Summary
-
1.
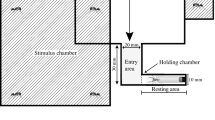
We report here a psychophysical technique for studying the spectral sensitivity of jumping spiders (family Salticidae), based on a newly discovered oculomotor reflex.
-
2.
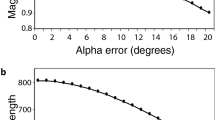
Our results, obtained fromMaevia inclemens (Salticidae), are compatible with electrophysiological findings of retinal cells maximally sensitive in the green and ultraviolet regions of the spectrum.
-
3.
Sensitivity to longer wavelengths (>650 nm) has been controversial. In our study jumping spiders are shown to have a broad spectral sensitivity function extending from the ultraviolet (330 nm) to the deep red (700 nm).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AL :
-
anterior lateral (eyes)
- AM :
-
anterior median (eyes)
References
Blest AD, Hardie RC, McIntyre P, Williams DS (1981) The spectral sensitivities of identified receptors and the function of retinal tiering in the principal eyes of a jumping spider. J Comp Physiol 145:227–239
Dartnall HJA (1953) The interpretation of spectral sensitivity curves. Br Med Bull 9:24–30
DeVoe RD (1975) Ultraviolet and green receptors in principal eyes of jumping spiders. J Gen Physiol 66:193–207
Kästner A (1950) Reaktion der Hüpfspinnen (Salticidae) auf unbewegte farblose und farbige Gesichtsreize. Zool Beitr NS 1:12–50
Land MF (1969a) Structure of the retinae of the principal eyes of jumping spiders (Salticidae: Dendryphantinae) in relation to visual stimuli. J Exp Biol 51:443–470
Land MF (1969b) Movement of the retinae of jumping spiders (Salticidae: Dendryphantinae) in response to visual stimuli. J Exp Biol 51:471–493
Langer H, Hamann B, Meinecke CC (1979) Tetrachromatic visual system in the moth (Insecta: Noctuidae). J Comp Physiol 129:235–239
Menzel R (1979) Spectral sensitivity and color vision in invertebrates. In: Autrum H (ed) Handbook of sensory physiology, vol VII/6A. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 560–566
Oberdorfer MD (1975) The neural organization of the first optic ganglion of the principal eyes of jumping spiders (Salticidae). J Comp Neurol 174:95–118
Yamashita S, Tateda H (1976) Spectral sensitivities of jumping spider eyes. J Comp Physiol 105:29–41
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peaslee, A.G., Wilson, G. Spectral sensitivity in jumping spiders (Araneae, Salticidae). J. Comp. Physiol. 164, 359–363 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00612995
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00612995