Abstract
Background:
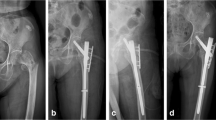
Extraarticular distal tibial fractures are among the most challenging fractures encountered by an orthopedician for treatment because of its subcutaneous location, poor blood supply and decreased muscular cover anteriorly, complications such as delayed union, nonunion, wound infection, and wound dehiscence are often seen as a great challenge to the surgeon. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) and intramedullary interlocking nail (IMLN) are two well-accepted and effective methods, but each has been historically related to complications. This study compares clinical and radiological outcome in extraarticular distal tibia fractures treated by intramedullary interlocking nail (IMLN) and minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO).
Materials and Methods:
42 patients included in this study, 21 underwent IMLN and 21 were treated with MIPO who met the inclusion criteria and operated between June 2014 and May 2015. Patients were followed up for clinical and radiological evaluation.
Results:
In IMLN group, average union time was 18.26 weeks compared to 21.70 weeks in plating group which was significant (P < 0.0001). Average time required for partial and full weight bearing in the nailing group was 4.95 weeks and 10.09 weeks respectively which was significantly less (P < 0.0001) as compared to 6.90 weeks and 13.38 weeks in the plating group. Lesser complications in terms of implant irritation, ankle stiffness, and infection, were seen in interlocking group as compared to plating group. Average functional outcome according to American Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Society score was measured which came out to be 96.67.
Conclusion:
IMLN group was associated with lesser duration of surgery, earlier weight bearing and union rate, lesser incidence of infection and implant irritation which makes it a preferable choice for fixation of extra-articular distal tibial fractures. However, larger randomized controlled trials are required for confirming the results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schatzker J, Tile M. The Rationale of Operative Fracture Care. 3rd ed. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2005. p. 475–6.
Bucholz R, Court-Brown C, Rockwood C. Rockwood and Green’s Fractures in Adults. New York: Lippincott; 2015. p. 98.
Müller M, Nazarian S, Koch P, Schatzker J. The Comprehensive Classification of Fractures of Long Bones. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1990.
Duda GN, Mandruzzato F, Heller M, Goldhahn J, Moser R, Hehli M, et al. Mechanical boundary conditions of fracture healing: Borderline indications in the treatment of unreamed tibial nailing. J Biomech 2001;34:639–50.
Habernek H, Kwasny O, Schmid L, Ortner F. Complications of interlocking nailing for lower leg fractures: A 3-year follow up of 102 cases. J Trauma 1992;33:863–9.
Borrelli J Jr., Prickett W, Song E, Becker D, Ricci W. Extraosseous blood supply of the tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: A human cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma 2002;16:691–5.
Nork SE, Schwartz AK, Agel J, Holt SK, Schrick JL, Winquist RA. Intramedullary nailing of distal metaphyseal tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2005;87:1213–21.
Johner R, Wruhs O. Classification of tibial shaft fractures and correlation with results after rigid internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1983; Sep; (178):7–25.
Mushtaq A, Shahid R, Asif M, Maqsood M. Distal tibial fracture fixation with locking compression plate (LCP) using the minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009;35:159–64.
Kumar D, Ram GG, Vijayaraghavan PV. Minimally invasive plate versus intramedullary interlocking nailing in distal third tibia fractures. IOSR J Dent Med Sci 2014;13:15–7.
Ram GG, Kumar D, Phagal VV. Surgical dilemma’s in treating distal third leg fractures. Int Surg J 2014;1:13–6.
Li Y, Liu L, Tang X, Pei F, Wang G, Fang Y, et al. Comparison of low, multidirectional locked nailing and plating in the treatment of distal tibial metadiaphyseal fractures. Int Orthop 2012;36:1457–62.
Vallier HA, Cureton BA, Patterson BM. Randomized, prospective comparison of plate versus intramedullary nail fixation for distal tibia shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2011;25:736–41.
Pawar ED, Agrawal SR, Patil AW, Choudhary S, Asadi G. A comparative study of intramedullary interlocking nail and locking plate fixation in the management of extra articular distal tibial fractures. J Evol Med Dent Sci 2014;3:6812–26.
Guo JJ, Tang N, Yang HL, Tang TS. A prospective, randomised trial comparing closed intramedullary nailing with percutaneous plating in the treatment of distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2010;92:984–8.
Yao Q, Ni J, Peng LB, Yu DX, Yuan XM. Locked plating with minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis versus intramedullary nailing of distal extra-articular tibial fracture: A retrospective study. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2013;93:3748–51.
Jorgensen TE. The influence of the intact fibula on the compression of a tibial fracture or pseudoarthrosis. Acta Orthop Scand 1974;45:119–29.
Richmond J, Colleran K, Borens O, Kloen P, Helfet DL. Nonunions of the distal tibia treated by reamed intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma 2004;18:603–10.
Schmidt AH, Finkemeier CG, Tornetta P 3rd. Treatment of closed tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;85:352–68.
Teitz CC, Carter DR, Frankel VH. Problems associated with tibial fractures with intact fibulae. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1980;62:770–6.
Vallier HA, Le TT, Bedi A. Radiographic and clinical comparisons of distal tibia shaft fractures (4 to 11 cm proximal to the plafond): Plating versus intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma 2008;22:307–11.
Ronga M, Longo UG, Maffulli N. Minimally invasive locked plating of distal tibia fractures is safe and effective. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2010;468:975–82.
Ehlinger M, Adam P, Gabrion A, Jeunet L, Dujardin F, Asencio G; Sofcot. Distal quarter leg fractures fixation: The intramedullary nailing alone option. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2010;96:674–82.
Bahari S, Lenehan B, Khan H, McElwain JP. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures. Acta Orthop Belg 2007;73:635–40.
Redfern DJ, Syed SU, Davies SJ. Fractures of the distal tibia: Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury 2004;35:615–20.
Collinge C, Kuper M, Larson K, Protzman R. Minimally invasive plating of high-energy metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2007;21:355–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daolagupu, A.K., Mudgal, A., Agarwala, V. et al. A comparative study of intramedullary interlocking nailing and minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in extra articular distal tibial fractures. IJOO 51, 292–298 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.205674
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.205674