Abstract
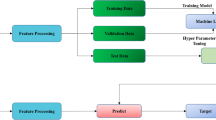
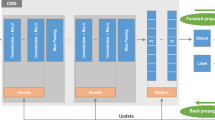
Neuroimaging science has seen a recent explosion in dataset size driving the need to develop database management with efficient processing pipelines. Multi-center neuroimaging databases consistently receive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data with unlabeled or incorrectly labeled contrast. There is a need to automatically identify the contrast of MRI scans to save database-managing facilities valuable resources spent by trained technicians required for visual inspection. We developed a deep learning (DL) algorithm with convolution neural network architecture to automatically infer the contrast of MRI scans based on the image intensity of multiple slices. For comparison, we developed a random forest (RF) algorithm to automatically infer the contrast of MRI scans based on acquisition parameters. The DL algorithm was able to automatically identify the MRI contrast of an unseen dataset with <0.2% error rate. The RF algorithm was able to identify the MRI contrast of the same dataset with 1.74% error rate. Our analysis showed that reduced dataset sizes caused the DL algorithm to lose generalizability. Finally, we developed a confidence measure, which made it possible to detect, with 100% specificity, all MRI volumes that were misclassified by the DL algorithm. This confidence measure can be used to alert the user on the need to inspect the small fraction of MRI volumes that are prone to misclassification. Our study introduces a practical solution for automatically identifying the MRI contrast. Furthermore, it demonstrates the powerful combination of convolution neural networks and DL for analyzing large MRI datasets.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Rfou, R., Alain, G., Almahairi, A., Angermueller, C., Bahdanau, D., Ballas, N., et al. (2016). Theano: A Python framework for fast computation of mathematical expressions arXiv preprint arXiv:1605.02688.
Bengio, Y. (2009). Learning deep architectures for AI. Foundations and trends® in Machine Learning, 2(1), 1–127 %@ 1935–8237.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Mach Learn, 45(1), 5–32 %@ 0885–6125.
Cheng, X., Pizarro, R., Tong, Y., Zoltick, B., Luo, Q., Weinberger, D. R., et al. (2009). Bio-swarm-pipeline: A light-weight, extensible batch processing system for efficient biomedical data processing. Front Neuroinform, 3, 35. https://doi.org/10.3389/neuro.11.035.2009.
Chollet, F. (2015). Keras.
Dahl, G. E., Sainath, T. N., & Hinton, G. E. (2013). Improving deep neural networks for LVCSR using rectified linear units and dropout (acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), 2013 IEEE international conference on): IEEE.
Dozat, T. (2015). Incorporating Nesterov momentum into Adam. Stanford University, Tech Rep, 2015. [Online]. Available: http://cs229.stanford.edu/proj2015/054_report.pdf
Dunne, R. A., & Campbell, N. A. (1997). On the pairing of the softmax activation and cross-entropy penalty functions and the derivation of the softmax activation function (Vol. 185, proc. 8th Aust. Conf. On the neural networks, Melbourne, 181).
Gardner, E. A., Ellis, J. H., Hyde, R. J., Aisen, A. M., Quint, D. J., & Carson, P. L. (1995). Detection of degradation of magnetic resonance (MR) images: Comparison of an automated MR image-quality analysis system with trained human observers. Acad Radiol, 2(4), 277–281.
Ioffe, S., & Szegedy, C. (2015). Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift arXiv preprint arXiv:1502.03167.
Krizhevsky, A., & Hinton, G. (2009). Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Hinton, G. E. (2012). Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks (advances in neural information processing systems).
Marcus, D. S., Harms, M. P., Snyder, A. Z., Jenkinson, M., Wilson, J. A., Glasser, M. F., Barch, D. M., Archie, K. A., Burgess, G. C., Ramaratnam, M., Hodge, M., Horton, W., Herrick, R., Olsen, T., McKay, M., House, M., Hileman, M., Reid, E., Harwell, J., Coalson, T., Schindler, J., Elam, J. S., Curtiss, S. W., van Essen, D., & WU-Minn HCP Consortium. (2013). Human connectome project informatics: Quality control, database services, and data visualization. Neuroimage, 80, 202–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.077.
Murphy, K. P. (2012). Machine learning : a probabilistic perspective (adaptive computation and machine learning). Cambridge, mass.: MIT Press.
Pizarro, R. A., Cheng, X., Barnett, A., Lemaitre, H., Verchinski, B. A., Goldman, A. L., Xiao, E., Luo, Q., Berman, K. F., Callicott, J. H., Weinberger, D. R., & Mattay, V. S. (2016). Automated quality assessment of structural magnetic resonance brain images based on a supervised machine learning algorithm. Front Neuroinform, 10, 52. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2016.00052.
Ripley, B. D. (2007). Pattern recognition and neural networks: Cambridge university press.
Weiner, M. W., Veitch, D. P., Aisen, P. S., Beckett, L. A., Cairns, N. J., Green, R. C., Harvey, D., Jack, C. R., Jagust, W., Liu, E., Morris, J. C., Petersen, R. C., Saykin, A. J., Schmidt, M. E., Shaw, L., Shen, L., Siuciak, J. A., Soares, H., Toga, A. W., Trojanowski, J. Q., & Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. (2013). The Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative: A review of papers published since its inception. Alzheimers Dement, 9(5), e111–e194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2013.05.1769.
Youden, W. J. (1950). Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer, 3(1), 32–35.
Zuo, X. N., Anderson, J. S., Bellec, P., Birn, R. M., Biswal, B. B., Blautzik, J., Breitner, J. C. S., Buckner, R. L., Calhoun, V. D., Castellanos, F. X., Chen, A., Chen, B., Chen, J., Chen, X., Colcombe, S. J., Courtney, W., Craddock, R. C., di Martino, A., Dong, H. M., Fu, X., Gong, Q., Gorgolewski, K. J., Han, Y., He, Y., He, Y., Ho, E., Holmes, A., Hou, X. H., Huckins, J., Jiang, T., Jiang, Y., Kelley, W., Kelly, C., King, M., LaConte, S. M., Lainhart, J. E., Lei, X., Li, H. J., Li, K., Li, K., Lin, Q., Liu, D., Liu, J., Liu, X., Liu, Y., Lu, G., Lu, J., Luna, B., Luo, J., Lurie, D., Mao, Y., Margulies, D. S., Mayer, A. R., Meindl, T., Meyerand, M. E., Nan, W., Nielsen, J. A., O’Connor, D., Paulsen, D., Prabhakaran, V., Qi, Z., Qiu, J., Shao, C., Shehzad, Z., Tang, W., Villringer, A., Wang, H., Wang, K., Wei, D., Wei, G. X., Weng, X. C., Wu, X., Xu, T., Yang, N., Yang, Z., Zang, Y. F., Zhang, L., Zhang, Q., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Z., Zhao, K., Zhen, Z., Zhou, Y., Zhu, X. T., & Milham, M. P. (2014). An open science resource for establishing reliability and reproducibility in functional connectomics. Sci Data, 1, 140049. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2014.49.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Mathematics of Information Technology and Complex Systems (Mitacs) Canada through the Mitacs Elevate grant. This research was undertaken thanks in part to funding from the Canada First Research Excellence Fund, awarded to McGill University for the Healthy Brains for Healthy Lives initiative.
We thank Laura Diamond and Micah Watts for English editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pizarro, R., Assemlal, HE., De Nigris, D. et al. Using Deep Learning Algorithms to Automatically Identify the Brain MRI Contrast: Implications for Managing Large Databases. Neuroinform 17, 115–130 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9387-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-018-9387-8