- 1Department of Breast Surgery, Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 2School of Artificial Intelligence, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing, China
- 3Breast Disease Prevention and Treatment Center, Haidian Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Beijing, China
- 4Department of Breast Surgery, The Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
- 5Department of General Surgery , Beijing Huairou Hospital, Beijing, China
- 6Department of Breast Surgery, Beijing Yanqing District Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital, Beijing, China
- 7Department of General Surgery, Beijing Pinggu Hospital, Beijing, China
Objective: As a common breast cancer-related complaint, pathological nipple discharge (PND) detected by ductoscopy is often missed diagnosed. Deep learning techniques have enabled great advances in clinical imaging but are rarely applied in breast cancer with PND. This study aimed to design and validate an Intelligent Ductoscopy for Breast Cancer Diagnostic System (IDBCS) for breast cancer diagnosis by analyzing real-time imaging data acquired by ductoscopy.
Materials and methods: The present multicenter, case-control trial was carried out in 6 hospitals in China. Images for consecutive patients, aged ≥18 years, with no previous ductoscopy, were obtained from the involved hospitals. All individuals with PND confirmed from breast lesions by ductoscopy were eligible. Images from Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital were randomly assigned (8:2) to the training (IDBCS development) and internal validation (performance evaluation of the IDBCS) datasets. Diagnostic performance was further assessed with internal and prospective validation datasets from Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital; further external validation was carried out with datasets from 5 primary care hospitals. Diagnostic accuracies, sensitivities, specificities, and positive and negative predictive values for IDBCS and endoscopists (expert, competent, or trainee) in the detection of malignant lesions were obtained by the Clopper-Pearson method.
Results: Totally 11305 ductoscopy images in 1072 patients were utilized for developing and testing the IDBCS. Area under the curves (AUCs) in breast cancer detection were 0·975 (95%CI 0·899-0·998) and 0·954 (95%CI 0·925-0·975) in the internal validation and prospective datasets, respectively, and ranged between 0·922 (95%CI 0·866-0·960) and 0·965 (95%CI 0·892-0·994) in the 5 external validation datasets. The IDBCS had superior diagnostic accuracy compared with expert (0.912 [95%CI 0.839-0.959] vs 0.726 [0.672-0.775]; p<0.001), competent (0.699 [95%CI 0.645-0.750], p<0.001), and trainee (0.703 [95%CI 0.648-0.753], p<0.001) endoscopists.
Conclusions: IDBCS outperforms clinical oncologists, achieving high accuracy in diagnosing breast cancer with PND. The novel system could help endoscopists improve their diagnostic efficacy in breast cancer diagnosis.
Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) accounts for 24.2% of all cancers diagnosed in women worldwide, constituting the first female cancer (1). Pathological nipple discharge (PND) represents a common BC-related complaint (2). Compared to other imaging methods such as sonography, mammography and MRI, ductoscopy is currently the only intuitive and effective technique for clinical screening and diagnosis of BC because it allows for direct visualization of intraductal lesions that cause PND (3). Meanwhile, ductoscopy solves the problem of intraductal lesion localization and reduces the scope of surgery in most PND cases. Additionally, some surgical indications for PND have been revised, avoiding unnecessary surgery in some patients. However, early BC with PND often lacks typical endoscopic features leading to a missed diagnosis. Besides, intraductal biopsy under ductoscopy makes it difficult to diagnose the tumor histologically without surgery (4). On the other hand, there is a huge deficit of endoscopists in China, whose number is far from meeting the actual clinical needs. In addition, endoscopists in different levels of hospitals have distinct levels of expertise. As a result, there is a low detection rate for breast cancer with PND, which seriously affects the prognosis and aggravates the economic pressure on patients.
Deep-leaning (DL) methods have been utilized more commonly compared with other traditional machine-learning techniques (5). DL approaches have an outstanding capability of retracting visual properties of objects, even those not detectable by humans, and quickly analyzing large datasets (6, 7). DL-based approaches are increasingly applied to real-time computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems in gastrointestinal endoscopy (8–10). Mounting evidence reveals advantages for DL CAD models in detecting and characterizing diverse cancerous tumors (11, 12), at all levels of the gastrointestinal tract (13). To improve the diagnosis of intraductal lesions, especially BC, by ductoscopy, we aim to design tools that enhance real-time detection of intraductal cancers, providing guidance utilizing a pre-trained deep learning algorithm.
In this work, a deep learning model was designed for BC detection based on a fully convolutional network, called the Intelligent Ductoscopy for Breast Cancer Diagnostic System (IDBCS). The IDBCS and oncologists were comparatively assessed for diagnostic performance in internal test and prospective sets based on endoscopic images in patients administered routine ductoscopy screening for pathological nipple discharge. The IDBCS was next validated in other external validation sets in five municipal hospitals. The current study demonstrated that IDBCS had encouraging performance in distinguishing cancerous lesions. The novel IDBCS-based artificial intelligence platform could yield higher malignancy detection rates, thus improving patient survival.
Methods
Study design and patients
The present multicenter, case-control, diagnostic trial was carried out in 6 hospitals in China. Endoscopic images were retrospectively retrieved for the design and validation of an Intelligent Ductoscopy for Breast Cancer Diagnostic System (IDBCS) from the imaging database of Beijing Chao-Yang hospital (BCYH) between January 2018 and December 2020.
To generalize IDBCS applicability in clinic, endoscopic images were also retrieved from 5 municipal/provincial hospitals in China, including Beijing Haidian District Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital (HDH), the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University (DLH), Beijing Huairou Hospital (HRH), Beijing Pinggu Hospital (PGH), and Beijing Yanqing District Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital (YQH).
All images were acquired at high-resolution but utilizing multiple endoscopes (FVY-680, Blade, China; Schoelly, German) and saved as jpeg files. Five endoscopists at BCYH, with at least 5 years of experience and >500 examinations performed, evaluated the image quality.
Inclusion criteria were: 1) PND with unilateral single duct; 2) postoperative histopathology; 3) complete baseline data, including age, duration of PND, characteristics of PND, color of nipple fluid, lesion base, intraductal location and morphology of tumor, and palpable mass; 4) ductoscopy carried out for pretreatment examination; 5) ductoscopy images with standard white light.
Exclusion criteria were: 1) PND during pregnancy or lactation; 2) incomplete postsurgical pathological data; 3) poor quality ductoscopy images such as narrow-band imaging, motion-blurring, blank and out-of-focus; 4) PND manifested as multiple ducts.
The present trial had approval from the respective institutional review boards of various participating hospitals, and followed the Helsinki declaration. Each patient assessed in the prospective validation dataset (BCYH) provided signed informed consent prior to enrolment. In individuals with endoscopic images stored in retrospective databases at various participating hospitals, the requirement for informed consent was waived by the respective institutional review boards.
Development of the IDBCS algorithm
Dataset
Images from Chaoyang Hospital were divided into training and internal validation datasets according to a ratio of 8:2. To better train the AI model, image augmentation methods (14), e.g., horizontal and vertical flipping, were adopted. The training dataset was employed for model training, and the internal validation dataset was utilized to evaluate the model’s performance.
Overview
The IDBCS algorithm was developed based on a deep Convolutional Neural Network (15) (CNN), and achieved patient-level diagnosis using a voting mechanism. Specifically, the IDBCS algorithm consists of two stages. In the first stage, multiple images from the same patient are fed into the backbone (DenseNet) to obtain a series of positive probability scores. In the second stage, the model uses a voting mechanism where the positive probability scores of all images are averaged to obtain an average score, and when the average score exceeds a threshold, the patient is classified as positive.
Backbone
During the development of the IDBCS algorithm, we applied four deep learning models, including VGG (16), Inception-v3 (17), ResNet (18), and DenseNet (19), which were all trained using the same dataset. DenseNet had the best performance in the validation dataset. Therefore, DenseNet was selected to develop IDBCS. DenseNet consists of multiple dense blocks and connects each layer to the others by feed-forward. In DenseNet, every layer takes supplemental input from the previous layers and transmits the extracted features to following layers. Thus, every layer can receive collective knowledge from the previous ones. The DenseNet structure solves the problem of vanishing gradient during the training process, reduces the number of parameters, and improves the inference speed while ensuring high performance, which matches the real-time diagnosis characteristics of IDBCS. (Figure 1).
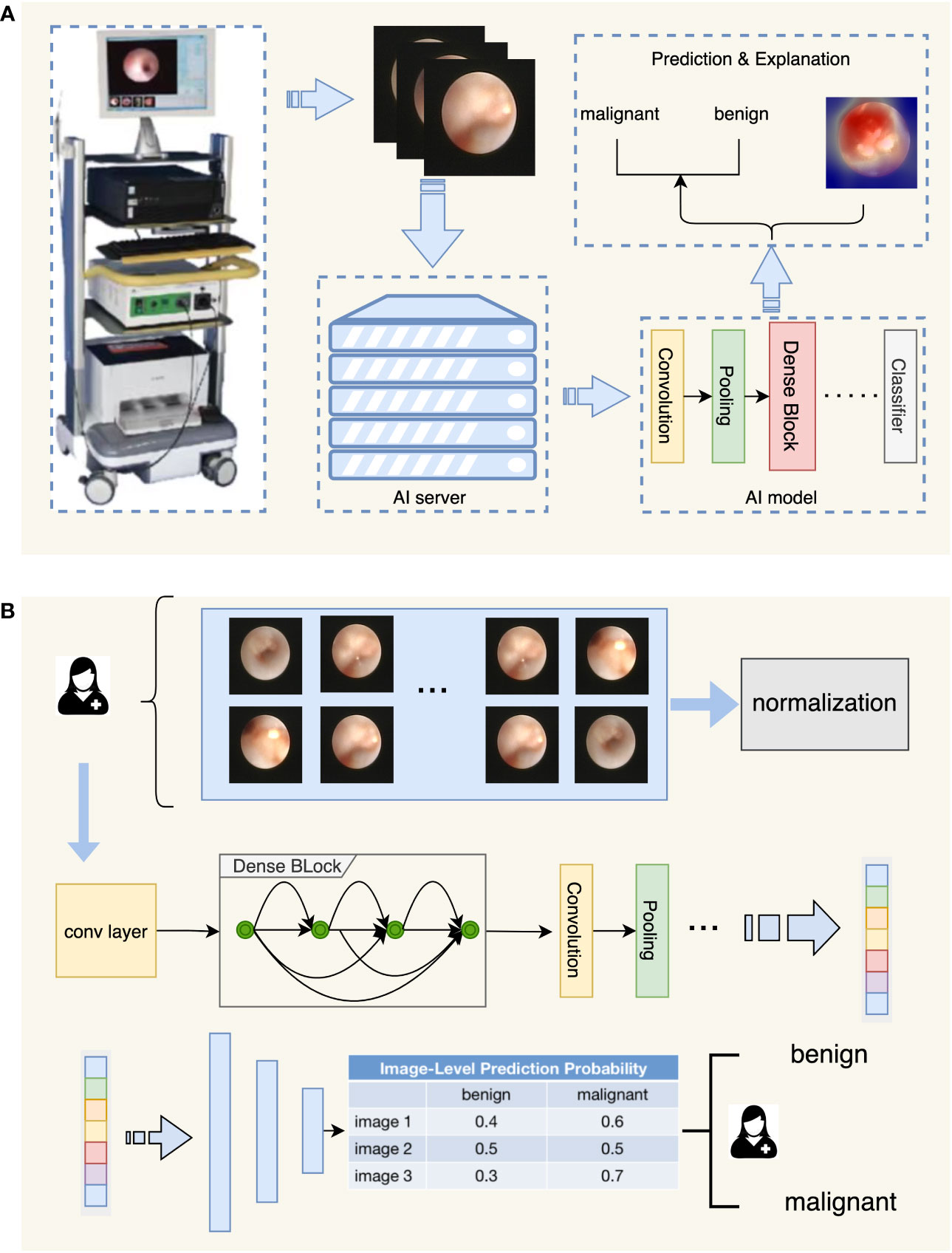
Figure 1 Flowchart depicting the diagnostic process of IDBCS. Part (A) in this figure shows the whole process of automatic diagnosis of ductoscopy images. The image obtained by the ductoscopy machine is transmitted to the server containing the AI algorithm in real-time, and the result is given after the automatic diagnosis of the AI algorithm, and the corresponding explanation is given for the diagnosis result. Part (B) in this figure shows the model structure of the diagnosing algorithm. Ductoscopy images were normalized first and then fed into the DenseNet model. DenseNet contains several Dense Blocks and calculates features of the input images. The output features were fed into the classifier with a voting mechanism and the diagnosing result was given.
Training
For each ductoscopy image, we scale the image to 224 pixels in length and width, and normalize the image with a mean set to [0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465], variance set to [0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010]. We train the model on Tesla T4 GPU with the learning rate set to 0.01 and the batch size set to 32.
Validation of the IDBCS algorithm
We first used the internal validation and prospective datasets retrieved from Chaoyang Hospital to preliminarily assess the model’s performance. To further assess the model’s robustness and generalization, 5 external validation datasets from different hospitals were utilized for model testing.
For performance comparison between IDBCS and endoscopists, we invited 3 experts, 3 competent, and 3 trainees to diagnose 102 patients in the prospective Chaoyang dataset. Before the diagnosis, all 9 doctors had no information about the dataset to ensure the authenticity of the experiment.
Statistical analysis
Diagnostic accuracy (ACC), sensitivity (SENS), specificity (SPEC), positive (PPV) and negative (NPV) predictive values, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic (20) (ROC) curve (AUC) were determined to evaluate the performance of the IDBCS in breast ductal tumor diagnosis.
All the metrics are calculated based on patient-level malignant probability according to the following equation.
where p1,p2,…,pn are the malignant probability of all the images from the same patient. All the metrics are calculated according to the following equations.
where TP, TN, FP, and FN represent true positives, true negatives, false positives, and false negatives, respectively.
For the comparison of IDBCS and endoscopists for diagnostic performance, we collected the diagnostic results of expert, competent and trainee endoscopists. According to these diagnostic results, ACC, SENS, SPEC, PPV and NPV were calculated to assess the difference in diagnostic performance between IDBCS and endoscopists. Meanwhile, all statistics were two-sided, and 95% confidence intervals for various metrics were determined by the Bootstrap method (21). All continuous variables were compared by the t-test. All statistical analyses were performed with the MedCalc software (22) and python 3.7.
Results
Baseline features of the training and test datasets
Between January 1, 2018, and December 31, 2020, 456 patients were treated at BCYH (Figure 2). Due to unknown pathological diagnosis and incomplete pathological data, 107 patients were excluded. Following quality control, 8033 images were excluded as tumor-free or poor-quality images. For cancer cases, only the images of cancerous tumors were examined (n=1552); for those with no malignancy, 1720 images were utilized as controls (Figure 2). In the prospective validation dataset, 151 cancerous tumors and 360 control images were prospectively obtained between January 1, 2021, and December 31, 2021.
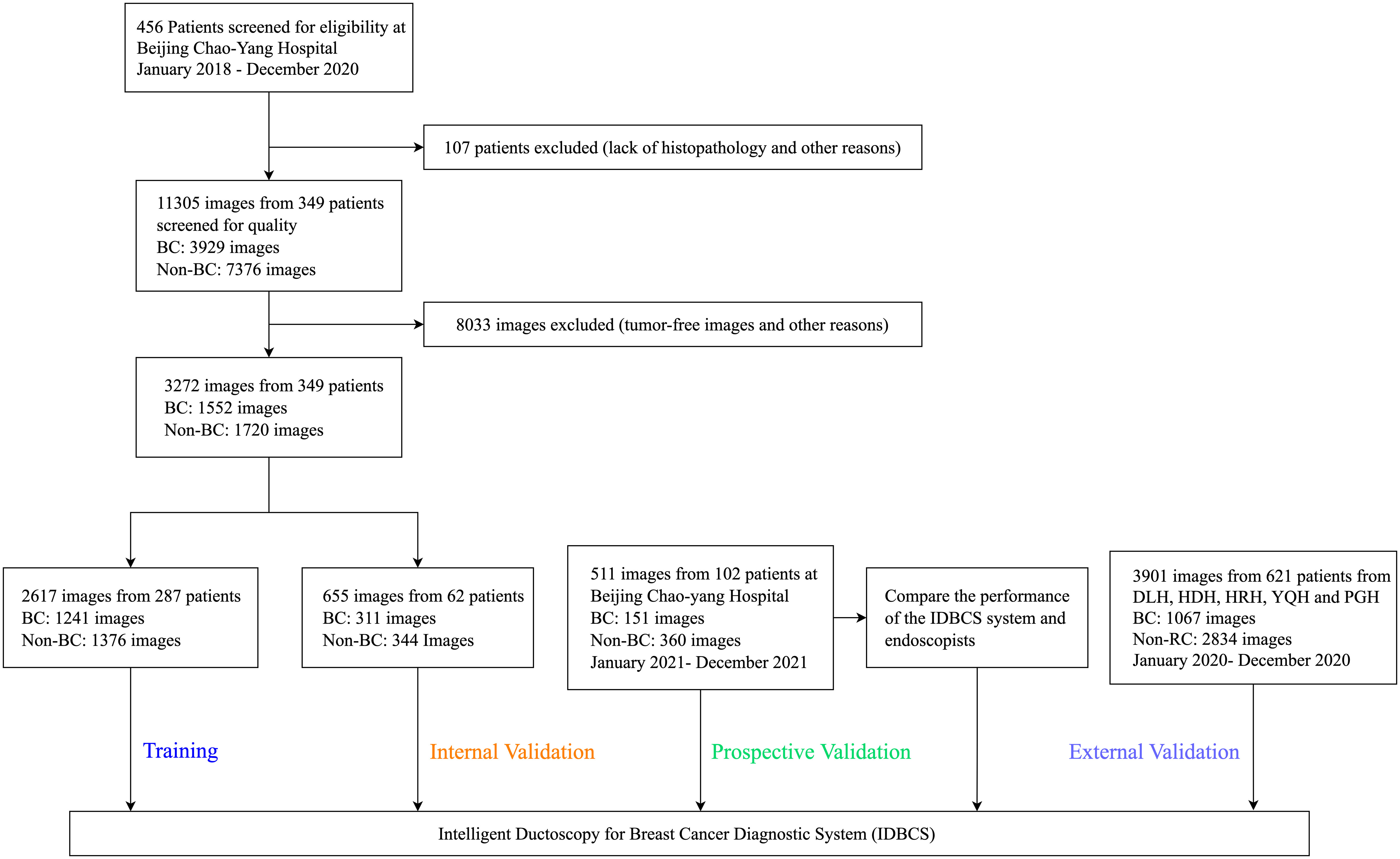
Figure 2 Flowchart for the development and validation of the IDBCS system for diagnosing breast cancer with pathological nipple discharge.
At the other five participating hospitals, between January 1, 2020, and December 31, 2020, 793 cancer and 242 control images were obtained from DLH, 902 cancer and 400 control images from HDH, 583 cancer and 276 control images from HRH, 185 cancer and 50 control images from YQH, and 371 cancer and 99 control images from PGH. Overall, 7684 ductoscopy images in 1072 participants were utilized for IDBCS development and testing.
BC prevalence rates were 26.8% (77/287) in the training dataset, 29.0% (18/62) in the internal validation dataset, 31.4% (32/102) in the prospective validation dataset, 27.7% (41/148) in DLH, 34.1% (73/214) in HDH, 26.7% (32/120) in HRH, 22.4% (15/67) in YQH, and 23.6% (17/72) in PGH (Table 1).
In the training set, bloody PND accounted for 35.1% (27/77) in the BC patient group versus 13.3% (28/210) in control patients (p<0.001). Ages were 46 (23-85) and 43 (19-80) years in the BC and control groups, respectively. Compared with non-BC patients, PND colors in BC patients were: colorless (n=2 vs. n=51), yellow (n = 48 vs. n=131), brown (n = 17 vs. n=18), and red (n = 10 vs. n=10) (p<0.001). There were 16.9% BC patients with palpable masses, whereas 5.2% of patients with palpable masses were pathologically proven as non-BC (p=0.002) (Table 1). In addition, irregular lesions that were visible by ductoscopy accounted for 57.1% (44/77) in the BC patient group versus 32.4% (68/210) in control patients (p<0.001). The detailed baseline characteristics in other test datasets and a study flowchart are shown in Table 1 and Figure 2, respectively.
Diagnostic performance of IDBCS
In order to identify the most suitable base model for breast cancer diagnosis, the performances of Resnet, DenseNet, Inception and VGG were compared. Finally, we trained and assessed the performance of DenseNet as the best model in all seven validation sets (Supplemental Figure 1). We found that the Intelligent Ductoscopy for Breast Cancer Diagnostic System (IDBCS) had high performance in identifying BC patients. In internal and prospective BCYH validation datasets, diagnostic accuracies were 88.7% and 91.2%, respectively. In external validation datasets, accuracies were 84.2% for HDH, 86.6% for YQH, 87.8% for DLH, 89.7% for HRH, and 90.3% for PGH. The sensitivity and specificity of the novel IDBCS were >80% in the totality of validation datasets; its NPVs were higher than 90%, and PPVs were 66.7-76.7% (Table 2). IDBCS’ specificity and PPV were the lowest in DLH among all validation datasets. Elevated AUCs (0.922-0.965) suggested a great diagnostic performance for the IDBCS in the five validation datasets (Figure 3).
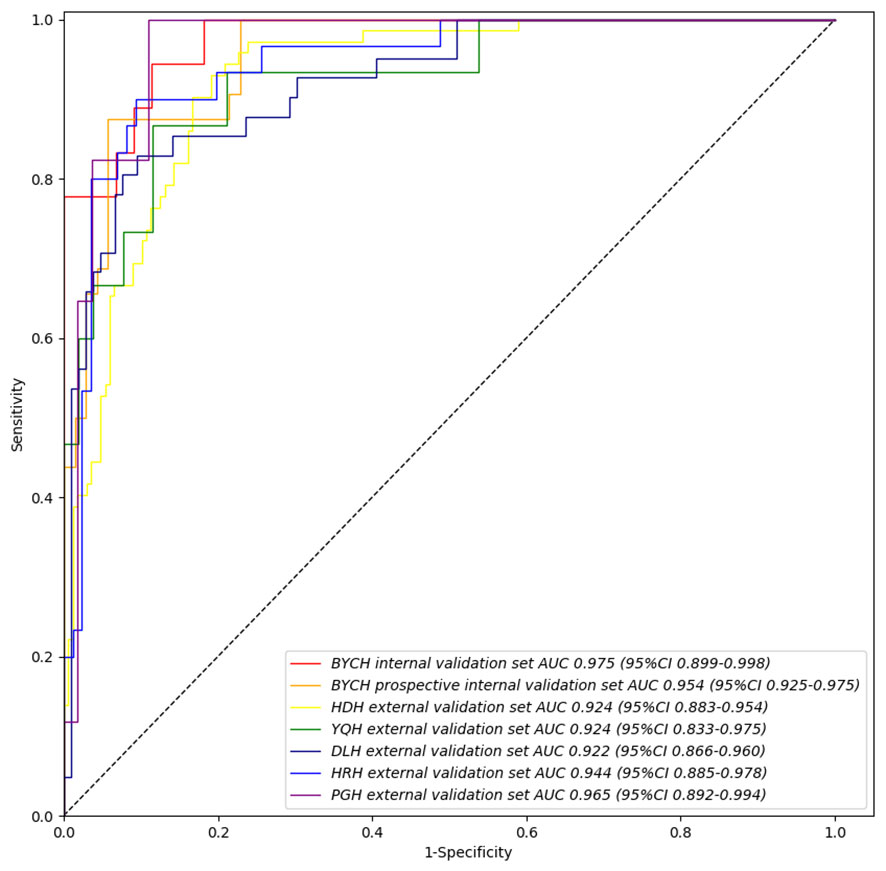
Figure 3 IDBCS’s performance on different validation datasets. The datasets contain BCYH internal validation set, BCYH prospective internal validation set, HDH external validation set, YQH external validation set, DLH external validation set, HRH external validation set, and PGH external validation set. The ROC curve and AUC were all calculated on the patient level, which has been clarified in equation (1).
Furthermore, this model was extended to be compatible with two groups of tasks for cancer subtype prediction. The numbers of lesions in the two categories were 170 (ductal carcinoma in situ, DCIS) and 40 (invasive breast carcinoma, IBC), respectively. The overall accuracies in differentiating the two groups ranged from 50.0% to 70.3% in all validation datasets (Supplemental Figure 2). The model performed well in distinguishing benign from malignant tumors, while showing lower potential in differentiating cancer subtypes (DCIS vs. IBC).
Performance of IDBCS versus endoscopists
Table 3 summarizes the results of the IDBCS and 9 endoscopists for differentiating between 511 (151 [29.5%] cancer and 360 [70.5%] control images) in the prospective validation dataset. IDBCS detected BC with an accuracy of 0.912 (95%CI 0.839-0.959). In comparison, expert endoscopists had markedly reduced accuracy (0·726, 95%CI 0.672-0.775; p<0.001), as well as competent endoscopists (0.699, 95%CI 0.645-0.750; p<0.001) and trainee endoscopists (0.702, 95%CI 0.648-0.753; p<0.001). Moreover, there was no statistical difference in specificities. However, sensitivities, PPVs and NPVs for all three categories of endoscopists were significantly lower than those of IDBCS (p<0.001).
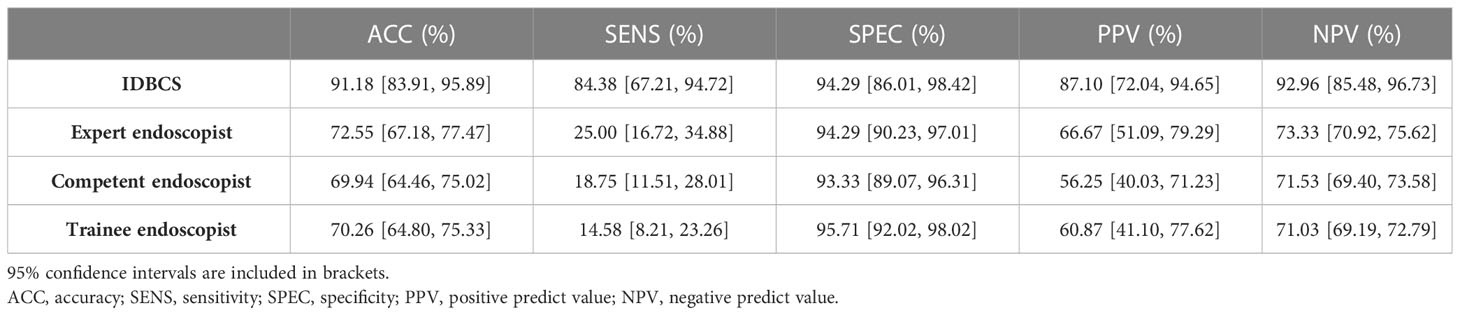
Table 3 Performance of IDBCS versus human endoscopists in identifying breast cancer in a randomly selected subset of patients (n=102) from the prospective validation group.
Among endoscopists, expert endoscopists had significantly higher sensitivity than the competent (0.250, 95%CI 0.167-0.349 vs. 0.188, 95%CI 0.115-0.280; p<0.001) and trainee (0.146, 95%CI 0.082-0.233; p<0.001) endoscopist groups. Other diagnostic indicators such as accuracy, specificity, PPV and NPV were similar among these endoscopist groups. Here we also attached our model and the data of previous articles for comparison in Supplemental Table 1.
Visual explanation of the decision made by the IDBCS
To investigate IDBCS interpretability, we used the Score-CAM (23) algorithm to identify important regions on a single tumor image that supports the algorithm’s decision. The heatmap in Figure 4 highlights the important regions in red and the less important ones in blue. In the heatmaps, the important regions in malignant tumors were often accompanied by hemorrhage. Therefore, we designed a study to further investigate the correlation between hemorrhage and IDBCS interpretability. According to the study results, the average intersection over union (IoU) value between the areas of malignant tumors and those of hemorrhage was 0.598, which was higher than the average IoU (0.175, p<0.001) in benign intraductal lesions.
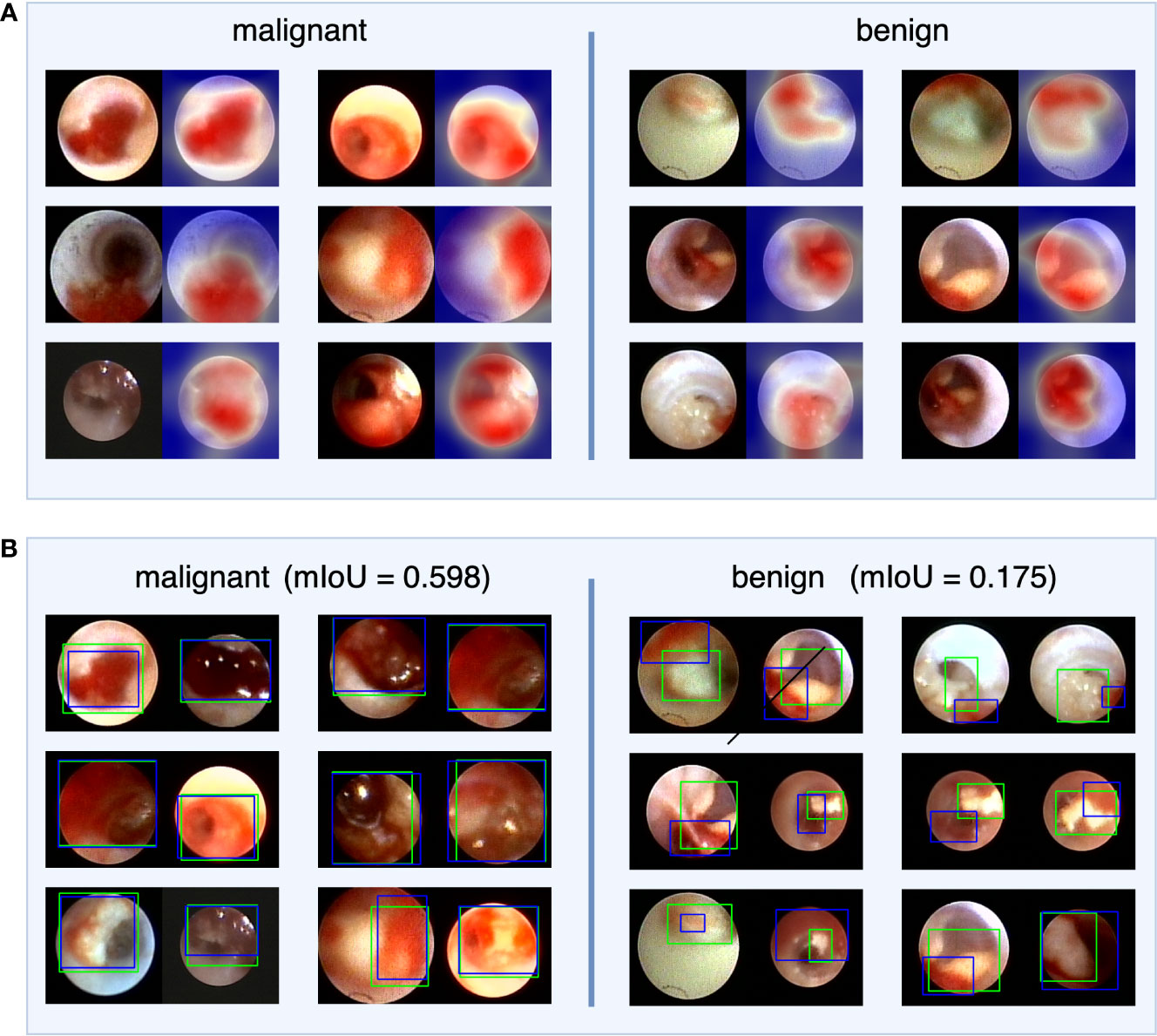
Figure 4 The visual explanation of IDBCS. The part (A) of this figure shows the decision-supported regions. For each image pair, the left image is the original ductoscopy image and the right image is the heatmap. In the heatmap, the red regions are the important regions that support the diagnosing result of IDBCS. In part (B) of this figure, the blue rectangle represents the annotated hemorrhage area and the green rectangle represents the decision-supported area. As we can see in this figure, the decision-supported area and the hemorrhage area has a higher mIoU in malignant tumors. This phenomenon means that the hemorrhage is an important reason for malignant tumor diagnosing.
Diagnosing system based on IDBCS
The developed IDBCS with DenseNet was able to analyze and process as many as 31 images per second (32ms per image) on average for real-time ductoscopy diagnosis using Nvidia Tesla T4 GPU. We also test the diagnosing speed of IDBCS under the other backbones: VGG (250 images per second), ResNet (70 images per second), and Inception (43 images per second). Our IDBCS can meet real-time requirements under all the above four backbones. Although the diagnosing speeds under VGG, ResNet and Inception are faster, IDBCS with DenseNet can achieve higher diagnostic accuracy. In addition, we apply the IDBCS algorithm to the current ductoscopy system. Specifically, the ductoscopy images were transmitted to our computing server and then the diagnosing result given by IDBCS will be shown on the monitor in real-time. The demo video in our supplementary file shows an example of IDBCS real-time diagnosing.
Discussion
Here, a deep learning model was utilized for constructing an artificial intelligence-based BC diagnostic system, termed IDBCS, which was trained and validated with 11305 endoscopy images acquired in 1072 individuals in 6 hospitals with diverse experiences and amounts of pathological nipple discharge cases. The IDBCS had high accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity for BC detection in retrospective and prospective observational settings. This study first performed artificial intelligence-guided breast cancer detection according to PND endoscopic images. We demonstrated that the IDBCS was superior to endoscopists in differentiating malignancy from benignity for intraductal tumors. Additionally, an evidence-based visual explanation derived from the IDBCS was provided, which may be used routinely in the clinic.
PND is one of the three major symptoms of breast disease. Malignancy rates between 1% and 23% have been reported in PND cases (24). To characterize PND, mammography and ultrasonography are frequently employed, but the results are often negative (25). Moreover, breast MRI does not add much (26). Furthermore, galactography and cytological analysis of nipple discharge have low sensitivities, and generally do not identify the associated pathology (27). Currently, ductoscopy that visualizes intraductal lesions as a minimally invasive procedure is the most commonly utilized imaging modality for evaluating PND. However, the learning curve of ductoscopy is long, and its routine use in PND cases is limited in clinic. A recent meta-analysis (28) showed pooled sensitivity and specificity for ductoscopy of 50% (36-64%) and 83% (81-86%), respectively, which is similar to the detection ability of endoscopists in this study. Therefore, novel tools for helping endoscopists differentiate benign tumors from cancerous ones on ductoscopy images are urgently needed.
DL methods have been predominantly utilized for image processing. An advantage of DL models is the possibility of immediate and consistent data reporting, thus reducing the workload, as well as inconsistencies, and misdiagnoses. Additionally, it overcomes the inherent limitations of doctors, including perceptual bias and visual fatigue (29). Besides, the DL model-associated visual display further provides evidence-based classification to help endoscopists interpret the images. Recently, DL has been broadly employed in endoscopy. Previously published reports have developed DL models based on gastroscopy and colonoscopy images for identifying gastrointestinal tumors (10–12). Li Caofeng et al. developed an endoscopic image-based nasopharyngeal cancer detection model to diagnose nasopharyngeal cancer (30). In this study, the IDBCS was designed for visual diagnosis of breast cancer including the largest amount of ductoscopy images from routine white-light imaging methods.
The IDBCS could decrease the reliance upon the endoscopists’ expertise for visual breast cancer diagnosis and increase diagnostic consistency. A strength of this work is that it included diverse noncancerous pathologies (i.e., intraductal papilloma, inflammation, and ductal hyperplasia) in the control group and utilized pathological assessment as the gold standard. Consequently, IDBCS could learn noncancerous properties that usually complicate breast cancer diagnosis, likely enhancing model performance and avoiding verification bias. The IDBCS underwent training and fine-tuning with multiple images acquired in individuals diagnosed at our center over 3 years, with encouraging performance in a short learning time, indicating IDBCS ‘learns’ efficiently and has high productivity. The overall accuracy of the novel IDBCS system was 91.2%, which surpasses the value reported for endoscopists’ diagnosis (31, 32). At our center, the IDBCS system also had markedly elevated accuracy and specificity compared with endoscopists at various levels of expertise. The above findings suggest the IDBCS system has great potential for improving the diagnosis of breast cancer with PND.
Retrospective trials have assessed the association between nipple discharge and BC. Ye Han (33) reported the endoscopic characteristics of bloody discharge, morphology and a wide tumor base independently predict breast cancer with PND. A meta-analysis (34) showed that bloody nipple discharge is a predictive factor of BC risk among diverse discharge colors. However, few reports focused on the interpretability between bloody nipple discharge and BC risk. In the current study, the important regions of malignant tumors were often accompanied by hemorrhage based on the Score-CAM algorithm. To our knowledge, marked redness could be associated with dilated tumor vessels, and the abrupt rupture and necrosis of the local tissue are associated with tumor-induced fibrosis. Currently, IDBCS is included in the routine endoscopic workflow with real-time evaluation at BCYH, providing free-access to deep learning-aided breast cancer screening and diagnosis.
There were several limitations in this study. Firstly, the number of enrolled participants was not large. To overcome this limitation of small sample size, extensive data augmentation was carried out in model training. In addition, the proposed model can only differentiate malignant tumors from benign ones. Although two BC types were included, i.e., ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive BC, the overall accuracy of the model in differentiating them was poor due to their small sample sizes. Future investigation will expand the new model to further determine whether the malignant lesions detected are DCIS or IBC. Furthermore, the training and test datasets mostly included northern Chinese cases, and IDBCS’ performance in other ethnicities is unknown. Finally, other clinical data, e.g., age, PND characteristics and tumor morphology were not considered. Therefore, a multi-source imaging diagnosis model should be established for clinical application in breast cancer detection based on deep learning.
Overall, an efficient real-time AI system using ductoscopy images was developed for breast cancer detection in the real world. The IDBCS system had excellent performance in BC detection in independent validation datasets. However, since this study was limited by a poor diagnostic value for different BC subtypes, multicenter prospective validation with larger datasets is warranted for high-level evidence in breast cancer subtype analysis.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
FX, CZhu, JLiu, and HJ contributed to the study concept and design. ZW, LZ, HG, ZM, YGa, YGu, and XL contributed to acquisition of data. YZL, ML, GS, HL, YSL, CZha, JC, JLi, JLiu, and HJ contributed to analysis and interpretation of data. All authors contributed to writing, reviewing, and approval of the final version of this work.
Funding
This study was supported by the General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 62176167) and Beijing Hospitals Authority Youth Programme, code: QML20210305.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2023.1103145/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Video 1 | Instruction of IDBCS real-time diagnostic video. This video shows the real-time diagnostic process of IDBCS. The diagnostic results are marked in the upper left corner of the video, with 0 for benign tumor and 1 for malignant tumor. In this video, all tumors appeared are benign. They appeared at seconds 11, 18, 21, 24, 54, and 84 of the video, and were all successfully diagnosed by the algorithm.
References
1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin (2018) 68(6):394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492
2. Xu F, Gao Y, Diao X, Li J, Jiang H, Zhao H. Diagnostic value of sialyl-tn immunocytochemistry in breast cancer presenting with pathological nipple discharge. Cancer Med (2021) 10(5):1783–90. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3793
3. Filipe MD, Patuleia SIS, de Jong VMT, Vriens MR, van Diest PJ, Witkamp AJ. Network meta-analysis for the diagnostic approach to pathologic nipple discharge. Clin Breast Cancer (2020) 20(6):e723–e48. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2020.05.015
4. Hünerbein M, Dubowy A, Raubach M, Gebauer B, Topalidis T, Schlag P. Gradient index ductoscopy and intraductal biopsy of intraductal breast lesions. Am J Surg (2007) 194(4):511–4. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.07.001
5. Le EPV, Wang Y, Huang Y, Hickman S, Gilbert FJ. Artificial intelligence in breast imaging. Clin Radiol (2019) 74(5):357–66. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2019.02.006
6. Ahamed KU, Islam M, Uddin A, Akhter A, Paul BK, Yousuf MA, et al. A deep learning approach using effective preprocessing techniques to detect COVID-19 from chest CT-scan and X-ray images. Comput Biol Med (2021) 139(105014):1–19. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.105014
7. Hossain U, Rahman A, Islam M, Akhter A, Uddin A, Paul BK. Automatic driver distraction detection using deep convolutional neural networks. Intelligent Syst Applications (2022) 14:200075. doi: 10.1016/j.iswa.2022.200075
8. Luo H, Xu G, Li C, He L, Luo L, Wang Z, et al. Real-time artificial intelligence for detection of upper gastrointestinal cancer by endoscopy: A multicentre, case-control, diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol (2019) 20(12):1645–54. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30637-0
9. Zhou D, Tian F, Tian X, Sun L, Huang X, Zhao F, et al. Diagnostic evaluation of a deep learning model for optical diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Nat Commun (2020) 11(1):2961. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16777-6
10. Ueyama H, Kato Y, Akazawa Y, Yatagai N, Komori H, Takeda T, et al. Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for diagnosis of early gastric cancer based on magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging. J Gastroenterol Hepatol (2021) 36(2):482–9. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15190
11. Zhu Y, Wang QC, Xu MD, Zhang Z, Cheng J, Zhong YS, et al. Application of convolutional neural network in the diagnosis of the invasion depth of gastric cancer based on conventional endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc (2019) 89(4):806–15e1. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2018.11.011
12. Wang P, Xiao X, Glissen Brown JR, Berzin TM, Tu M, Xiong F, et al. Development and validation of a deep-learning algorithm for the detection of polyps during colonoscopy. Nat Biomed Eng (2018) 2(10):741–8. doi: 10.1038/s41551-018-0301-3
13. Tang D, Wang L, Ling T, Lv Y, Ni M, Zhan Q, et al. Development and validation of a real-time artificial intelligence-assisted system for detecting early gastric cancer: A multicentre retrospective diagnostic study. EBioMedicine (2020) 62:103146. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103146
14. Chlap P, Min H, Vandenberg N, Dowling J, Holloway L, Haworth A. A review of medical image data augmentation techniques for deep learning applications. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol (2021) 65(5):545–63. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.13261
15. LeCun Y, Bottou L. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE (1998) 86(11):2278–324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791
16. Simonyan K, Zisserman A. (2015). Very deep convolutional networks for Large-scale image recognition, in: International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), IEEE, Canada. pp. 1–14.
17. Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z. (2016). Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision, in: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, IEEE, USA. pp. 2818–26.
18. He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition, in: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, IEEE, USA. pp. 770–8.
19. Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten L, Weinberger KQ. (2017). Densely connected convolutional networks, in: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, IEEE, USA. pp. 4700–8.
20. Fawcett T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern recognition Lett (2006) 27(8):861–74. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
21. DiCiccio TJ, Efron B. Bootstrap confidence intervals. Stat Sci (1996) 11(3):189–228. doi: 10.1214/ss/1032280214
22. Schoonjans F, Zalata A, Depuydt CE, Comhaire FH. MedCalc: A new computer program for medical statistics. Comput Methods Programs Biomed (1995) 48(3):257–62. doi: 10.1016/0169-2607(95)01703-8
23. Wang H, Wang Z, Du M, Yang F, Hu X. (2020). Score-CAM: Score-weighted visual explanations for convolutional neural networks, in: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, IEEE, virtual. pp. 24–5.
24. Paterok EM, Rosenthal H, Sabel M. Nipple discharge and abnormal galactogram. results of a long-term study (1964-1990). Eur J obstetrics gynecology Reprod Biol (1993) 50(3):227–34. doi: 10.1016/0028-2243(93)90205-Q
25. Boisserie-Lacroix M, Doutriaux-Dumoulin I, Chopier J, Boyer B, Depetiteville MP, Hoppe S, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of breast MRI for patients with suspicious nipple discharge and negative mammography and ultrasound: a prospective study. Eur Radiol (2021) 31(10):7783–91. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07790-4
26. Zacharioudakis K, Kontoulis T, Vella JX, Zhao J, Ramakrishnan R, Cunningham DA, et al. Can we see what is invisible? the role of MRI in the evaluation and management of patients with pathological nipple discharge. Breast Cancer Res Treat (2019) 178(1):115–20. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05321-w
27. Baitchev G, Gortchev G, Todorova A, Dikov D, Stancheva N, Daskalova I. Intraductal aspiration cytology and galactography for nipple discharge. Int Surg (2003) 88(2):83–6. doi: 10.1177/106689690301100217
28. Waaijer L, Simons JM, Borel Rinkes IH, van Diest PJ, Verkooijen HM, Witkamp AJ. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of ductoscopy in patients with pathological nipple discharge. Br J Surg (2016) 103(6):632–43. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10125
29. Nagendran M, Chen Y, Lovejoy CA, Gordon AC, Komorowski M, Harvey H, et al. Artificial intelligence versus clinicians: systematic review of design, reporting standards, and claims of deep learning studies. BMJ (Clinical Res ed) (2020) 368:m689. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m689
30. Li C, Jing B, Ke L, Li B, Xia W, He C, et al. Development and validation of an endoscopic images-based deep learning model for detection with nasopharyngeal malignancies. Cancer Commun (London England) (2018) 38(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0325-9
31. Ohlinger R, Flieger C, Hahndorf W, Paepke S, Blohmer JU, Grunwald S, et al. Correlation of ductoscopic and histopathological findings and their relevance as predictors for malignancy: A German multicenter study. Anticancer Res (2020) 40(4):2185–90. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14179
32. Yilmaz R, Bender O, Celik Yabul F, Dursun M, Tunacı M, Acunas G. Diagnosis of nipple discharge: Value of magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonography in comparison with ductoscopy. Balkan Med J (2017) 34(2):119–26. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.2016.0184
33. Han Y, Li J, Han S, Jia S, Zhang Y, Zhang W. Diagnostic value of endoscopic appearance during ductoscopy in patients with pathological nipple discharge. BMC Cancer (2017) 17(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3288-3
Keywords: breast cancer, deep learning, pathological nipple discharge, ductoscopy, diagnosis
Citation: Xu F, Zhu C, Wang Z, Zhang L, Gao H, Ma Z, Gao Y, Guo Y, Li X, Luo Y, Li M, Shen G, Liu H, Li Y, Zhang C, Cui J, Li J, Jiang H and Liu J (2023) Deep learning for real-time detection of breast cancer presenting pathological nipple discharge by ductoscopy. Front. Oncol. 13:1103145. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1103145
Received: 20 November 2022; Accepted: 22 February 2023;
Published: 22 March 2023.
Edited by:
Annarita Fanizzi, National Cancer Institute Foundation (IRCCS), ItalyReviewed by:
Bikash Kumar Paul, Mawlana Bhashani Science and Technology University, BangladeshYuanpin Zhou, Sun Yat-sen University, China
Copyright © 2023 Xu, Zhu, Wang, Zhang, Gao, Ma, Gao, Guo, Li, Luo, Li, Shen, Liu, Li, Zhang, Cui, Li, Jiang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Feng Xu, drxufeng@mail.ccmu.edu.cn; Chuang Zhu, czhu@bupt.edu.cn; Hongchuan Jiang, drjhc@sina.com; Jun Liu, breast_surgeon@sina.com
†Present address: Lei Zhang, Department of General Surgery, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing, China
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Feng Xu
Feng Xu Chuang Zhu
Chuang Zhu Zhihao Wang
Zhihao Wang Lei Zhang1†‡
Lei Zhang1†‡ Yanshuang Li
Yanshuang Li Chao Zhang
Chao Zhang Hongchuan Jiang
Hongchuan Jiang
