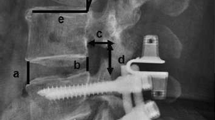
Abstract
Background
Decompression and fusion is considered as the ‘gold standard’ for the treatment of degenerative lumbar diseases, however, many disadvantages have been reported in several studies, recently like donor site pain, pseudoarthrosis, nonunion, screw loosening, instrumentation failure, infection, adjacent segment disease (ASDis) and degeneration. Dynamic neutralization system (Dynesys) avoids many of these disadvantages. This system is made up of pedicle screws, polyethylene terephthalate cords, and polycarbonate urethane spacers to stabilize the functional spinal unit and preserve the adjacent motion after surgeries. This was a retrospective cohort study to compare the effect of Dynesys for treating degenerative lumbar diseases with posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) based on short term followup.
Materials and Methods
Seventy five consecutive patients of lumbar degenerative disease operated between October 2010 and November 2012 were studied with a minimum followup of 2 years. Patients were divided into two groups according to the different surgeries. 30 patients underwent decompression and implantation of Dynesys in two levels (n = 29) or three levels (n = 1) and 45 patients underwent PLIF in two levels (n = 39) or three levels (n = 6). Clinical and radiographic outcomes between two groups were reviewed.
Results
Thirty patients (male:17, female:13) with a mean age of 55.96 ± 7.68 years were included in Dynesys group and the PLIF group included 45 patients (male:21, female:24) with a mean age of 54.69 ± 3.26 years. The average followup in Dynesys group and PLIF group was 2.22 ± 0.43 year (range 2-3.5 year) and 2.17 ± 0.76 year (range 2-3 year), respectively. Dynesys group showed a shorter operation time (141.06 ± 11.36 min vs. 176.98 ± 6.72 min, P < 0.001) and less intraoperative blood loss (386.76 ± 19.44 ml vs. 430.11 ± 24.72 ml, P < 0.001). For Dynesys group, visual analogue scale (VAS) for back and leg pain improved from 6.87 ± 0.80 to 2.92 ± 0.18 and 6.99 ± 0.81 to 3.25 ± 0.37, (both P < 0.001) and for PLIF, VAS for back and leg pain also improved significantly (6.97 ± 0.84–3.19 ± 0.19 and 7.26 ± 0.76–3.56 ± 0.38, both P < 0.001). Significant improvement was found at final followup in both groups in Oswestry disability index (ODI) score (both P < 0.001). Besides, Dynesys group showed a greater improvement in ODI and VAS back and leg pain scores compared with the PLIF group (P < 0.001, P = 0.009 and P = 0.031, respectively). For radiological, height of the operated level was found increased in both groups (both P < 0.001), but there was no difference between two groups (P = 0.93). For range of motion (ROM) of operated level, significant decrease was found in both groups (P < 0.001), but Dynesys showed a higher preservation of motion at the operative levels (P < 0.001). However, no significant difference was found in the percentage change of ROM of adjacent levels between Dynesys and PLIF (0.74 ± 8.92% vs. 0.92 ± 4.52%, P = 0.91). Some patients suffered from degeneration of adjacent intervertebral disc at final followup, but there was no significant difference in adjacent intervertebral disc degeneration between two groups (P = 0.71). Moreover, there were no differences in complications between Dynesys and PLIF (P = 0.90), although the incidence of complication in Dynesys was lower than PLIF (16.67% vs. 17.78%).
Conclusion
Dynamic stabilization system treating lumbar degenerative disease showed clinical benefits with motion preservation of the operated segments, but does not have the significant advantage on motion preservation at adjacent segments, to avoid the degeneration of adjacent intervertebral disk.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang RC, Girardi FP, Lim MR, Cammisa FP Jr. Advantages and disadvantages of nonfusion technology in spine surgery. Orthop Clin North Am 2005;36:263–9.
Miyakoshi N, Abe E, Shimada Y, Okuyama K, Suzuki T, Sato K. Outcome of one-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis and postoperative intervertebral disc degeneration adjacent to the fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000;25:1837–42.
Okuda S, Iwasaki M, Miyauchi A, Aono H, Morita M, Yamamoto T. Risk factors for adjacent segment degeneration after PLIF. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2004;29:1535–40.
Chou WY, Hsu CJ, Chang WN, Wong CY. Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar spinal posterolateral fusion with instrumentation in elderly patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2002;122:39–43.
Kumar MN, Baklanov A, Chopin D. Correlation between sagittal plane changes and adjacent segment degeneration following lumbar spine fusion. Eur Spine J 2001;10:314–9.
Resnick DK, Choudhri TF, Dailey AT, Groff MW, Khoo L, Matz PG, et al. Guidelines for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 5: Correlation between radiographic and functional outcome. J Neurosurg Spine 2005;2:658–61.
Würgler-Hauri CC, Kalbarczyk A, Wiesli M, Landolt H, Fandino J. Dynamic neutralization of the lumbar spine after microsurgical decompression in acquired lumbar spinal stenosis and segmental instability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008;33:E66–72.
Davis R J, Maxwell J H. Dynesys LIS surgical technique [J]. Dynesys LIS Less Invasive Surgery, The Dynamic Stabilization System, 2005.
Lin HM, Pan YN, Liu CL, Huang LY, Huang CH, Chen CS. Biomechanical comparison of the K-ROD and Dynesys dynamic spinal fixator systems-A finite element analysis. Biomed Mater Eng 2013;23:495–505.
Erbulut DU, Zafarparandeh I, Ozer AF, Goel VK. Biomechanics of posterior dynamic stabilization systems. Adv Orthop 2013;2013:451956.
Ilharreborde B, Shaw MN, Berglund LJ, Zhao KD, Gay RE, An KN. Biomechanical evaluation of posterior lumbar dynamic stabilization: An in vitro comparison between Universal Clamp and Wallis systems. Eur Spine J 2011;20:289–96.
Beastall J, Karadimas E, Siddiqui M, Nicol M, Hughes J, Smith F, et al. The Dynesys lumbar spinal stabilization system: A preliminary report on positional magnetic resonance imaging findings. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:685–90.
Yu SW, Yen CY, Wu CH, Kao FC, Kao YH, Tu YK. Radiographic and clinical results of posterior dynamic stabilization for the treatment of multisegment degenerative disc disease with a minimum followup of 3 years. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2012;132:583–9.
Schnake KJ, Schaeren S, Jeanneret B. Dynamic stabilization in addition to decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2006;31:442–9.
Bordes-Monmeneu M, Bordes-Garcia V, Rodrigo-Baeza F, Saez D. System of dynamic neutralization in the lumbar spine: Experience on 94 cases. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2005;16:499–506.
Stoll TM, Dubois G, Schwarzenbach O. The dynamic neutralization system for the spine: A multi-center study of a novel non-fusion system. Eur Spine J 2002;11 Suppl 2:S170–8.
Lee SE, Park SB, Jahng TA, Chung CK, Kim HJ. Clinical experience of the dynamic stabilization system for the degenerative spine disease. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2008;43:221–6.
Reyes-Sánchez A, Zárate-Kalfópulos B, Ramírez-Mora I, Rosales-Olivarez LM, Alpizar-Aguirre A, Sánchez-Bringas G. Posterior dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine with the Accuflex rod system as a stand-alone device: Experience in 20 patients with 2-year followup. Eur Spine J 2010;19:2164–70.
Mandigo CE, Sampath P, Kaiser MG. Posterior dynamic stabilization of the lumbar spine: Pedicle based stabilization with the AccuFlex rod system. Neurosurg Focus 2007;22:E9.
Meyers K, Tauber M, Sudin Y, Fleischer S, Arnin U, Girardi F, et al. Use of instrumented pedicle screws to evaluate load-sharing in posterior dynamic stabilization systems. Spine J 2008;8:926–32.
Zhou ZJ, Xia P, Zhao X, Fang XQ, Zhao FD, Fan SW. Can posterior dynamic stabilization reduce the risk of adjacent segment deterioration? Turk Neurosurg 2013;23:579–89.
Grob D, Benini A, Junge A, Mannion AF. Clinical experience with the Dynesys semi-rigid fixation system for the lumbar spine: Surgical and patient-oriented outcome in 50 cases after an average of 2 years. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30:324–31.
Cakir B, Carazzo C, Schmidt R, Mattes T, Reichel H, Käfer W. Adjacent segment mobility after rigid and semi-rigid instrumentation of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009;34:1287–91.
Fay LY, Wu JC, Tsai TY, Wu CL, Huang WC, Cheng H. Dynamic stabilization for degenerative spondylolisthesis: Evaluation of radiographic and clinical outcomes. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2013;115:535–41.
Chow JH, Chan CC. Validation of the Chinese version of the Oswestry Disability Index. Work 2005;25:307–14.
Bijur PE, Silver W, Gallagher EJ. Reliability of the visual analog scale for measurement of acute pain. Acad Emerg Med 2001;8:1153–7.
Yang B, Jiang T. Comparative study of dynamic neutralization system and posterior lumbar interbody fusion in treating lumbar degenerative disease. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 2013;27:140–4.
Haddad B, Makki D, Konan S, Park D, Khan W, Okafor B. Dynesys dynamic stabilization: Less good outcome than lumbar fusion at 4-year followup. Acta Orthop Belg 2013;79:97–103.
Wang M, Li K, Wang F, Zhang Y. The early clinical observation about Dynesys and lumbar interbody fusion in treatment of lumbar degenerative disease. J Clin Orthop 2012;15:10–2.
Li Z, Li F, Yu S, Ma H, Chen Z, Zhang H, et al. Two-year followup results of the Isobar TTL Semi-Rigid Rod System for the treatment of lumbar degenerative disease. J Clin Neurosci 2013;20:394–9.
Canbay S, Aydin AL, Aktas E, Erten SF, Basmaci M, Sasani M, et al. Posterior dynamic stabilization for the treatment of patients with lumbar degenerative disc disease: Long term clinical and radiological results. Turk Neurosurg 2013;23:188–97.
Hoppe S, Schwarzenbach O, Aghayev E, Bonel H, Berlemann U. Long term outcome after monosegmental L4/5 stabilization for degenerative spondylolisthesis with the dynesys device. J Spinal Disord Tech 2012.
Sapkas G, Mavrogenis AF, Starantzis KA, Soultanis K, Kokkalis ZT, Papagelopoulos PJ. Outcome of a dynamic neutralization system for the spine. Orthopedics 2012;35:e1497–502.
Hoff E, Strube P, Gross C, Putzier M. Sequestrectomy with additional transpedicular dynamic stabilization for the treatment of lumbar disc herniation: No clinical benefit after 10 years followup. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2013;38:887–95.
Yu SW, Yang SC, Ma CH, Wu CH, Yen CY, Tu YK. Comparison of Dynesys posterior stabilization and posterior lumbar interbody fusion for spinal stenosis L4L5. Acta Orthop Belg 2012;78:230–9.
Fayyazi AH, Ordway NR, Park SA, Fredrickson BE, Yonemura K, Yuan HA. Radiostereometric analysis of postoperative motion after application of dynesys dynamic posterior stabilization system for treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord Tech 2010;23:236–41.
Zhong H. Effectiveness of Dynesys for treating degeneration and instability of lumbar. Chin Manipulation Rehabil Med 2012;3:417–8.
Ko CC, Tsai HW, Huang WC, Wu JC, Chen YC, Shih YH, et al. Screw loosening in the Dynesys stabilization system: Radiographic evidence and effect on outcomes. Neurosurg Focus 2010;28:E10.
Schaeren S, Broger I, Jeanneret B. Minimum four-year followup of spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis treated with decompression and dynamic stabilization. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008;33:E636–42.
Putzier M, Schneider SV, Funk JF, Tohtz SW, Perka C. The surgical treatment of the lumbar disc prolapse: Nucleotomy with additional transpedicular dynamic stabilization versus nucleotomy alone. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30:E109–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Li, C., Chen, Z. et al. Short term outcome of posterior dynamic stabilization system in degenerative lumbar diseases. IJOO 48, 574–581 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.144222
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.144222