Abstract
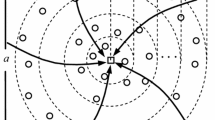
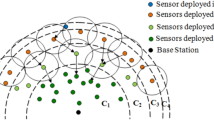
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) incorporate small devices known as sensors. These sensors monitor the deployment field and are responsible for communicating the sensed data periodically to the base station. Therefore, conserving the battery power of these sensors and the efficient coverage are the two important issues that need to be addressed especially in the cases where the sensors are having limited sensing range. In this paper, we intent to address the above mentioned issues by judiciously deploying the sensor nodes in WSN such that the energy efficient network along with the desirable coverage is obtained. In this paper, the considered deployment field is divided into concentric circles such that the area of each annulus is equal. Probability density function (PDF) is designed based on node density in each annulus. A node distribution algorithm is then proposed using the above PDF. The execution of the proposed distribution scheme is assessed with regard to the network life, energy balancing and the coverage obtained in the network. The results of the proposed scheme is compared with the other present schemes through simulation. It is noticed that the suggested scheme shows better results than other node distribution schemes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mathew, J., Hauser, C., Stoll, P., Kenel, C., Polyzos, D., Havermann, D., et al. (2017). Integrating fiber fabry-perot cavity sensor into 3-d printed metal components for extreme high-temperature monitoring applications. IEEE Sensors Journal, 17(13), 4107–4114.
Mishra, R., Jha, V., Tripathi, R. K., & Sharma, A. K. (2017). Energy efficient approach in wireless sensor networks using game theoretic approach and ant colony optimization. Wireless Personal Communications, 95(3), 3333–3355.
Mishra, R., Kumar, P., Chaudhury, S. & Indu, S. (2013). Monitoring a large surveillance space through distributed face matching. In 2013 Fourth national conference on computer vision, pattern recognition, image processing and graphics (NCVPRIPG) (pp. 1–5).
Rajwade, K. C., & Gawali, D. H. (2016). Wearable sensors based pilgrim tracking and health monitoring system. In 2016 International conference on computing communication control and automation (ICCUBEA) (pp. 1–5).
Lin, S. C., Alshehri, A. A., Wang, P., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2017). Magnetic induction-based localization in randomly deployed wireless underground sensor networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 4(5), 1454–1465.
Tanenbaum, A. S., Gamage, C., & Crispo, B. (2006). Taking sensor networks from the lab to the jungle. Computer, 39(8), 98–100.
Meng, S., Kashyap, S. R., Venkatramani, C., & Liu, L. (2012). Resource-aware application state monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 23(12), 2315–2329.
Dempsey, T., Sahin, G., Morton, Y. T., & Hopper, C. M. (2009). Intelligent sensing and classification in ad hoc networks: A case study. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 24(8), 23–30.
Li, J., & Mohapatra, P. (2007). Analytical modeling and mitigation techniques for the energy hole problem in sensor networks. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 3(3), 233–254.
Li, J., & Mohapatra, P. (2005). An analytical model for the energy hole problem in many-to-one sensor networks. In 2005 IEEE 62nd vehicular technology conference on VTC-2005-Fall (Vol. 4, pp. 2721–2725).
Olariu, S. & Stojmenovic, I. (2006). Design guidelines for maximizing lifetime and avoiding energy holes in sensor networks with uniform distribution and uniform reporting. In Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM 2006, 25th IEEE international conference on computer communications (pp. 1–12).
Stojmenovi, I., & Olariu, S. (2005). Data-centric protocols for wireless sensor networks (pp. 417–456). New York: Wiley.
Lian, J., Naik, K., & Agnew, G. B. (2006). Data capacity improvement of wireless sensor networks using non-uniform sensor distribution. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2(2), 121–145.
Liu, Y., Ngan, H., & Ni, L. M. (2006). Power-aware node deployment in wireless sensor networks. In IEEE international conference on sensor networks, ubiquitous, and trustworthy computing (SUTC’06) (Vol. 1, p. 8).
Halder, S., Ghosal, A., Chaudhuri, A., & DasBit, S. (2011). A probability density function for energy-balanced lifetime-enhancing node deployment in WSN (pp. 472–487). Berlin: Springer.
Halder, S., & DasBit, S. (2014). Design of a probability density function targeting energy-efficient node deployment in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 11(2), 204–219.
Halder, S., Ghosal, A., Chaudhuri, A., & DasBit, S. (2011). A probability density function for energy-balanced lifetime-enhancing node deployment in wsn. In Proceedings of the 2011 international conference on computational science and its applications-volume part IV (ICCSA’11) (pp. 472–487). Berlin: Springer.
Heinzelman, W. B., Chandrakasan, A. P., & Balakrishnan, H. (2002). An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 1(4), 660–670. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2002.804190.
Farooq, M. O., Dogar, A. B., & Shah, G. A. (2010). Mr-leach: Multi-hop routing with low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy. In 2010 Fourth international conference on sensor technologies and applications (SENSORCOMM) (pp. 262–268).
Ye, M., Li, C., Chen, G., & Wu, J. (2005). Eecs: An energy efficient clustering scheme in wireless sensor networks. In IPCCC.
Lara, R., Bentez, D., Caamao, A., Zennaro, M., & Rojo-lvarez, J. L. (2015). On real-time performance evaluation of volcano-monitoring systems with wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(6), 3514–3523.
Younis, O., & Fahmy, S. (2004). Heed: A hybrid, energy-efficient, distributed clustering approach for ad hoc sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 3(4), 366–379.
Soro, S., & Heinzelman, W. B. (2005). Prolonging the lifetime of wireless sensor networks via unequal clustering. In 19th IEEE international parallel and distributed processing symposium (p. 8).
Ye, M., Li, C., Chen, G., & Wu, J. (2005). An energy-efficient unequal clustering mechanism for wireless sensor networks. In IEEE international conference on mobile adhoc and sensor systems conference (pp. 8–604).
Perillo, M., Cheng, Z., & Heinzelman, W. (2004). On the problem of unbalanced load distribution in wireless sensor networks. In IEEE global telecommunications conference workshops. GlobeCom Workshops 2004. (pp. 74–79).
Giridhar, A., & Kumar, P. R. (2005). Maximizing the functional lifetime of sensor networks. In IPSN 2005, Fourth international symposium on information processing in sensor networks (pp. 5–12).
Wang, W., Srinivasan, V., & Chua, K. C. (2005). Using mobile relays to prolong the lifetime of wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 11th annual international conference on mobile computing and networking (MobiCom ’05) (pp. 270–283). New York, NY: ACM.
Luo, J., & Hubaux, J. P. (2005). Joint mobility and routing for lifetime elongation in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings IEEE 24th annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies (Vol. 3, pp. 1735–1746).
Bandyopadhyay, S., & Coyle E. J. (2003). An energy efficient hierarchical clustering algorithm for wireless sensor networks. In INFOCOM 2003, twenty-second annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications (Vol. 3, pp. 1713–1723). IEEE Societies.
Wang, D., Xie, B., & Agrawal, D. P. (2008). Coverage and lifetime optimization of wireless sensor networks with Gaussian distribution. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 7(12), 1444–1458.
Wu, X., Chen, G., & Das, S. K. (2008). Avoiding energy holes in wireless sensor networks with nonuniform node distribution. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 19(5), 710–720.
Mishra, R., Jha, V., Tripathi, R. K., & Sharma, A. K. (2017). Design of probability density function targeting energy efficient network for coalition based WSNS. Wireless personal communications, 99(2), 651–680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-5134-y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, R., Tripathi, R.K. & Sharma, A.K. Design of Probability Density Function Targeting Efficient Coverage in Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 105, 61–85 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-6103-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-018-6103-9