Abstract
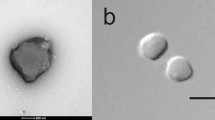
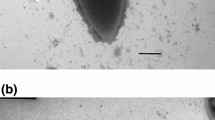
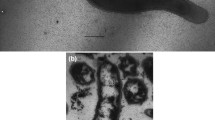
A novel, irregular, coccoid-shaped archaeum was isolated from a hydrothermally heated black smoker wall at the TAG site at the Mid Atlantic Ridge (depth 3650 meters). It grew at between 90°C and 113°C (optimum 106°C) and pH 4.0–6.5 (optimum 5.5) and 1%–4% salt (optimum 1.7%). The organism was a facultatively aerobic obligate chemolithoautotroph gaining energy by H2-oxidation. Nitrate, S2O3 2–, and low concentrations of O2 (up to 0.3% v/v) served as electron acceptors, yielding NH+ 4, H2S, and H2O as end products, respectively. Growth was inhibited by acetate, pyruvate, glucose, starch, or sulfur. The new isolate was able to form colonies on plates (at 102°C) and to grow at a pressure of 25000 kPa (250 bar). Exponentially growing cultures survived a one-hour autoclaving at 121°C. The GC content was 53mol%. The core lipids consisted of glycerol–dialkyl glycerol tetraethers and traces of 2,3-di-O-phytanyl-sn-glycerol. The cell wall was composed of a surface layer of tetrameric protein complexes arranged on a p4-lattice (center-to-center distance 18.5nm). By its 16S rRNA sequence, the new isolate belonged to the Pyrodictiaceae. Based on its GC-content, DNA homology, S-layer composition, and metabolism, we describe here a new genus, which we name Pyrolobus (the "fire lobe"). The type species is Pyrolobus fumarii (type strain 1A; DSM).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 September 1996 / Accepted: 17 October 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blöchl, E., Rachel, R., Burggraf, S. et al. Pyrolobus fumarii, gen. and sp. nov., represents a novel group of archaea, extending the upper temperature limit for life to 113°C. Extremophiles 1, 14–21 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007920050010
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007920050010