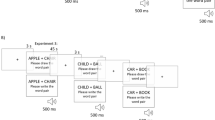
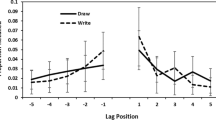
Abstract
The hippocampus plays a critical role in the formation of declarative memories, and hippocampal damage leads to significant impairments in new memory formation. Drawing can serve as a form of multi-modal encoding that improves declarative memory performance relative to other multimodal encoding strategies such as writing. We examined whether, and to what extent, patients with hippocampal damage could benefit from the mnemonic strategy of drawing. Three patients with focal hippocampal damage, and one patient with both hippocampal and cortical lesions, in addition to 22 age-, sex-, and education-matched controls, were shown a list of words one at a time during encoding and instructed to either draw a picture or repeatedly write each word for 40 s. Following a brief filled delay, free recall and recognition memory for words from both encoding trial types were assessed. Controls showed enhanced recall and recognition memory for words drawn versus those that were written, an effect that was even more pronounced in patients with focal hippocampal damage. By contrast, the patient with both hippocampal and cortical lesions showed no drawing-mediated boost in either recall or recognition memory. These findings demonstrate that drawing is an effective encoding strategy, likely accruing from the engagement of extra-hippocampal processes including the integration of cortical-based motor, visual, and semantic processing, enabling more elaborative encoding.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the authors upon request
References
Aggleton, J. P., & Brown, M. W. (1999). Episodic memory, amnesia and the hippocampal-anterior thalamic axis. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 22(3), 425–444.
Aggleton, J. P., Vann, S. D., Denby, C., Dix, S., Mayes, A. R., Roberts, N., & Yonelinas, A. P. (2005). Sparing of the familiarity component of recognition memory in a patient with hippocampal pathology. Neuropsychologia, 43(12), 1810–1823.
Ally, B. A. (2012). Using pictures and words to understand recognition memory deterioration in amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: A review. Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports, 12(6), 687–694.
Ally, B. A., Gold, C. A., & Budson, A. E. (2009). The picture superiority effect in patients with Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neuropsychologia, 47(2), 595–598.
Amlien, I. K., Sneve, M. H., Vidal-Piñeiro, D., Walhovd, K. B., & Fjell, A. M. (2019). Elaboration benefits source memory encoding through centrality change. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–13.
Antony, J. W., Ferreira, C. S., Norman, K. A., & Wimber, M. (2017). Retrieval as a fast route to memory consolidation. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 21(8), 573–576.
Arndt, S., Cizadlo, T., O'Leary, D., Gold, S., & Andreasen, N. C. (1996). Normalizing counts and cerebral blood flow intensity in functional imaging studies of the human brain. Neuroimage, 3(3), 175–184.
Baker, S., Vieweg, P., Gao, F., Gilboa, A., Wolbers, T., Black, S. E., & Rosenbaum, R. S. (2016). The human dentate gyrus plays a necessary role in discriminating new memories. Current Biology, 26(19), 2629–2634.
Barbeau, E. J., Felician, O., Joubert, S., Sontheimer, A., Ceccaldi, M., & Poncet, M. (2005). Preserved visual recognition memory in an amnesic patient with hippocampal lesions. Hippocampus, 15(5), 587–596.
Carr, V. A., Castel, A. D., & Knowlton, B. J. (2015). Age-related differences in memory after attending to distinctiveness or similarity during learning. Aging, Neuropsychology, and Cognition, 22(2), 155–169.
Clark, I. A., & Maguire, E. A. (2016). Remembering preservation in hippocampal amnesia. Annual Review of Psychology, 67, 51–82.
Cohen, N. J., & Eichenbaum, H. (1995). Memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal system. MIT Press.
Cohen, N. J., Ryan, J., Hunt, C., Romine, L., Wszalek, T., & Nash, C. (1999). Hippocampal system and declarative (relational) memory: Summarizing the data from functional neuroimaging studies. Hippocampus, 9(1), 83–98.
Craik, F. I. (2002). Levels of processing: Past, present... And future? Memory, 10(5-6), 305–318.
Craik, F. I., & Lockhart, R. S. (1972). Levels of processing: A framework for memory research. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 11(6), 671–684.
Craik, F. I., & Rose, N. S. (2012). Memory encoding and aging: A neurocognitive perspective. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 36(7), 1729–1739.
Crawford, J. R., & Garthwaite, P. H. (2002). Investigation of the single case in neuropsychology: Confidence limits on the abnormality of test scores and test score differences. Neuropsychologia., 40, 1196–1208.
Crawford, J. R., & Garthwaite, P. H. (2007). Comparison of a single case to a control or normative sample in neuropsychology: Development of a Bayesian approach. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 24(4), 343–372.
Crawford, J. R., Garthwaite, P. H., & Porter, S. (2010). Point and interval estimates of effect sizes for the case-controls design in neuropsychology: Rationale, methods, implementations, and proposed reporting standards. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 27, 245–260.
Crawford, J. R., & Howell, D. C. (1998). Comparing an individual's test score against norms derived from small samples. The Clinical Neuropsychologist, 12, 482–486.
Eichenbaum, H. (2004). Hippocampus: Cognitive processes and neural representations that underlie declarative memory. Neuron, 44(1), 109–120.
Eichenbaum, H., Yonelinas, A. R., & Ranganath, C. (2007). The medial temporal lobe and recognition memory. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 30, 123.
Engelkamp, J., & Zimmer, H. D. (1989). Memory for action events: A new field of research. Psychological Research Psychologische Forschung.
Engelkamp, J., & Zimmer, H. D. (1997). Sensory factors in memory for subject-performed tasks. Acta Psychologica, 96(1-2), 43–60.
Fan, J. E., Wammes, J. D., Gunn, J. B., Yamins, D. L., Norman, K. A., & Turk-Browne, N. B. (2020). Relating visual production and recognition of objects in human visual cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 40(8), 1710–1721.
Favila, S. E., Chanales, A. J., & Kuhl, B. A. (2016). Experience-dependent hippocampal pattern differentiation prevents interference during subsequent learning. Nature Communications, 7(1), 1–10.
Fernandes, M. A., Wammes, J. D., & Meade, M. E. (2018). The surprisingly powerful influence of drawing on memory. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 27(5), 302–308.
Gardiner, J. M. (2001). Episodic memory and autonoetic consciousness: A first–person approach. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 356(1413), 1351–1361.
Gilboa, A., & Marlatte, H. (2017). Neurobiology of schemas and schema-mediated memory. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 21(8), 618–631.
Gilboa, A., & Moscovitch, M. (2021). No consolidation without representation: Correspondence between neural and psychological representations in recent and remote memory. Neuron, 109(14), 2239–2255.
Gómez-Isla, T., Price, J. L., McKeel, D. W., Jr., Morris, J. C., Growdon, J. H., & Hyman, B. T. (1996). Profound loss of layer II entorhinal cortex neurons occurs in very mild Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neuroscience, 16(14), 4491–4500.
Guttentag, R. E., & Hunt, R. R. (1988). Adult age differences in memory for imagined and performed actions. Journal of Gerontology, 43(4), P107–P108.
Hautus, M. J. (1995). Corrections for extreme proportions and their biasing effects on estimated values of d′. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers, 27(1), 46–51.
Hebscher, M., Wing, E., Ryan, J., & Gilboa, A. (2019). Rapid cortical plasticity supports long-term memory formation. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 23(12), 989–1002.
Hilverman, C., Cook, S. W., & Duff, M. C. (2018). Hand gestures support word learning in patients with hippocampal amnesia. Hippocampus, 28(6), 406–415.
Iani, F., & Bucciarelli, M. (2017). Mechanisms underlying the beneficial effect of a speaker’s gestures on the listener. Journal of Memory and Language, 96, 110–121.
Koolschijn, R. S., Emir, U. E., Pantelides, A. C., Nili, H., Behrens, T. E., & Barron, H. C. (2019). The hippocampus and neocortical inhibitory engrams protect against memory interference. Neuron, 101(3), 528–541.
Lockhart, R. S., & Craik, F. I. (1990). Levels of processing: A retrospective commentary on a framework for memory research. Canadian Journal of Psychology/Revue Canadienne de Psychologie, 44(1), 87.
MacLeod, C. M., Gopie, N., Hourihan, K. L., Neary, K. R., & Ozubko, J. D. (2010). The production effect: Delineation of a phenomenon. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 36(3), 671.
Marlatte, H., Belchev, Z., Fraser, M., & Gilboa, A. (2023). The effect of hippocampal subfield damage on rapid temporal integration through statistical learning and associative inference. Neuropsychologia, 108755.
Mayes, A. R., Holdstock, J. S., Isaac, C. L., Hunkin, N. M., & Roberts, N. (2002). Relative sparing of item recognition memory in a patient with adult-onset damage limited to the hippocampus. Hippocampus, 12(3), 325–340.
McGhee, J. D., Cowan, N., Beschin, N., Mosconi, C., & Della Sala, S. (2020). Wakeful rest benefits before and after encoding in anterograde amnesia. Neuropsychology, 34(5), 524.
Meade, M. E., Ahmad, M., & Fernandes, M. A. (2020). Drawing pictures at encoding enhances memory in healthy older adults and in individuals with probable dementia. Aging, Neuropsychology, and Cognition, 27(6), 880–901.
Meade, M. E., Wammes, J. D., & Fernandes, M. A. (2019). Comparing the influence of doodling, drawing, and writing at encoding on memory. Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology/Revue canadienne de psychologie expérimentale, 73(1), 28.
Meade, M. E., Wammes, J. D., & Fernandes, M. A. (2018). Drawing as an encoding tool: Memorial benefits in younger and older adults. Experimental Aging Research, 44(5), 369–396.
Mitchnick, K. A., Ahmad, Z., Mitchnick, S. D., Ryan, J. D., Rosenbaum, R. S., & Freud, E. (2022). Damage to the human dentate gyrus impairs the perceptual discrimination of complex, novel objects. Neuropsychologia, 172, 108238.
Merhav, M., Karni, A., & Gilboa, A. (2014). Neocortical catastrophic interference in healthy and amnesic adults: A paradoxical matter of time. Hippocampus, 24(12), 1653–1662.
Moscovitch, M., & Gilboa, A. (2021, May 10). Systems consolidation, transformation and reorganization: Multiple trace theory, trace transformation theory and their competitors. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/yxbrs
Nee, D. E., Wager, T. D., & Jonides, J. (2007). Interference resolution: Insights from a meta-analysis of neuroimaging tasks. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 7(1), 1–17.
Norman, K. A., & O'Reilly, R. C. (2003). Modeling hippocampal and neocortical contributions to recognition memory: A complementary-learning-systems approach. Psychological Review, 110(4), 611.
O’Reilly, R. C., & Norman, K. A. (2002). Hippocampal and neocortical contributions to memory: Advances in the complementary learning systems framework. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 6(12), 505–510.
Paivio, A. (1971). Imagery and language. In Imagery (pp. 7–32). Academic Press.
Paivio, A. (1991). Dual coding theory: Retrospect and current status. Canadian Journal of Psychology/Revue Canadienne de Psychologie, 45(3), 255.
Paivio, A., Rogers, T. B., & Smythe, P. C. (1968). Why are pictures easier to recall than words? Psychonomic Science, 11(4), 137–138.
Patterson, K., Nestor, P. J., & Rogers, T. T. (2007). Where do you know what you know? The representation of semantic knowledge in the human brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 8(12), 976–987.
Pierce, J., Gray, J. R., Simpson, S., MacAskill, M., Höchenberger, R., Sogo, H., & Lindeløv, J. K. (2019). PsychoPy2: Experiments in behavior made easy. Behavior Research Methods, 51(1), 195–203.
Pöhlchen, D., & Schönauer, M. (2020). Sleep-dependent memory consolidation in the light of rapid neocortical plasticity. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 33, 118–125.
Prinz, W. (1990). A common coding approach to perception and action. In Relationships between perception and action (pp. 167–201). Springer.
Ralph, M. A. L., Jefferies, E., Patterson, K., & Rogers, T. T. (2017). The neural and computational bases of semantic cognition. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 18(1), 42–55.
Rolls, E. T. (2013). The mechanisms for pattern completion and pattern separation in the hippocampus. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 7, 74.
Rolls, E. T., & Kesner, R. P. (2006). A computational theory of hippocampal function, and empirical tests of the theory. Progress in Neurobiology, 79(1), 1–48.
Rosenbaum, R. S., Moscovitch, M., Foster, J. K., Schnyer, D. M., Gao, F., Kovacevic, N., & Levine, B. (2008). Patterns of autobiographical memory loss in medial-temporal lobe amnesic patients. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 20(8), 1490–1506.
Rosenbaum, R. S., Murphy, K. J., & Rich, J. B. (2012). The amnesias. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science, 3(1), 47–63.
Ryan, J. D., Moses, S. N., Barense, M., & Rosenbaum, R. S. (2013). Intact learning of new relations in amnesia as achieved through unitization. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(23), 9601–9613.
Slamecka, N. J., & Graf, P. (1978). The generation effect: Delineation of a phenomenon. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Learning and Memory, 4(6), 592.
Squire, L. R. (1992). Memory and the hippocampus: A synthesis from findings with rats, monkeys, and humans. Psychological Review, 99(2), 195.
Stamenova, V., Nicola, R., Aharon-Peretz, J., Goldsher, D., Kapeliovich, M., & Gilboa, A. (2018). Long-term effects of brief hypoxia due to cardiac arrest: Hippocampal reductions and memory deficits. Resuscitation, 126, 65–71.
Squire, L. R., & Zola, S. M. (1996). Structure and function of declarative and nondeclarative memory systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 93(24), 13515–13522.
Tran, S. H., Beech, I., & Fernandes, M. A. (2022). Drawing compared to writing in a diary enhances recall of autobiographical memories. Aging, Neuropsychology, and Cognition, 1–17.
Tulving, E. (1983). Elements of episodic memory.
Vann, S. D., Tsivilis, D., Denby, C. E., Quamme, J. R., Yonelinas, A. P., Aggleton, J. P., & Mayes, A. R. (2009). Impaired recollection but spared familiarity in patients with extended hippocampal system damage revealed by 3 convergent methods. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106(13), 5442–5447.
Waidergoren, S., Segalowicz, J., & Gilboa, A. (2012). Semantic memory recognition is supported by intrinsic recollection-like processes: “The butcher on the bus” revisited. Neuropsychologia, 50(14), 3573–3587.
Wammes, J. D., Jonker, T. R., & Fernandes, M. A. (2019). Drawing improves memory: The importance of multimodal encoding context. Cognition, 191, 103955.
Wammes, J. D., Meade, M. E., & Fernandes, M. A. (2016). The drawing effect: Evidence for reliable and robust memory benefits in free recall. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 69(9), 1752–1776.
Wammes, J. D., Meade, M. E., & Fernandes, M. A. (2018). Creating a recollection-based memory through drawing. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 44(5), 734.
Wing, E. A., Burles, F., Ryan, J. S., & Gilboa, A. (2022). The structure of prior knowledge enhances memory in experts by reducing interference Proceedings of the National Academy for Sciences of the USA.
Wilson, M. (1988). MRC psycholinguistic database: Machine-usable dictionary, version 2.00. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers, 20(1), 6–10.
Yassa, M. A., & Stark, C. E. (2011). Pattern separation in the hippocampus. Trends in Neurosciences, 34(10), 515–525.
Yonelinas, A. P., Kroll, N. E., Dobbins, I., Lazzara, M., & Knight, R. T. (1998). Recollection and familiarity deficits in amnesia: Convergence of remember-know, process dissociation, and receiver operating characteristic data. Neuropsychology, 12(3), 323.
Zaiser, A. K., Bader, R., & Meyer, P. (2022a). High feature overlap reveals the importance of anterior and medial temporal lobe structures for learning by means of fast mapping. Cortex, 146, 74–88.
Zaiser, A. K., Meyer, P., & Bader, R. (2022b). High feature overlap and incidental encoding drive rapid semantic integration in the fast mapping paradigm. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 151(1), 97.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Patricia Aguiar for her assistance in data collection.
Funding
This study was funded by the Ontario Graduate Scholarship (OGS) to A.L., by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada discovery grant #378291 to A.G, and discovery grant #03917 to M.F., as well as by Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) grant #PJT175159 to A.G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
No conflicts of interest were reported by the authors.
Ethics approval
Approval was obtained from the Research Ethics Board at the Rotman Research Institute at Baycrest Hospital. The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
All participants signed informed consent regarding publishing their data from this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
A. Levi and A. Pugsley are co-first authors
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Levi, A., Pugsley, A., Fernandes, M.A. et al. Drawing improves memory in patients with hippocampal damage. Mem Cogn (2024). https://doi.org/10.3758/s13421-023-01505-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3758/s13421-023-01505-4