Corrigendum: Contactless and robust dielectric microspheres-assisted surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensitivity improvement for anthrax biomarker detection
- School of Chemistry and Materials Science, Jiangsu Normal University, Xuzhou, Jiangsu Province, China
A Corrigendum on:
Contactless and robust dielectric microspheres-assisted surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensitivity improvement for anthrax biomarker detection
by Ge M, Zhao W, Han Y, Gai H and Zong C (2022). Front. Chem. 10:1057241. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1057241
In the original article, there was a spelling mistake in the name of the second author. The correct name appears above.
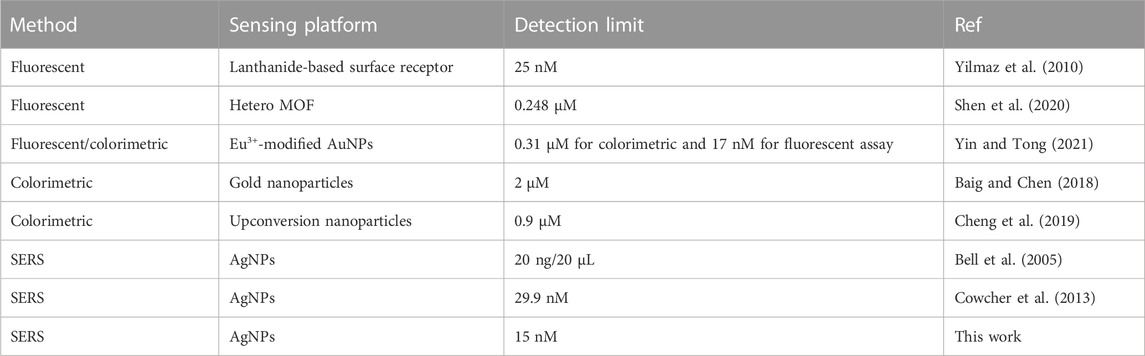
In the original article, there were errors in Table 1, page 7, as published. Three reference links and their corresponding references were missing; “Eu3−” should have been “Eu3+”; “0.248 p.m.” should have been “0.248 μM”; “0.13 p1\4” should have been “0.31 μM”; “0.9 [tM” should have been “0.9 μM”; “20 n9.120 pL” should have been “20 ng/20 μL”; the reference Baiv et al. (2018) should have been Baig and Chen (2018) and Cheng et al. (2009) should have been Cheng et al. (2019). There was also a typo in the caption. The corrected Table 1 and its caption, as well as the additional references, appear below.
In the original article, the abbreviation of DMs-PDMS was wrongly modified during production. Corrections have been made to the abstract, page 1. The third sentence previously stated:
“The as prepared DMs embedded PDMS DMs PD MS film was integrated with a microfluidic technique to enhance the SERS signal of a liquid substrate.”
The corrected sentence is as follows:
“The as prepared DMs embedded PDMS (DMs-PDMS) film was integrated with a microfluidic technique to enhance the SERS signal of a liquid substrate.”
Additionally, all instances of the abbreviation “DMs PDMS” have been corrected to “DMs-PDMS” throughout the abstract, page 1; Introduction, page 2, last paragraph; Material and methods sub-heading, “Fabrication of the DMs PDMS film”, page 2; as well as the Results and discussion subheading, “DERS effect investigation of the DMs PDMS film”, page 3.
In the original article, there was an error in Figure 3 as published. For the repeatability study, the SERS spectra and the relative standard deviation value were obtained from 20 random spots, as shown in Figure 3C, not 15. The corrected Figure 3 and its caption appear below.
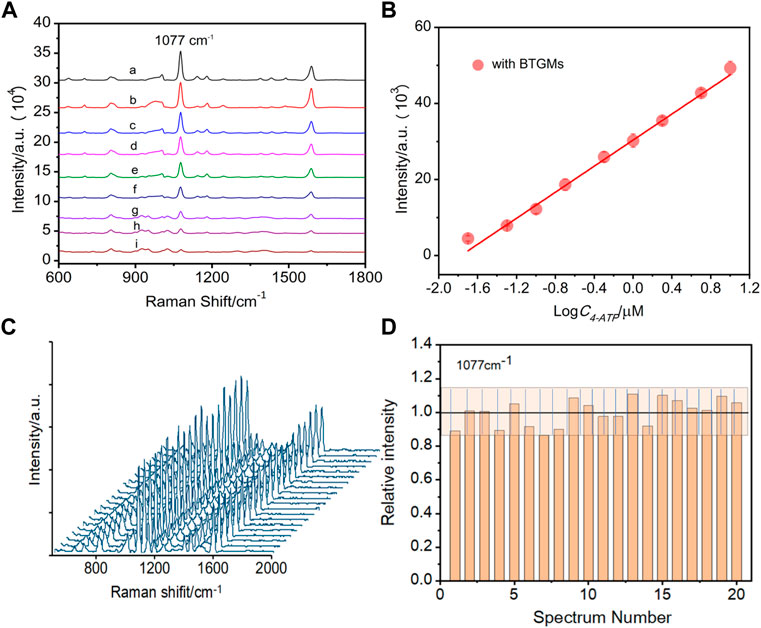
FIGURE 3. SERS spectra of different concentrations of 4-ATP obtained in the presence of BTGMs (A) (a–i: 10 μM, 5 μM, 2 μM, 1 μM, 0.5 μM, 0.2 μM, 0.1 μM, 50 nM and 20 nM, respectively). (B) Linear relationship between the intensity at 1,077 cm−1 of 4-ATP with its concentration. (C) SERS spectra of 4-ATP were acquired from 20 random sites with the DERS effect (in the presence of the BTGMs). (D) Corresponding bar chart for the peak intensity at 1,077 cm−1, the grating zone is indicated with ±13% intensity variation. DMs of 650 μm and microchannel with a width and depth of 600 and 360 μm, respectively, were used.
Consequently, in Results and discussion, “Sensing performance evaluation”, page 4, “15 randomly selected spots” should be “20 randomly selected spots”.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Baig, M. M. F., and Chen, Y. C. (2018). Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric sensing of dipicolinic acid from complex samples. Anal. Bioanal.Chem. 410, 1805–1815. doi:10.1007/s00216-017-0836-2
Cheng, Z. H., Liu, X., Zhang, S. Q., Yang, T., Chen, M.-L., and Wang, J.-H. (2019). Placeholder strategy with upconversion Nanoparticles−Eriochrome black T conjugate for a colorimetric assay of an anthrax biomarker. Anal. Chem. 91, 12094–12099. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03342
Keywords: surface-enhanced Raman scattering, dielectric microsphere, detection, dipicolinic acid, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)
Citation: Ge M, Zhao W, Han Y, Gai H and Zong C (2023) Corrigendum: Contactless and robust dielectric microspheres-assisted surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensitivity improvement for anthrax biomarker detection. Front. Chem. 11:1161985. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1161985
Received: 09 February 2023; Accepted: 27 February 2023;
Published: 09 March 2023.
Edited and reviewed by:
Xiu Liang, Qilu University of Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2023 Ge, Zhao, Han, Gai and Zong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chenghua Zong, zongch@jsnu.edu.cn
 Mengyi Ge
Mengyi Ge  Yue Han
Yue Han Chenghua Zong
Chenghua Zong