Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Bernat, Julien
2008.
Study of irreducible balanced pairs for substitutive languages.
RAIRO - Theoretical Informatics and Applications,
Vol. 42,
Issue. 4,
p.
663.
Shieh, Jiunn-I
Wu, Hsin-Hung
and
Yang, Wei-Zu
2009.
Finding behavior patterns and evaluating orderliness of dynamical systems by spanning tree invariants.
Quality & Quantity,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 6,
p.
1011.
Akiyama, Shigeki
and
Lee, Jeong-Yup
2011.
Algorithm for determining pure pointedness of self-affine tilings.
Advances in Mathematics,
Vol. 226,
Issue. 4,
p.
2855.
Barge, Marcy
Štimac, Sonja
and
F. Williams, R.
2013.
Pure discrete spectrum in substitution tiling spaces.
Discrete & Continuous Dynamical Systems - A,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 2,
p.
579.
Akiyama, Shigeki
and
Lee, Jeong-Yup
2014.
Overlap coincidence to strong coincidence in substitution tiling dynamics.
European Journal of Combinatorics,
Vol. 39,
Issue. ,
p.
233.
Jolivet, Timo
and
Siegel, Anne
2015.
Machines, Computations, and Universality.
Vol. 9288,
Issue. ,
p.
3.
Sellami, Tarek
and
Sirvent, Víctor F.
2016.
Symmetric Intersections of Rauzy Fractals.
Quaestiones Mathematicae,
Vol. 39,
Issue. 3,
p.
289.
Barge, Marcy
2016.
Geometrical and spectral properties of Pisot substitutions.
Topology and its Applications,
Vol. 205,
Issue. ,
p.
28.
Adiceam, Faustin
Damanik, David
Gähler, Franz
Grimm, Uwe
Haynes, Alan
Julien, Antoine
Navas, Andrés
Sadun, Lorenzo
and
Weiss, Barak
2016.
Open Problems and Conjectures Related to the Theory of Mathematical Quasicrystals.
Arnold Mathematical Journal,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 4,
p.
579.
Spindeler, Timo
2017.
Diffraction intensities of a class of binary Pisot substitutions via exponential sums.
Monatshefte für Mathematik,
Vol. 182,
Issue. 1,
p.
143.
Ammar, Hamdi
Cassaigne, Julien
and
Sellami, Tarek
2021.
On the symmetric intersection of Rauzy fractals associated with the k-bonacci substitution.
Quaestiones Mathematicae,
Vol. 44,
Issue. 2,
p.
199.
Scheicher, Klaus
Sirvent, Víctor F.
and
Surer, Paul
2021.
Measure-wise disjoint Rauzy fractals with the same incidence matrix.
Monatshefte für Mathematik,
Vol. 194,
Issue. 4,
p.
857.
Nagai, Yasushi
2021.
Absence of absolutely continuous diffraction spectrum for certain S-adic tilings.
Nonlinearity,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 11,
p.
7963.
Creutz, Darren
and
Pavlov, Ronnie
2023.
Low complexity subshifts have discrete spectrum.
Forum of Mathematics, Sigma,
Vol. 11,
Issue. ,
 $\mathbb{Z}$-action on a sequence space, and the
$\mathbb{Z}$-action on a sequence space, and the 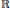 $\mathbb{R}$-action, which can be defined as a tiling dynamical system or as a suspension flow. We describe procedures for checking when these systems have pure discrete spectrum (the “balanced pairs algorithm” and the “overlap algorithm”) and study the relation between them. In particular, we show that pure discrete spectrum for the
$\mathbb{R}$-action, which can be defined as a tiling dynamical system or as a suspension flow. We describe procedures for checking when these systems have pure discrete spectrum (the “balanced pairs algorithm” and the “overlap algorithm”) and study the relation between them. In particular, we show that pure discrete spectrum for the 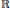 $\mathbb{R}$-action implies pure discrete spectrum for the
$\mathbb{R}$-action implies pure discrete spectrum for the  $\mathbb{Z}$-action, and obtain a partial result in the other direction. As a corollary, we prove pure discrete spectrum for every
$\mathbb{Z}$-action, and obtain a partial result in the other direction. As a corollary, we prove pure discrete spectrum for every 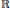 $\mathbb{R}$-action associated with a two-symbol substitution of Pisot type (this is conjectured for an arbitrary number of symbols).
$\mathbb{R}$-action associated with a two-symbol substitution of Pisot type (this is conjectured for an arbitrary number of symbols).



