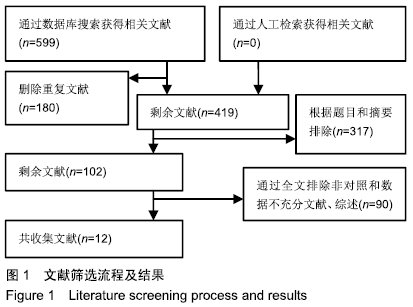
2.1 文献检索结果 根据检索策略,初步检出599篇文献,通过去除重复文献,浏览标题、阅读摘要、全文进一步排除不符合标准文献,最终纳入12篇文献[9,11-21]。文献筛选流程见图1。
2.2 纳入文献基本特征 纳入的12篇文献全部为英文文献,总样本量包括945个膝关节,其中运动学对线组470个膝关节,机械力学对线组475个膝关节,收集的文献随访时间6个月至8年。12篇文献中9篇文献为随机对照研究,2篇为回顾性队列研究,1篇为前瞻性队列研究。纳入研究的一般资料见表1,2。
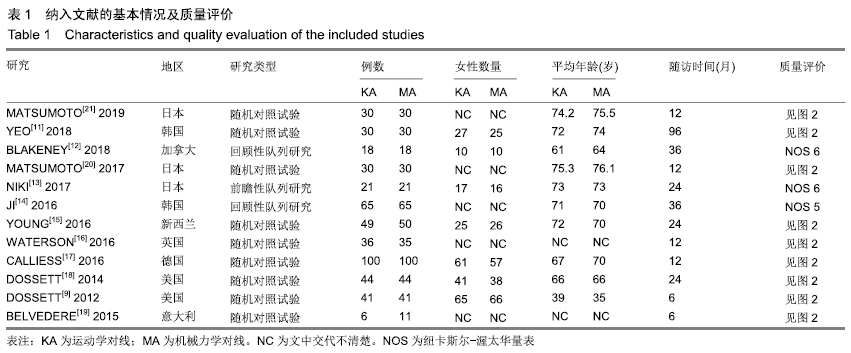
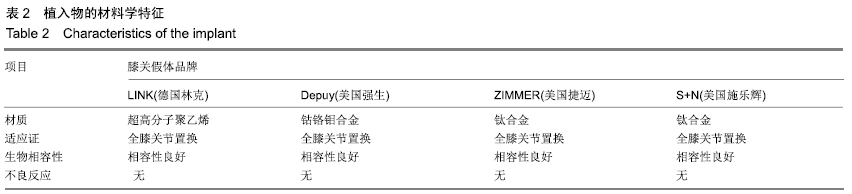
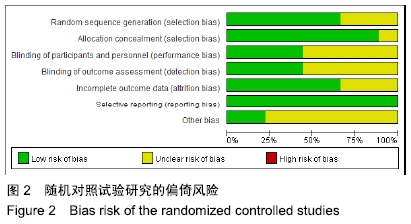
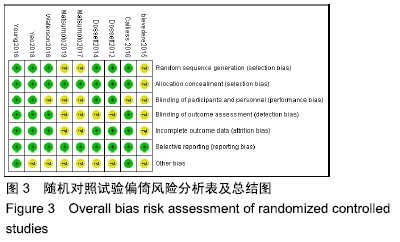
2.3 纳入研究的质量评价 2位评价员独立评估纳入研究的方法学质量,使用Cochrane协作工具对随机对照试验研究进行了偏倚风险评估。在9项随机对照试验研究中,随访偏倚和报告偏倚风险较小,无高风险研究;6项研究存在不明确的选择偏倚风险,2项研究的选择偏倚风险较高;在任何包括的研究中,没有发现任何其他明显的偏倚,见图2,3。对于非随机对照试验(即前瞻性队列研究和回顾性队列研究)的质量评估使用NOS量表,高质量的研究得分4-8分,低质量的研究得分0-3分,3项非随机对照试验研究NOS评分高于5分,均属于高质量研究,见表1。
2.4 Meta分析结果
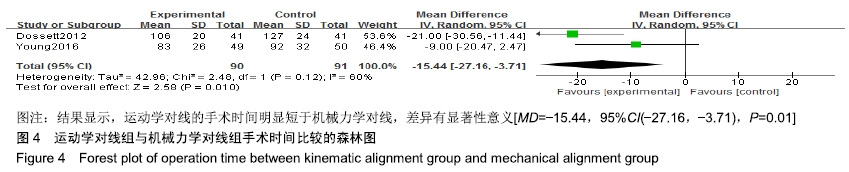
2.4.1 手术时间比较 有2个研究比较了运动学对线组与机械力学对线组的手术时间[9,15],共含膝关节181例(90例运动学对线,91例机械力学对线),根据提取的数据资料,异质性检测结果提示各研究之间无统计学异质性(P=0.12,I2=60%),采用随机效应模型进行分析,结果显示,MD=-15.44,95%CI(-27.16,-3.71),P=0.01,差异有显著性意义,表明运动学对线的手术时间明显短于机械力学对线,见图4。
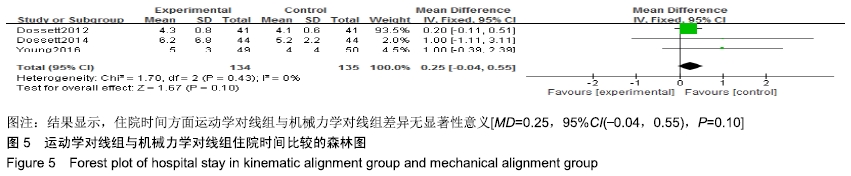
2.4.2 平均住院日比较 有3个研究比较了运动学对线组与机械力学对线组的住院时间[9,15,18],共含膝关节269例(134例运动学对线,135例机械力学对线),根据提取的数据资料,异质性检测结果提示各研究之间无统计学异质性(P=0.43,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示,MD=0.25,95%CI(-0.04,0.55),P=0.10,住院时间方面运动学对线组与机械力学对线组差异无显著性意义,见图5。
2.4.3 出院前行走距离比较 有3个研究比较了运动学对线组与机械力学对线组的出院前行走距离[9,16,18],共含膝关节241例(121例运动学对线,120例机械力学对线),根据提取的数据资料,异质性检测结果提示各研究之间无统计学异质性(P=0.13,I2=51%),采用随机效应模型进行分析,结果显示,MD=8.17,95%CI(-7.96,24.31),P=0.32,在出院前行走距离方面2组差异无显著性意义,见图6。
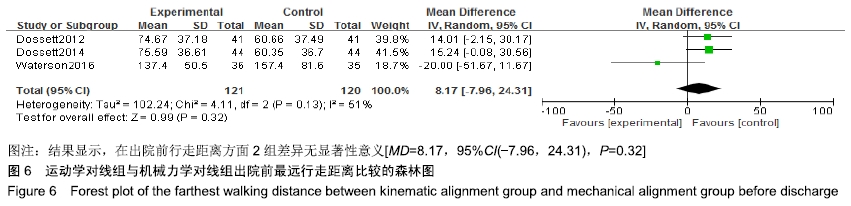
2.4.4 美国膝关节协会评分比较 有8个研究比较了运动学对线组与机械力学对线组的术后美国膝关节协会评分[9,13,15-16,18-21],共含膝关节499例(257例运动学对线,242例机械力学对线),根据提取的数据资料,异质性检测结果提示各研究之间无统计学异质性(P=0.005,I2=66%),采用随机效应模型进行分析,结果显示,MD=2.80,95%CI(-0.18,5.78),P=0.07,运动学对线组与机械力学对线组在美国膝关节协会评分方面差异无显著性意义,见图7。
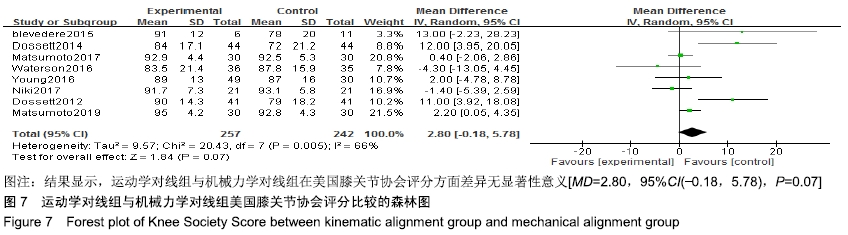
2.4.5 膝关节屈曲角度比较 有8项研究比较了运动学对线组与机械力学对线组的术后膝关节屈曲度[9,11,13,15-16,18,20-21],共含膝关节562例(281例运动学对线,281例机械力学对线),根据提取的数据资料,异质性检测结果提示各研究之间存在统计学异质性(P=0.07,I2=47%),采用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示,MD=2.97,95%CI(1.23,4.71),P=0.000 8,差异有显著性意义,认为运动学对线组相比机械力学对线组术后具有更大的膝关节屈曲度,见图8。
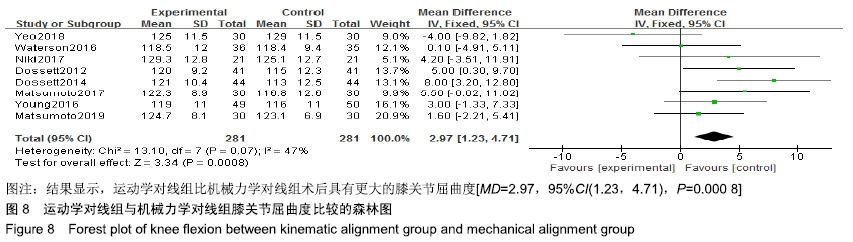
2.4.6 膝关节伸直角度比较 有3个研究比较了运动学对线组与机械力学对线组的术后膝关节伸直度[9,18,21],共含膝关节230例(115例运动学对线,115例机械力学对线),根据提取的数据资料,异质性检测结果提示各研究之间无统计学异质性(P=0.19,I2=41%),采用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示,MD=-0.05,95%CI(-0.73,0.63),P=0.89,说明运动学对线组与机械力学对线组术后膝关节伸直度差异无显著性意义,见图9。
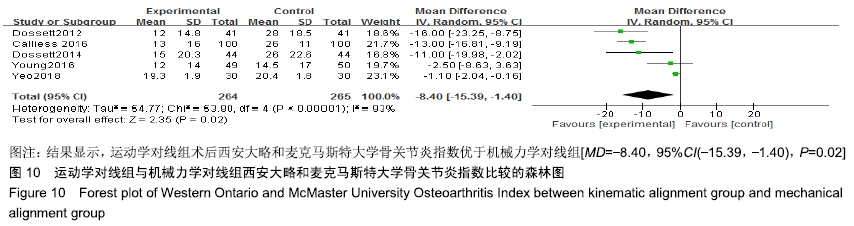
2.4.7 西安大略和麦克马斯特大学骨关节炎指数比较 有5个研究比较了运动学对线组与机械力学对线组的术后西安大略和麦克马斯特大学骨关节炎指数[9,11,15,17-18],共含膝关节529例(264例运动学对线,265例机械力学对线),根据提取的数据资料,异质性检测结果提示各研究之间存在统计学异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=93%),采用随机效应模型进行分析,结果显示,MD=-8.40,95%CI(-15.39,-1.40),P=0.02,差异有显著性意义,说明运动学对线组术后西安大略和麦克马斯特大学骨关节炎指数优于机械力学对线组,见图10。
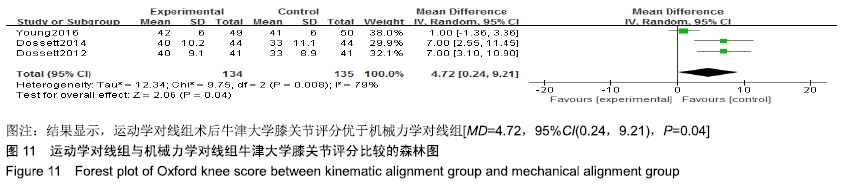
2.4.8 牛津大学膝关节评分比较 有3个研究比较了运动学对线组与机械力学对线组的术后牛津大学膝关节评 分[9,15,18],共含膝关节269例(134例运动学对线,135例机械力学对线),根据提取的数据资料,异质性检测结果提示各研究之间存在统计学异质性(P=0.008,I2=79%),采用随机效应模型进行分析,结果显示,MD=4.72,95%CI(0.24,9.21),P=0.04,差异有显著性意义,认为运动学对线组术后牛津大学膝关节评分优于机械力学对线组,见图11。
2.4.9 术后影像学指标比较
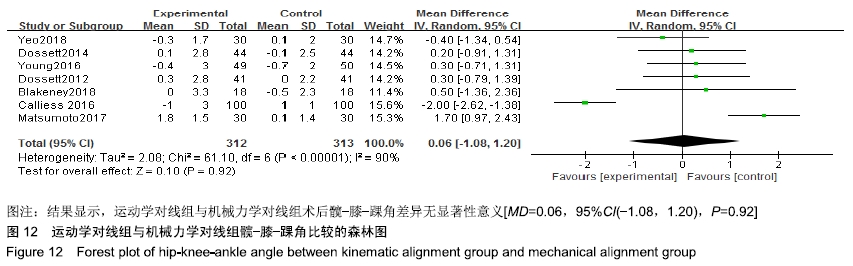
髋-膝-踝角比较:有7个研究比较了运动学对线组与机械力学对线组的术后髋-膝-踝角[9,11-12,15,17-18,20],共含膝关节625例(312例运动学对线,313例机械力学对线),根据提取的数据资料,异质性检测结果提示各研究之间存在统计学异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=90%),采用随机效应模型进行分析,结果显示,MD=0.06,95%CI(-1.08,1.20),P=0.92,认为运动学对线组与机械力学对线组术后髋-膝-踝角差异无显著性意义,见图12。
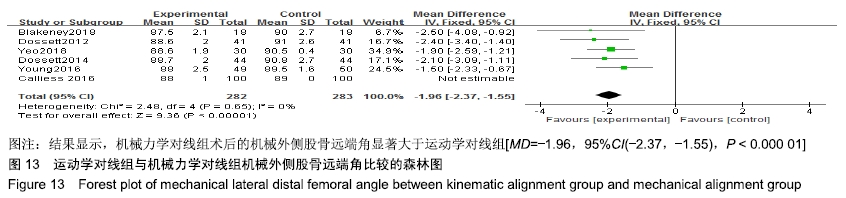
机械外侧股骨远端角比较:有6个研究比较了运动学对线组与机械力学对线组的术后机械外侧股骨远端角[9,11-12,15,17-18],共含膝关节565例(282例运动学对线,283例机械力学对线),根据提取的数据资料,异质性检测结果提示各研究之间无统计学异质性(P=0.65,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示,MD=-1.96,95%CI(-2.37,-1.55),P < 0.000 01,差异有显著性意义,认为机械力学对线组术后的机械外侧股骨远端角显著大于运动学对线组,见图13。
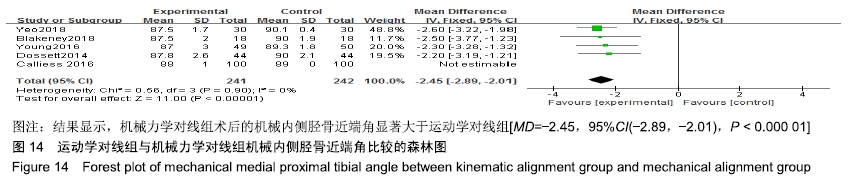
机械内侧胫骨近端角比较:有5个研究比较了运动学对线组与机械力学对线组的术后机械内侧胫骨近端 角[11-12,15,17-18],共含膝关节483例(241例运动学对线,242例机械力学对线),根据提取的数据资料,异质性检测结果提示各研究之间无统计学异质性(P=0.9,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示,MD=-2.45,95%CI(-2.89,-2.01),P < 0.000 01,差异有显著性意义,认为机械力学对线组术后的机械内侧胫骨近端角显著大于运动学对线组,见图14。
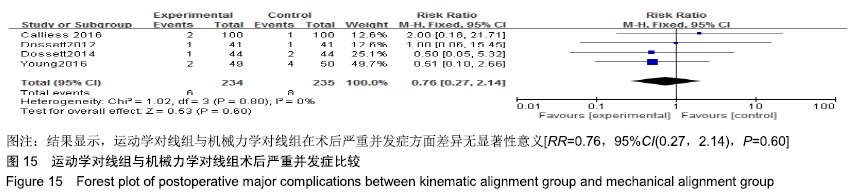
2.4.10 并发症比较 有4个研究比较了运动学对线组与机械力学对线组的术后严重并发症[9,15,17-18],共含膝关节469例(234例运动学对线,235例机械力学对线),根据提取的数据资料,异质性检测结果提示各研究之间无统计学异质性(P=0.79,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行分析,结果显示,RR=0.76,95%CI(0.27,2.14),P=0.60,认为运动学对线组与机械力学对线组在术后严重并发症方面差异亦无显著性意义,见图15。