toxicity. In: Rand GM (ed) Fundamental of aquatic toxicology—effects, environmental fate and risk assessment, 2nd edn. Taylor and Francis, Washington, DC, pp 523–561
Ellman G, Courtney K, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Elumalai M, Antunes C, Guilhermino L (2002) Single metals and their mixtures on selected enzymes of Carcinus maenas. Water Air Soil Pollut 141:273–280. doi:10.1023/A:1021352212089
Falfushynska HI, Stolyar OB (2009) Responses of biochemical markers in carp Cyprinus carpio from two field sites in Western Ukraine. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:729–736. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.04.006
Forget J, Pavillon JF, Beliaeff B, Bocquené G (1999) Joint action of pollutant combinations (pesticides and metals) on survival (LC50 values) and acetylcholinesterase activity of Tigriopus brevicornis (Copepoda Harpacticoida). Environ Toxicol Chem 18:912–918. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1999)018<0912:JAOPCP>2.3.CO;2
Forget J, Beliaeff B, Bocquené G (2003) Acetylcholinesterase activity in copepods (Tigriopus brevicornis) from the Vilaine River estuary, France, as a biomarker of neurotoxic contaminants. Aquat Toxicol 62:195–204. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(02)00084-X
Frova C (2006) Glutathione transferases in the genomics era: new insights and perspectives. Biomol Eng 23:149–169. doi:10.1016/j.bioeng.2006.05.020
Galgani F, Bocquene G (1990) In vitro inhibition of acetylcholinesterase from four marine species by organophosphates and carbamates. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 45:243–249. doi:10.1007/BF01700191
George SG, Hodgson P, Todd K, Tyter P (1996) Metallothionein protects against cadmium toxicity-proof from studies developing turbot larvae. Marine Environ Res 42:1–4. doi:10.1016/0141-1136(95)00046-1
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine, 3rd edn. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Hanas JS, Gunn CG (1996) Inhibition of transcription factor IIIA-DNA interactions by xenobiotic metal ions. Nucleic Acids Res 24:924–930. doi:10.1093/nar/24.5.924
Hissin PJ, Hilf R (1976) A fluoremetric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal Biochem 74:214–226. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90326-2
Hwang C, Sinskey AJ, Lodish HF (1992) Oxidized redox state of glutathione in the endoplasmic-reticulum. Science 57:1496–1502. doi:10.1126/science.1523409
Jemec A, Drobne D, Tisler T et al (2007) The applicability of acetylcholinesterase and glutathione S-transferase in Daphnia magna toxicity test. Comp Biochem Physiol 144C:303–309
Jo PG, Choi YK, Choi CY (2008) Cloning and mRNA expression of antioxidant enzymes in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas in response to cadmium exposure. Comp Biochem Physiol 147C:460–469
Jung S-O, Lee Y-M, Park T-J et al (2006) The complete mitochondrial genome of the intertidal copepod Tigriopus sp. (Copepoda, Harpactidae) from Korea and phylogenetic considerations. J Exp Marine Biol Ecol 333:251–262. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2005.12.047
Kwok KWH, Leung KMY (2005) Toxicity of antifouling biocides to the intertidal harpacticoid copepod Tigriopus japonicus (Crustacea, Copepoda): effects of temperature and salinity. Marine Pollut Bull 51:830–837. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.02.036
Lee KW, Raisuddin S, Hwang DS, Park HG, Lee J-S (2007a) Acute toxicities of trace metals and common xenobiotics to the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicus: evaluation of its use as a benchmark species for routine ecotoxicity tests in Western Pacific coastal regions. Environ Toxicol 22:532–538. doi:10.1002/tox.20289
Lee Y-M, Lee KW, Seo JS et al (2007b) Sequence, biochemical characteristics and expression of a novel sigma class of glutathione S-transferase of intertidal copepod, Tigriopus japonicus with a possible role in antioxidant defense. Chemosphere 69:893–902. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.05.087
Lionetto MG, Maffia M, Cappello MS et al (1998) Effect of cadmium on carbonic anhydrase and Na+-K+-ATPase in eel, Anguilla anguilla, intestine and gills. Comp Biochem Physiol 120A:89–91
Marcial HS, Hagiwara A, Snell TW (2003) Estrogenic compounds affect development of harpacticoid copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:3025–3030. doi:10.1897/02-622
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase: an enzymatic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244:6049–6055
Novelli ELB, Vieir EP, Rodrigues NL, Ribas BO (1998) Risk assessment of cadmium toxicity on hepatic and renal tissues of rats. Environ Res 79:102–105. doi:10.1006/enrs.1998.3865
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Omaye ST, Tappel AL (1975) Effect of cadmium chloride on the rat testicular soluble seleno-enzyme glutathione peroxidase. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 12:695–711
Ozmen M, Sener S, Mete A, Kukucbay H (1998) In vitro and in vivo acetylcholinesterase-inhibiting effect of new classes of organophosphorus compounds. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:241–246. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1999)018<0241:IVAIVA>2.3.CO;2
Pan LQ, Zhang HX (2006) Metallothionein, antioxidant enzymes and DNA strand breaks as biomarkers of Cd exposure in a marine crab, Charybdis japonica. Comp Biochem Physiol 144C:67–75
Paris-Palacios S, Biagianti-Risbourg S, Vernet G (2003) Metallothionein induction related to hepatic structural perturbations and antioxidative defenses in roach (Rutilus rutilus) exposed to the fungicide procymidone. Biomarkers 8:128–141. doi:10.1080/1354750021000050511
Pourahmad J, O’Brien PJ, Jokar F, Daraei B (2003) Carcinogenic metal induced sites of reactive oxygen species formation in hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro 17:803–810. doi:10.1016/S0887-2333(03)00123-1
Raisuddin S, Kwok KWH, Leung KMY, Schlenk D, Lee J-S (2007) The copepod Tigriopus: a promising marine model organism for ecotoxicology and environmental genomics. Aquat Toxicol 83:161–173. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.04.005
Roesijadi G (1996) Metallothionein and its role in toxic metal regulation. Comp Biochem Physiol 113C:117–123
Roesijadi G, Robinson W (1994) Metal regulation in aquatic animals: mechanisms of uptake, accumulation and release. In: Malins D, Ostrander G (eds) Aquatic toxicology—molecular, biochemical and cellular perspectives. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL, pp 387–420
Ruppert EE, Fox RS, Barnes RD (2003) Invertebrate zoology. A functional evolutionary approach, 7th edn. Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning, Belmont, CA
Scheuhammer AM, Cherian MG (1991) Quantification of metallothionein by silver saturation. Methods Enzymol 205:78–83. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(91)05088-D
Schlenk D, Rice CD (1998) Effects of zinc and cadmium treatment on hydrogen peroxide-induced mortality and expression of glutathione and metallothionein in a teleost hepatoma cell line. Aquat Toxicol 43:121–129. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(98)00050-2
Seo JS, Lee Y-M, Park HG, Lee J-S (2006a) The intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus small heat shock protein 20 gene (Hsp20) enhances thermotolerance of transformed Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 340:901–908. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.12.086
Seo JS, Park T-J, Lee Y-M et al (2006b) Small heat shock protein 20 gene (Hsp20) of the intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus as a possible biomarker for exposure to endocrine disruptors. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 76:566–572. doi:10.1007/s00128-006-0957-3
Seo JS, Lee K-W, Rhee J-S et al (2006c) Environmental stressors (salinity, heavy metals, H2O2) modulate expression of glutathione reductase (GR) gene from the intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Aquat Toxicol 80:281–289. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.09.005
Sies H (1999) Glutathione and its role in cellular functions. Free Radic Biol Med 27:916–921. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(99)00177-X
Splittgerber AG, Tapple AL (1979) Inhibition of glutathione peroxidase by cadmium and other metals. Arch Biochem Biophys 197:534–542. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(79)90277-7
Stohs ST, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metals. Free Radic Biol Med 18:321–326. doi:10.1016/0891-5849(94)00159-H
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D, Hassoun E, Bagchi M (2000) Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of chromium and cadmium ions. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 19:201–213
Tsuzuki K, Sugiyama M, Haramaki N (1994) DNA-single strand break and cytotoxicity induced by chromate (VI), cadmium (II) and mercury (II) in hydrogen peroxide-resistant cell lines. Environ Health Perspect 102(Suppl 3):341–342. doi:10.2307/3431817
Vallee BL, Ulmer DD (1972) Biochemical effect of mercury, cadmium and lead. Annu Rev Biochem 41:91–130. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.000515
Venugopal NBRK, Ramesh TVDD, Reddy DS, Reddy SLN (1997) Effect of cadmium on antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in a freshwater field crab, Barytelphusa guerini. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 59:132–138. doi:10.1007/s001289900455
Viarengo A (1989) Heavy metals in marine invertebrates: mechanisms of regulation and toxicity at the cellular level. CRC Reviews in Aquatic Sciences. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 295–317
Wells PG (1984) Marine ecotoxicological tests with zooplankton. In: Persoone G, Jaspers E, Claus C (eds) Ecotoxicological testing for the marine environment. State University of Ghent and Institute of Marine Scientific Research, Bredene, Belgium, pp 215–256
Xia YM, Zhu LZ (1987) Measurement method of glutathione peroxidase activity in blood and tissue. J Hyg Res 16:29–33
Xiang LX, Shao JZ (2003) Role of intracellular Ca2+, reactive oxygen species, mitochondria transmembrane potential and antioxidant enzymes in heavy metal-induced apoptosis in fish cells. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 71:114–122. doi:10.1007/s00128-003-0137-7
Acknowledgments
The work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40806051). Professor John Hodgkiss is thanked for his assistance with English in an earlier draft of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9412-x
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, MH., Wang, GZ. Biochemical Response of the Copepod Tigriopus japonicus Mori Experimentally Exposed to Cadmium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 57, 707–717 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9319-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9319-6