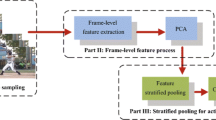
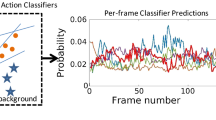
Abstract
Action recognition is one of the most difficult problems in computer vision and multimedia areas, since both spatial information and spatiotemporal semantic meaning should be taken into consideration. Moreover, the noisy and weakly annotated information make this task even harder. Nowadays, instead of the traditional features and classifiers, a lot of new attempts have made the task of action recognition promising. Noticing that there is no work on comparison of different combination of pooling and semi-supervised learning method under the same experiment setting, it would be interesting to apply different combination of pooling and semi-supervised learning method on both the synthetic and realistic action recognition datasets to see which combination or method performs better. In summary, we can obtain the following conclusions based on our experiments. Firstly, Second Order Pooling (Carreira et al. 2012) is worse than the traditional Bag of Words (Schmid and Mohr 1997; Dance et al. 2004) regarding to the overall performance in some dataset, but is a good way to speed up the coding stage of video classification with little sacrifice of performance. Secondly, Semi-supervised Hierarchical Regression Algorithm (MLHR) and Manifold Regularized Least Square Regression (MRLS) (Belkin et al. J Mach Learn Res 12:2399–2434, 2006) is better than some of the supervised learning methods (χ 2-SVM, SVM-2K (Farquhar et al. 2006)) in the real world action recognition problems which shares little available annotated information. Thirdly, for KTH, UCF50 and HMDB dataset, late fusion doesn’t necessarily improve the performance. In comparison, MLHR, SVM-2K and Multi-kernel Learning is a more natural way to deal with multi-feature problems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belkin M, Niyogi P, Sindhwani V (2006) Manifold regularization: a geometric framework for learning from labled and unlabeled examples. J Mach Learn Res 12:2399–2434
Carreira J, Caseiro R, Batista J, Sminchisescu C (2012) Semantic segmentation with second-order pooling. In: ECCV
Chen M, Hauptmann A (2009) Mosift, recognizing human actions in surveillance videos
Dance C, Willamowski J, Fan L, Bray C, Csurka G (2004) Visual categorization with bags of keypoints. In: ECCV SLCV workshop
Farquhar JDR, Meng H, Szedmak S, Hardoon DR, Shawe-taylor J (2006) Two view learning: svm-2k, theory and practice. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. MIT Press
Han Y, Xu Z, Ma Z, Huang Z (2013) Image classification with manifold learning for out-of-sample data. Signal Process 93(8):2169–2177
Han Y, Yang Y, Ma Z, Shen H, Sebe N, Zhou X (2014) Image attibute adaptation. IEEE Trans Multimed (IEEE T-MM). doi:10.1109/TMM.2014.2306092
Han Y, Zhang J, Xu Z, Yu S (2013) Discriminative multi-task feature selection. In: AAAI
Hotelling H (1936) Relations between two sets of variates. Biometrika 28(3):321–377
Kuehne H, Jhuang H, Garrote E, Poggio T, Serre T (2011) Hmdb: a large video database for human motion recognition. In: ICCV
Lan Z, Bao L, Yu S, Liu W, Hauptmann A (2012) Double fusion for multimedia event detection. In: ACM MM
Lew M, Sebe N, Djeraba C, Jain R (2006) Content-based multimedia information retrieval: state-of-the-art and challenges. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl 2(1):1–19
Ma Z, Nie F, Yang Y, Uijlings J, Sebe N, Hauptmann AG (2012) Discriminating joint feature analysis for multimedia data understanding. IEEE Trans Multimed (TMM) 14(6):1662–1672
Ma Z, Yang Y, Cai Y, Sebe N, Hauptmann A (2012) Transfer knowledge adaptation for ad hoc multimedia event detection with few examplars. In: ACM MM
Reddy K, Shah M (2012) Recognizing 50 human action categories of web videos. In: MVAP
Schmid C, Mohr R (1997) Local grayvalue invariants for image retrieval. In: TPAMI
Schuldt C, Laptev I, Caputo B (2004) Recognizing human actions: a local svm approach. In: ICPR
Snoek C, Worring M, Smeulders A (2005) Early versus late fusion in semantic video analysis. In: ACM MM
Sonnenburg S, Rtsch G, Schfer C, Schlkopf B (2006) Large scale multiple kernel learning. J Mach Learn Res 7:1531–1565
Vinokourov A, Shawe-taylor J, Cristianini N (2002) Inferring a semantic representation of text via cross-language correlation analysis
Wang H, Kläser A, Schmid C, Liu C (2011) Action recognition by dense trajectories. In: CVPR
Xu Z, Yang Y, Tsang I, Sebe N, Hauptmann A (2013) Feature weighting via optimal thresholding for video analysis. In: ICCV
Yan R (2006) Probabilistic latent query analysis for combining multiple retrieval sources. In: Proceedings of the 29th international ACM SIGIR conference. ACM Press, pp 324–331
Yan Y, Xu Z, Liu G, Ma Z, Sebe N (2013) Glocal structural feature selection with sparsity for multimedia data understanding. In: ACM MM
Yang Y, Ma Z, Hauptmann A, Sebe N (2013) Feature selection for multimedia analysis by sharing information among multiple tasks. IEEE Trans Multimedia 15(3):321–377
Yang Y, Nie F, Xu D, Luo J, Zhuang Y, Pan Y (2012) A multimedia retrieval framework based on semi-supervised ranking and relevance feedback. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell 34(4):723–742
Yang Y, Song J, Huang Z, Ma Z, Sebe N, Hauptmann A (2013) Multi-feature fusion via hierarchical regression for multimedia analysis. IEEE Trans Multimedia 15(3):572–581
Yang Y, Xu D, Nie F, Luo J, Zhuang Y (2009) Ranking with local regression and global alignment for cross media retrieval. In: ACM MM
Yang Y, Zhuang Y, Wu F, Pan Y (2008) Harmonizing hierarchical manifolds for multimedia document semantics understanding and cross-media retrieval. IEEE Trans Multimed 10(3):437–446
Zhan Y, Sun J, Niu D, Mao Q, Fan J (2014) A semi-supervised incremental learning method based on adaptive probabilistic hypergraph for video semantic detection. Multimed Tools Appl
Zhou D, Bousquet O, Lal TN, Weston J, Schlkopf B (2004) Learning with local and global consistency. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, vol 16. MIT Press, pp 321–328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, H., Yan, Y., Xu, S. et al. Evaluation of semi-supervised learning method on action recognition. Multimed Tools Appl 74, 523–542 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-014-1936-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-014-1936-z