Cationic Metal–Organic Framework-Based Mixed-Matrix Membranes for Fast Sensing and Removal of Cr2O72− Within Water
- Laboratory of Silicon Materials, Cyrus Tang Center for Sensor Materials and Applications, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Considering that metal–organic framework (MOF)-polymer mixed-matrix membranes (MMMs) can overcome the drawbacks of intrinsic fragility and poor processability of pure-MOF membranes, we designed MOF-based MMMs for efficient removal and fast fluorescence sensing of heavily toxic ions within water systems simultaneously. In this work, a series of MOF-based MMMs are prepared by mixing a hydrolytically stable cationic [Eu7 (mtb)5(H2O)16]·NO3 8DMA·18H2O (denoted as Eu-mtb) MOF material into poly (vinylidene fluoride) with high loadings up to 70%. The free volume at the interface between the polymer and Eu-mtb particles, combined with the permanent porosity and uniform distribution of Eu-mtb particles, enables these MMMs to show fast enrichment of Cr2O72- from solutions and consequently have a full contact between the analyte and MOFs. The developed Eu-mtb MMM (70wt% loading) thus shows both efficient removal and exceptional fluorescence sensing of Cr2O72- in aqueous media. The overall adsorption capacity of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt% loading) for Cr2O72- reaches up to 33.34 mg/g, which is 3.4 times that of powder-form Eu-mtb. The detection limit of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt% loading) for Cr2O72- is around 5.73 nM, which is lower than that of the reported powder-form Eu-mtb. This work demonstrates that it is feasible to develop flexible luminescent MOF-based MMMs as a significant platform for efficient removal and sensitive sensing of pollutants from water systems simultaneously.
1 Introduction
Heavy metal pollution has become a severe environment threat around the world. Hexavalent chromium ions, especially Cr2O72−, has been widely employed in various industrial applications, such as metallurgy, pigment production, leather tanning, electroplating, and other relevant fields (Desai et al., 2016; Lai et al., 2018; Li et al., 2018). According to the U.S. Environment Protection Agency (EPA), Cr2O72− is classified as Group “A” human carcinogen, which can accumulate in living organisms, leading to a series of health problems such as aberration, gene mutation, and cancer (Zhang et al., 2015; Shen et al., 2018; Zou et al., 2018). Therefore, it is of vital importance to explore an effective method for capturing and detecting Cr2O72− from water systems simultaneously. Up to now, a variety of adsorbents have been widely employed to remove Cr2O72− from aqueous solution, including ACs (Cheng et al., 2016), layered double hydroxides (LDHs) (Lei et al., 2017), and resigns (Bhatti et al., 2014), but these methods show slow sorption kinetic, inferior selectivity, and low stability. So far, the traditional detection of Cr2O72− mainly depends on instrumental methods, such as inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS), and electrochemical analysis (Araujo Barbosa et al., 2017; Bansod et al., 2017; Jiang et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2021), which are often high-cost and time-consuming. As a new class of sensing technique, fluorescence sensing has the advantages of real-time monitoring with better sensitivity, faster response time, lower cost, and less pretreatment of samples (Wu L. et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2021; Levine, 2021), which prompts the research of removing and detecting Cr2O72− simultaneously by developing a porous material with adsorption and fluorescence characteristics.
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), also known as the coordination polymer, are a promising class of porous materials constructed through the self-assembly of organic linkers and metal ions/clusters (Cui et al., 2018; Esrafili et al., 2020; Hu et al., 2020; Cao et al., 2021; Lv et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2021). Due to the merits of large surface areas, tunable structures, and excellent stability, MOFs have been widely employed in various applications, such as gas storage and separation, sensing, catalysis, and biomedicine (Wang et al., 2018; Zheng et al., 2018; Wu S. et al., 2020; Cheng et al., 2020; Hu E. et al., 2021; Hu M.-L. et al., 2021; Esrafili et al., 2021; Li et al., 2021; Zhou et al., 2021). Recently, several powder-form MOFs have been explored to remove and detect Cr2O72− from aqueous water simultaneously (Lin et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2019). However, it is noteworthy that only a part of MOFs can interact with analytes because of the difficulty of dispersing powder samples uniformly into the Cr2O72− solution, leading to the unsatisfied adsorption capacity and insufficient sensing sensitivity. The fabrication of powder-form MOFs into membranes is considered to be a valid and simple method to solve these drawbacks. Comparing to the harsh growth conditions and intrinsic fragility of pure MOF membranes, the incorporation of MOF particles into the polymer matrix to fabricate MOF-based mixed-matrix membranes (MMMs) is proved to be more competitive for realistic contaminant removal and sensing applications (Zhang et al., 2012; Dong J. et al., 2020; Wu T. et al., 2020). The integration of these two components has the ability to combine the flexibility and processability of polymers with the excellent properties of MOFs (Zhang et al., 2017; Li et al., 2019; Sousaraei et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2020; Muthukumaraswamy Rangaraj et al., 2020). Furthermore, the uniform distribution of MOF particles without aggregation within the polymers is beneficial for the sufficient interactions between MOFs and analytes (Denny Jr and Cohen, 2015; Semino et al., 2016; Jiang et al., 2021).
However, to the best of our knowledge, only two MMMs have been developed for the fluorescence sensing of Cr2O72− in aqueous solution (Qin et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2021), MMMs for the removal and sensing of Cr2O72− simultaneously within water have not been discussed yet. [Eu7 (mtb)5(H2O)16]·NO3 8DMA·18H2O (Eu-mtb, H4mtb = 4-[tris(4-carboxyphenyl)methyl]benzoic acid)) is a hydrolytically stable cationic MOF that has been reported to have the lowest detection limit for Cr2O72− (Liu et al., 2017). Therefore, in this work, Eu-mtb was selected to be incorporated into poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) to fabricate a series of Eu-mtb MMMs. A mass of Cr2O72− from water can be easily enriched inside the MMMs by virtue of the free volume at the interface between PVDF and Eu-mtb particles, permanent porosity of Eu-mtb, and the electrostatic interaction between Cr2O72− and the cationic framework. Thereupon, the sufficient interaction between Cr2O72− and the Eu-mtb framework is achievable due to the uniform distribution of Eu-mtb particles. The as-prepared Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) shows a highly remarkable removal efficiency and detection sensitivity toward Cr2O72− in aqueous media. The overall adsorption capacity of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) for Cr2O72- is 33.34 mg/g, which is 3.4 times that of the powder-form Eu-mtb. The detection limit of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) for Cr2O72− is calculated to be 5.73 nM, which is lower than that of the reported powder-form Eu-mtb. The combination of the enhanced removal and sensing properties with its processability and flexibility makes Eu-mtb MMMs (70 wt%) a promising candidate for practical applications.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and Chemicals
Starting reagents and solvents were purchased and used without further purification: 4-[tris(4-carboxyphenyl)methyl]benzoic acid (H4mtb, ≥98.0%, Jilin Chinese Academy of Sciences—Yanshen Technology Co., Ltd.), europium nitrate hexahydrate (Eu(NO3)3ྷ6H2O, ≥99.9%, Energy Chemical), poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF, average Mw ∼534,000, Aldrich), and N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA, 99.5%, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Limited Corporation). Deionized water and ethanol were utilized throughout all experiments.
2.2 Synthesis of Eu-mtb
Eu-mtb was prepared according to the published literature with some modifications (Liu et al., 2017). Briefly, 30 mg of H4mtb (0.06 mmol), 69 mg of Eu(NO3)3ྷ6H2O (0.15 mmol), N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA; 3 ml), and deionized water (6 ml) were mixed and ultrasonically dissolved. The mixture was then sealed in a 25-ml Teflon-lined stainless autoclave and heated at 90°C for 2 days and subsequently cooled to room temperature. White block crystals were collected after filtration and washing with DMA and ethanol several times.
2.3 Fabrication of MMMs
Eu-mtb MMMs were prepared according to the published literature with some modifications (Zhang et al., 2018). The pure polymer membrane was manufactured as follows: PVDF (0.15 g) was dissolved in DMF (1.9 ml) and stirred for 1 day to form a sticky solution. MOF-based MMMs with different loadings were manufactured by adding Eu-mtb into the above solution and stirring for another day to form a homogenous solution. Afterward, a certain amount of mixed solutions was then cast onto a glass plate by a scraper to fabricate a flat sheet membrane under ambient conditions. Soaking in deionized water led to fast delamination of the membranes. Delamination of the membranes in water is possibility attributed to swelling of the PVDF, leading to a morphological change at the membrane/substrate interface and resultant release. MMMs with different loadings of Eu-mtb (30, 50, and 70 wt%) were prepared with thicknesses around 30–40 µm.
2.4 Measurements and Analysis
Powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) patterns were collected in the 2θ = 5–50° range on a Shimadzu XRD-7000 diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.542 Å) at room temperature. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) analyses were conducted on a Hitachi S4800 field-emission scanning electron microscope with a HORIBA EMAX energy dispersive spectrometer. Excitation and emission spectra were taken with a Hitachi F-4600 spectrofluorometer at room temperature. UV-vis spectra were measured with a Hitachi U-4100 ultraviolet spectrophotometer at room temperature. All the experiments were performed at room temperature. All error bars represent standard deviations from three repeated experiments.
2.5 Adsorption Experiments
2.5.1 Adsorption Kinetics
2.1 ml of mixed solutions were cast onto a glass plate to fabricate membranes. During the adsorption process, the as-prepared MMMs were used for the removal of Cr2O72− with the concentration of 10 ppm. The Cr2O72− water solutions (48 ml) containing the MMMs were mixed well with magnetic stirring for 6 h at 25°C. During the stirring period, 2 ml of the mixture was taken out and filtered by syringe filters (PTFE, 0.25 μm), and the residual concentrations of Cr2O72- in the supernatant liquid were evaluated by UV-vis absorbance (monitor at λ = 257 nm).
2.5.2 Adsorption Isotherm
265 μL of dope solutions were cast onto a glass plate to fabricate membranes. To obtain the adsorption capacity, MMMs were dispersed in 10 ml of Cr2O72− water solutions with a known concentration between 10 and 600 ppm, respectively. The mixtures were stirred at 25°C for 24 h and then filtered by syringe filters (PTFE, 0.25 μm), and the residual concentrations of Cr2O72- were evaluated by UV-vis spectroscopy.
2.5.3 Adsorption Selectivity
440 μl of dope solutions were cast onto a glass plate to fabricate membranes. MMMs were dispersed in 10 ml of Cr2O72− water solutions (10 ppm) containing an n-fold molar excess of disturbing anions such as chloride (Cl−), nitrate (NO3−), and iodide (I−) (n is equal to 0, 1, 5, and 10). The mixtures were stirred at 25 °C for 24 h and then filtered by syringe filters (PTFE, 0.25 μm), and the residual concentrations of Cr2O72− were evaluated by UV-vis spectroscopy.
The equations related to the adsorption experiments are presented in the Supplementary Material.
2.6 Luminescent Sensing Experiments
The flow-through method: 300 μl of mixed solutions were cast onto a glass plate to fabricate membranes, and the areas of 2 cm2 were cut from the films for sensing tests. MMMs via cut were then fixed enclosed in a 250 ml micro vacuum suction device, the sand core diameter of which is 2 cm. Aqueous solutions (10–3 M, 100 ml) of K2Cr2O7, Ca(NO3)2, Zn(NO3)2, Pb(NO3)2, Al(NO3)3, Na2SO4, NaNO3, NaI, CH3COONa, and NaCl were respectively driven through the MMMs with a vacuum pump, and the treated MMMs were used for luminescent measurements.
The soaking method: For the purpose of comparison, a sample of as-prepared MMMs was soaked in the aqueous solutions (10–3 M, 100 ml) of K2Cr2O7.
3 Results and Discussion
3.1 Preparation and Characterization of Eu-mtb MMMs
As a kind of cationic MOFs, Eu-mtb was solvothermally synthesized from a mixture of europium nitrate hexahydrate (Eu(NO3)3·6H2O) and 4-[tris(4-carboxyphenyl)methyl]benzoic acid (H4mtb) in dimethylacetamide (DMA) and water solution. Eu-mtb is composed of 8-connected [Eu3O25]+ trinuclear core bound by mtb4− ligands with four carboxylic groups to give the 3D structure having rhombic channels with a size of 7.2 × 6.4 Å2 (Figure 1A). The existence of charge-balancing NO3− anions in the channels of Eu-mtb makes it possible for Cr2O72− in the aqueous solutions to enter into the pore surface of Eu-mtb through the anion-exchange process. The electrostatic interaction between the cationic framework and Cr2O72− is of great benefit for achieving efficient removal and sensitive fluorescence sensing of Cr2O72− within water simultaneously. The powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) pattern of the resulted Eu-mtb is shown in Figure 1B, which was in good agreement with that reported in the previous literature (Liu et al., 2017). It is reported that MOFs with micro- or nanoparticles are often preferred to fabricate MOF-based mixed-matrix membranes (MMMs) because they can provide larger interfacial areas at the MOF-polymer boundary to allow closer integration (Dechnik et al., 2017). Therefore, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images (Supplementary Figure S1) indicated that the size of the resulted Eu-mtb powder was around 10 μm, which is suitable for fabricating MMMs.
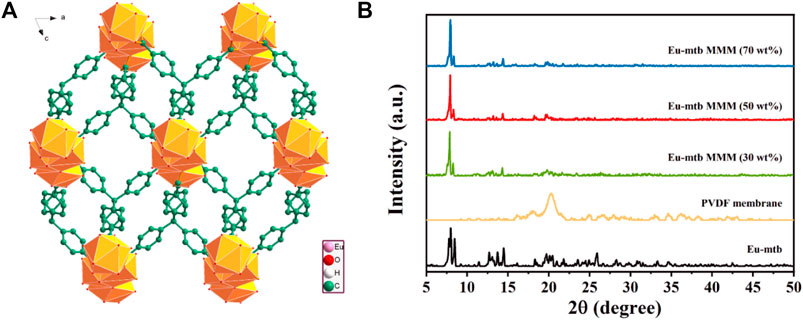
FIGURE 1. (A) 3D network structure of Eu-mtb viewed along the b axis. (B) PXRD patterns of Eu-mtb, PVDF membrane, and Eu-mtb MMMs.
MMMs were fabricated by a drawdown coating (doctor-blading) process (Zhang et al., 2018). For the purpose of comparison, the pure polymer membrane was manufactured first as follows: PVDF (0.15 g) was dissolved in DMF (1.9 ml) and stirred for 1 day to form a sticky solution. MOF-based MMMs with different loadings were manufactured by adding Eu-mtb into the above solution and stirring for another day to form a homogenous solution. Afterward, a certain amount of mixed solutions was then cast onto a glass plate by a scraper to fabricate a flat sheet membrane under ambient conditions. Soaking in deionized water led to fast delamination of the MMMs, which is possibility attributed to the swelling of PVDF, leading to a morphological change at the MMM/substrate interface and resultant release. Eu-mtb-based PVDF hybrid membranes (denoted as Eu-mtb MMMs) with different weight loadings of Eu-mtb (30, 50, and 70 wt%) were obtained.
The PXRD patterns of the resulted hybrid membranes are shown in Figure 1B. The broad peaks of the pure PVDF membrane are attributed to its amorphous properties. As the loading of Eu-mtb increases, these PVDF peaks decrease significantly, whereas the characteristic peaks of Eu-mtb appear and become predominant, which indicates that the crystallinity and structural features of Eu-mtb are maintained well in the MMMs. The SEM images of prepared Eu-mtb MMMs with different weight loadings (30, 50, and 70 wt%) are exhibited in Figure 2. Eu-mtb MMMs show morphologies similar to that of the pure PVDF membrane, demonstrating the incorporation of Eu-mtb particles causes almost no damage to the structural integrity of the polymer membrane. The Eu-mtb particles remain intact and are uniformly combined with the polymer binder without obvious aggregation.
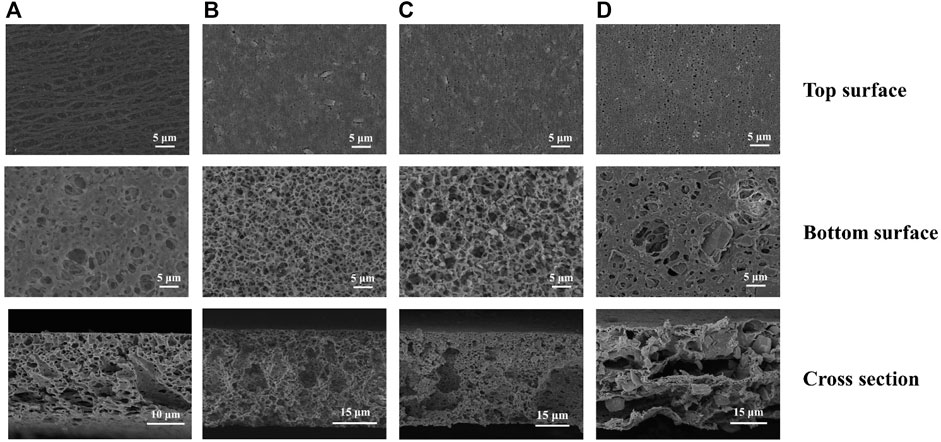
FIGURE 2. SEM images of (A) PVDF membrane, (B) Eu-mtb MMM (30 wt%), (C) Eu-mtb MMM (50 wt%), and (D) Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%). Top, bottom, and cross-section surface.
Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) was employed to characterize the distribution of Eu-mtb particles in MMMs. As shown in Supplementary Figure S2A–C, the fluorine element from PVDF and the europium element from Eu-mtb are both distributed uniformly in the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%), which confirms the well distribution of Eu-mtb particles in the PVDF matrix. Furthermore, the pure PVDF membrane is white and transparent; with the increase in the loading of white-powder Eu-mtb , the transparency of MMMs decreases gradually, which further demonstrates the successful incorporation and uniform distribution of Eu-mtb particles in the PVDF matrix (Supplementary Figure S3). The photograph of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) is shown in Supplementary Figure S2D. It can be seen that the membrane is free of macroscopic defects and has the characteristic of flexibility at the same time, making it suitable for practical sensing application.
As a fluorescent sensor for the removal and detection of Cr2O72- within industrial waste water, the thermal and acid–base stability are of great importance. The thermal and chemical stability of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) were investigated by immersing the membrane into aqueous solutions with different temperatures from 40 to 80°C and various pH values from 3.39 to 7.88. As shown in Supplementary Figure S4,5, the PXRD patterns under the aforementioned conditions for 8 h are identical to that of the original Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%), indicating the excellent chemical and thermal stability of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%), which makes it competent for the removal and detection of Cr2O72− under environmentally relevant conditions.
3.2 Adsorption Behaviors of Cr2O72− by Eu-mtb MMMs
Adsorption kinetics was investigated first to evaluate the removal efficiency of Cr2O72− over Eu-mtb MMMs. The effect of the contact time on the adsorption of Cr2O72- from aqueous solution is shown in Figure 3. The pure PVDF membrane displays no uptake of Cr2O72− (Eq. 1, Supporting information) after being immersed in the aqueous solution of Cr2O72− for 24 h, indicating that the polymer in MMMs has no effect on the removal properties. With the increased loading of Eu-mtb in MMMs, the uptake of Cr2O72− increases gradually (Supplementary Figure S6). When the loading of Eu-mtb reaches 70 wt%, the residual concentrations of Cr2O72− decreases significantly with immersion time, and around 84.0%, Cr2O72− can be removed from the aqueous solution after 24 h, whereas the uptake of Cr2O72− by powder-form Eu-mtb is only 59.8% (Figures 3A,B). Therefore, the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) was selected for the following adsorption experiments. In order to explore the adsorption mechanism, the kinetic data of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) were fitted with the pseudo–second-order kinetic model (Eq. 2, Supporting information). As shown in Figures 3C,D, an extremely high correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.9999) was obtained, suggesting that the adsorption kinetics of Cr2O72− follow well with the pseudo–second-order model. The calculated half-adsorption time t1/2 (Eq. 4, Supporting information) of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) is 1.62 min, indicating the quick response to Cr2O72− in aqueous solutions.
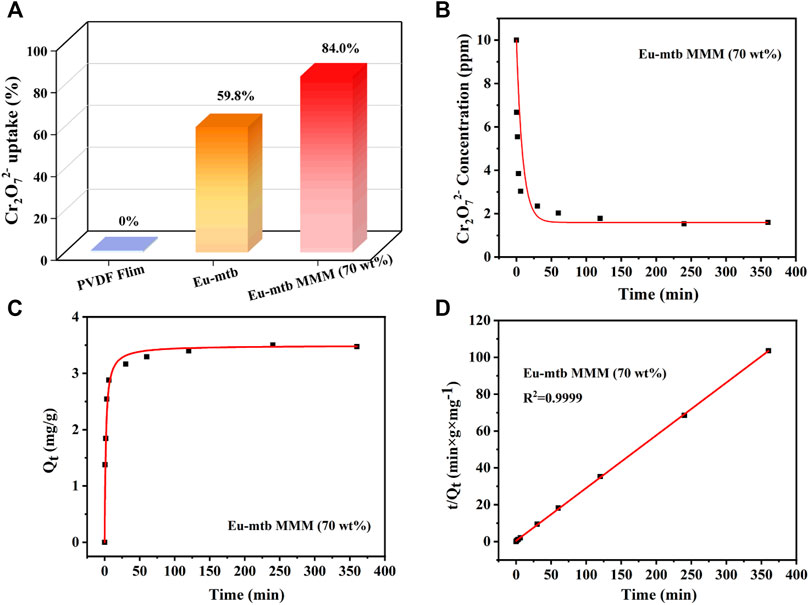
FIGURE 3. (A) Cr2O72− removal ability of powder-form Eu-mtb and MMMs with different Eu-mtb weight loadings (0 and 70 wt%). (B) Effect of time on the residual concentrations of Cr2O72− at different times. (C) Effect of time on the amount of Cr2O72− adsorbed by the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) at different times. (D) Corresponding linear fitting of the adsorption kinetics via the pseudo–second-order model.
To further confirm the adsorption capacities of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) toward Cr2O72−, the adsorption isotherms were carried out. The adsorption capacities of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) depend on the initial concentrations of Cr2O72− water solutions. Therefore, Cr2O72− solutions with various concentrations were used to determine the adsorption capacities. As shown in Figure 4, the adsorption isotherms of Cr2O72− could be well fitted using the Langmuir model (Eq. 5, Supporting information). The overall adsorption capacity of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) for Cr2O72− reaches up to 33.34 mg/g, which is 3.4 times that of the powder-form Eu-mtb (9.7 mg/g) and higher than some reported MOF-based adsorbents (Supplementary Table S1). It is speculated that the significantly enhanced adsorption rate and capacity of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) might be attributed to the synergy of free volume at the interface between PVDF and Eu-mtb particles, permanent porosity of Eu-mtb, and the electrostatic interaction between Cr2O72− and the cationic framework, facilitating the enrichment of Cr2O72− inside MMMs (Supplementary Figure S7).
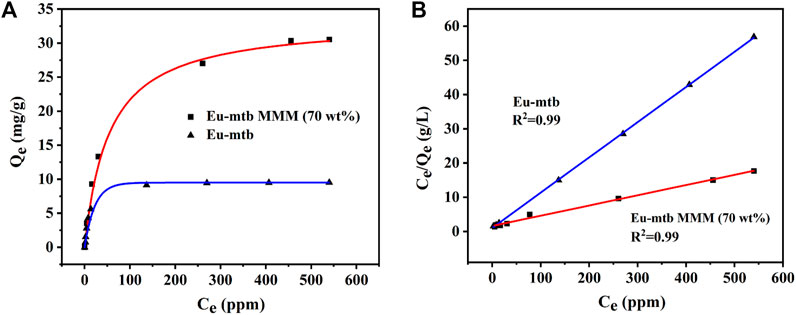
FIGURE 4. (A) Adsorption isotherms for Cr2O72− over the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) and powder-form Eu-mtb. (B) Corresponding linear fitting curve of the Langmuir isotherm model.
Considering that various anions frequently coexist with Cr2O72− in environment-related conditions, it is of vital importance to investigate the effect of competing ions on the sorption ability of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) toward Cr2O72−. As shown in Figure 5, the change of Cr2O72− uptake was negligible even when there was a 10-fold excess mole of Cl−. When there were 10-fold excess moles of NO3− and I−, the uptake of Cr2O72− was still at a high efficiency of 60.4%, indicating that the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) exhibits high selectivity to these environmental pollutants.
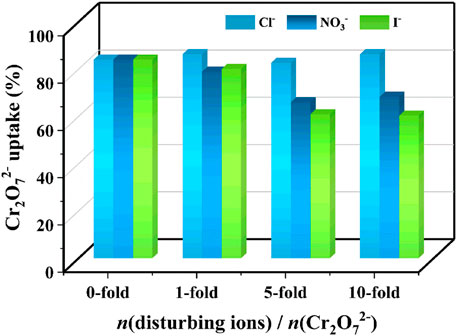
FIGURE 5. Effect of the disturbing ions (Cl−, NO3− and I−) on the Cr2O72− adsorption ability over the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%).
3.3 Fluorescence Sensing of Cr2O72− by Eu-mtb MMMs
By virtue of the massive enrichment of Eu-mtb inside MMMs, the sufficient interactions between Cr2O72− and the framework can be achieved, which is of great benefit for enhancing the sensing sensitivity towards Cr2O72− in aqueous media. Therefore, the fluorescence sensing of Cr2O72− by Eu-mtb MMMs is investigated in detail therewith. As shown in Supplementary Figure S8, the solid-state fluorescence measurements showed that H4mtb exhibits an intense broad band with a maximum at 416 nm upon excitation at 335 nm, whereas Eu-mtb exhibits characteristic Eu3+ emissions with the strongest emission peak at 616 nm from the 5D0→7F2 induced by the electronic dipole transition upon excitation at 280 nm. The absence of the emission peak of the ligand in Eu-mtb indicates that the ligand can sensitize the luminescent Eu3+ effectively through the “antenna effect” process.
The emission spectra of Eu-mtb MMMs with different weight loadings were investigated upon 280 nm UV radiation (Supplementary Figure S9). The pure PVDF membrane displays no fluorescence, indicating that the polymer in MMMs has no effect on the sensing test of Cr2O72−. With the increased loading of Eu-mtb in MMMs, the characteristic emission peak of Eu-mtb appears and increases, reaching maximum when the loading of Eu-mtb is 70 wt%. Therefore, the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) was selected for the following fluorescence sensing of Cr2O72−. Furthermore, it can be seen that the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) exhibits fluorescence intensity similar to powder-form Eu-mtb under the same experiment conditions, indicating that Eu-mtb doping with membranes almost has no effect on the fluorescence intensity of Eu-mtb particles (Supplementary Figure S10). As a fluorescent sensor for the detection of Cr2O72− within water, the fluorescence stability is a factor that should be concerned. As shown in Supplementary Figures S11,12, the emission intensity of Eu-mtb MMMs (70 wt%) at 616 nm under excitation at 280 nm shows negligible changes with the varied temperatures and pH values, which provides a prerequisite for the application of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) as a fluorescent sensor in the aqueous environment. In order to demonstrate the feasibility of as-prepared MMMs as a platform for sensitive fluorescence sensing, the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) was employed to detect Cr2O72- in aqueous solutions by the flow-through and soaking method (soaking for 8 h). As shown in Supplementary Figure S13, the fluorescence quenching of Eu-mtb MMMs (70 wt%) is more significant upon treatment with Cr2O72− aqueous solution (10–3 M, 100 ml) by the flow-through method, demonstrating that the flow-through method is preferable to conduct the following Cr2O72− sensing experiments. The time that has been consumed by the flow-through method is nearly 30 min, which is significantly shorter than the soaking method. Furthermore, as shown in Supplementary Figure S14, the repeated experiments of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) for Cr2O72− by the flow-through method indicate that this method is reliable and resultful.
To evaluate the sensing property of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%), the fluorescence of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) was monitored upon treatment with different concentrations of Cr2O72− aqueous solutions (100 ml) by the flow-through method. As shown in Figure 6A and Supplementary Figure S15, the emission intensity of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) gradually decreased with the increasing concentration of Cr2O72– from 0 to 10–3 M. When the concentration of Cr2O72– approached 10–3 M, the fluorescence signal of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) was almost completely quenched. In the range of 1–10 mM (Figure 6B), the luminescence intensity and concentration of Cr2O72– exhibited a good linear relationship with a correlation shown by the equation
where δ is the standard deviation calculated from blank measurements of the probe (Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%)), and S is the slope value obtained from the linear fit in the low-concentration region. The LOD value of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) toward Cr2O72– was calculated to be 5.73 nM. In order to verify MMMs have superior sensing properties than powder-form Eu-mtb, the sensing experiments of powder-form Eu-mtb were conducted according to published literatures. In brief, 1 mg finely ground Eu-mtb powders were dispersed into aqueous solutions of Cr2O72– (2 ml) with various concentrations, which were then treated by ultrasonication to form a homogenous suspension before fluorescence measurement. As shown in Supplementary Figure S16,17, in the range of 1–10 mM, the luminescence intensity and concentration of Cr2O72– exhibited a good linear relationship with a correlation shown by the equation
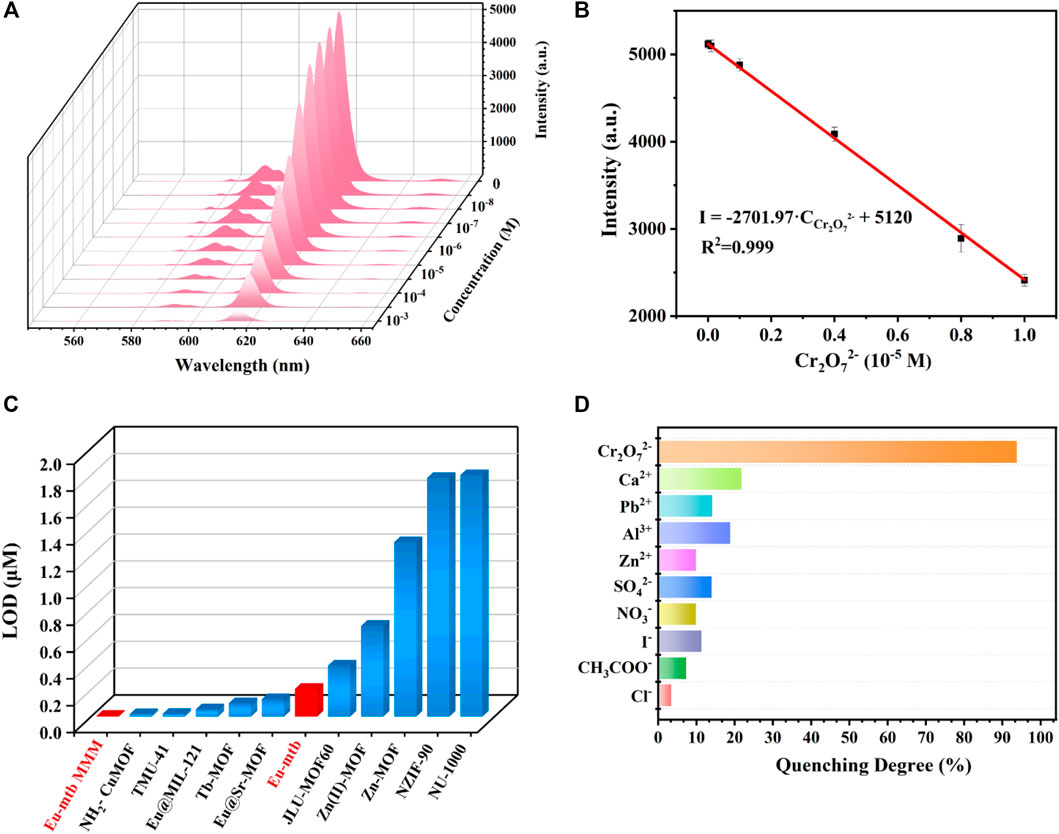
FIGURE 6. (A) Emission spectra of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) with increasing concentrations (0–10–3 M) of Cr2O72-. (B) Linear relationship (0–10–5 M) of the emission intensity of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) quenched by Cr2O72−. (C) The limit of detection of reported MOFs for the fluorescence sensing of Cr2O72−. (D) The fluorescence quenching degree of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) at 616 nm toward different aqueous solutions of various anions and cations (100 ml 10–3 M).
3.4 Mechanism for Sensing Cr2O72−
In order to explore the possible mechanism of the fluorescence quenching from the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) induced by Cr2O72−, UV-vis spectra of aqueous solutions of various anions and cations were investigated. As shown in Figure 7, it is notable that the excitation peak of Eu-mtb is partially overlapped by the strong absorption of Cr2O72−, resulting in the inner filter effect (IFE) (Mi et al., 2019; Guo et al., 2020). The competition of excitation light between the host material and Cr2O72− led to the selective fluorescence quenching response of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%). Apart from this, it is evident that the emission peak of H4mtb is also partially overlapped by the absorption of Cr2O72−, while no overlap between the emission band of H4mtb and the absorption bands of other ions is observed. Therefore, the resonance energy transfer from H4mtb to Cr2O72− might take place, and the “antenna effect” process from H4mtb to Eu3+ is inhibited to some extent (Dong Z.-P. et al., 2020). Based on these pieces of evidence, both competitive absorption and resonance energy transfer are responsible for the fluorescence quenching of the Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) toward Cr2O72−.
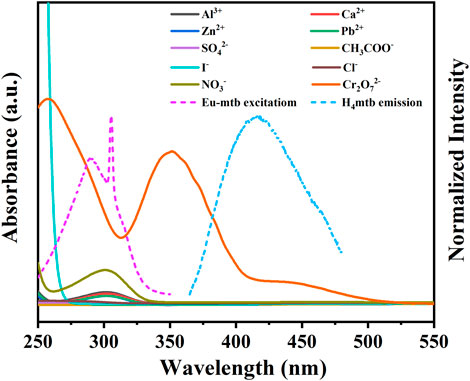
FIGURE 7. UV-vis spectra of different aqueous solutions of various ions and fluorescent spectra of Eu-mtb and H4mtb.
4 Conclusion
In summary, MOF-based MMMs have been evaluated as a candidate for the removal and detection of Cr2O72- in aqueous media simultaneously. The higher adsorption capacity (33.34 mg/g) and lower LOD value (5.73 nM) of the as-prepared Eu-mtb MMM (70 wt%) than powder-form Eu-mtb for Cr2O72− are attributed to the enrichment of Cr2O72− inside MMMs and the uniform distribution of cationic Eu-mtb particles within MMMs, which facilitate the interactions between Cr2O72− and the Eu-mtb framework sufficiently. Furthermore, the combination of the flexibility of the polymer and the excellent properties of MOFs provides the possibility to overcome the disadvantages of powder-form MOFs and pure MOF membranes. Therefore, MOF-based MMMs is a functional and promising platform for a wide range of practical applications.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52025131, 51772268, and 61721005).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2022.852402/full#supplementary-material
References
Abdollahi, N., and Morsali, A. (2019). Highly Sensitive Fluorescent Metal-Organic Framework as a Selective Sensor of MnVII and CrVI Anions (MnO4−/Cr2O72−/CrO42−) in Aqueous Solutions. Analytica Chim. Acta 1064, 119–125. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2019.02.061
Araujo-Barbosa, U., Peña-Vazquez, E., Barciela-Alonso, M. C., Costa Ferreira, S. L., Pinto dos Santos, A. M., and Bermejo-Barrera, P. (2017). Simultaneous Determination and Speciation Analysis of Arsenic and Chromium in Iron Supplements Used for Iron-Deficiency Anemia Treatment by HPLC-ICP-MS. Talanta 170, 523–529. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2017.04.034
Bansod, B., Kumar, T., Thakur, R., Rana, S., and Singh, I. (2017). A Review on Various Electrochemical Techniques for Heavy Metal Ions Detection with Different Sensing Platforms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 94, 443–455. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2017.03.031
Bhatti, A. A., Memon, S., and Memon, N. (2014). Dichromate Extraction by Calix[4]arene Appended Amberlite XAD-4 Resin. Sep. Sci. Tech. 49 (5), 664–672. doi:10.1080/01496395.2013.862722
Cao, Y., Mi, X., Li, X., and Wang, B. (2021). Defect Engineering in Metal‒Organic Frameworks as Futuristic Options for Purification of Pollutants in an Aqueous Environment. Front. Chem. 9, 338. doi:10.3389/fchem.2021.673738
Chen, S.-Y., Li, Z., Li, K., and Yu, X.-Q. (2021). Small Molecular Fluorescent Probes for the Detection of Lead, Cadmium and Mercury Ions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 429, 213691. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213691
Chen, W., Zhang, Z., Hou, L., Yang, C., Shen, H., Yang, K., et al. (2020). Metal-organic Framework MOF-801/PIM-1 Mixed-Matrix Membranes for Enhanced CO2/N2 Separation Performance. Sep. Purif. Tech. 250, 117198. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117198
Cheng, L., Liang, C., Liu, W., Wang, Y., Chen, B., Zhang, H., et al. (2020). Three-Dimensional Polycatenation of a Uranium-Based Metal-Organic Cage: Structural Complexity and Radiation Detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142 (38), 16218–16222. doi:10.1021/jacs.0c08117
Cheng, W., Ding, C., Wang, X., Wu, Z., Sun, Y., Yu, S., et al. (2016). Competitive Sorption of As(V) and Cr(VI) on Carbonaceous Nanofibers. Chem. Eng. J. 293, 311–318. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.073
Cui, Y., Zhang, J., He, H., and Qian, G. (2018). Photonic Functional Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47 (15), 5740–5785. doi:10.1039/C7CS00879A
Dechnik, J., Gascon, J., Doonan, C. J., Janiak, C., and Sumby, C. J. (2017). Mixed‐Matrix Membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56 (32), 9292–9310. doi:10.1002/anie.201701109
Denny, M. S., and Cohen, S. M. (2015). In Situ Modification of Metal-Organic Frameworks in Mixed-Matrix Membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54 (31), 9029–9032. doi:10.1002/anie.201504077
Desai, A. V., Manna, B., Karmakar, A., Sahu, A., and Ghosh, S. K. (2016). A Water-Stable Cationic Metal-Organic Framework as a Dual Adsorbent of Oxoanion Pollutants. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55 (27), 7811–7815. doi:10.1002/anie.201600185
Dong, J., Hou, S.-L., and Zhao, B. (2020a). Bimetallic Lanthanide-Organic Framework Membranes as a Self-Calibrating Luminescent Sensor for Rapidly Detecting Antibiotics in Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 12 (34), 38124–38131. doi:10.1021/acsami.0c09940
Dong, Z.-P., Zhao, F., Zhang, L., Liu, Z.-L., and Wang, Y.-Q. (2020b). A white-light-emitting Lanthanide Metal-Organic Framework for Luminescence Turn-Off Sensing of MnO4− and Turn-On Sensing of Folic Acid and Construction of a "Turn-On Plus" System. New J. Chem. 44 (25), 10239–10249. doi:10.1039/D0NJ02145H
Esrafili, L., Firuzabadi, F. D., Morsali, A., and Hu, M.-L. (2021). Reuse of Predesigned Dual-Functional Metal Organic Frameworks (DF-MOFs) after Heavy Metal Removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 403, 123696. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123696
Esrafili, L., Morsali, A., Hu, M.-L., Azhdari Tehrani, A., Carlucci, L., Mercandelli, P., et al. (2020). Size-Selective Urea-Containing Metal-Organic Frameworks as Receptors for Anions. Inorg. Chem. 59 (22), 16421–16429. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c02215
Guo, H., Wu, N., Xue, R., Liu, H., Wang, M., Yao, W., et al. (2020). An Eu(III)-functionalized Sr-Based Metal-Organic Framework for Fluorometric Determination of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) Ions. Microchim Acta 187 (7), 374. doi:10.1007/s00604-020-04292-w
Hao, J.-N., and Yan, B. (2016). Ln3+ post-functionalized Metal-Organic Frameworks for Color Tunable Emission and Highly Sensitive Sensing of Toxic Anions and Small Molecules. New J. Chem. 40 (5), 4654–4661. doi:10.1039/C5NJ03419A
Hu, E., Yao, Y., Chen, Y., Cui, Y., Wang, Z., and Qian, G. (2021a). Cu2+-Guided Construction of the Amorphous CoMoO3/Cu Nanocomposite for Highly Efficient Water Electrolysis. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 4 (7), 6740–6748. doi:10.1021/acsaem.1c00812
Hu, M.-L., Joharian, M., Razavi, S. A. A., Morsali, A., Wu, D.-Z., Azhdari Tehrani, A., et al. (2021b). Phenolic Nitroaromatics Detection by Fluorinated Metal-Organic Frameworks: Barrier Elimination for Selective Sensing of Specific Group of Nitroaromatics. J. Hazard. Mater. 406, 124501. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124501
Hu, M.-L., Razavi, S. A. A., Piroozzadeh, M., and Morsali, A. (2020). Sensing Organic Analytes by Metal-Organic Frameworks: A New Way of Considering the Topic. Inorg. Chem. Front. 7 (7), 1598–1632. doi:10.1039/C9QI01617A
Jiang, T.-J., Yang, M., Li, S.-S., Ma, M.-J., Zhao, N.-J., Guo, Z., et al. (2017). In Situ Underwater Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Analysis for Trace Cr(VI) in Aqueous Solution Supported by Electrosorption Enrichment and a Gas-Assisted Localized Liquid Discharge Apparatus. Anal. Chem. 89 (10), 5557–5564. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00629
Jiang, Y., Huang, Y., Shi, X., Lu, Z., Ren, J., Wang, Z., et al. (2021). Eu-MOF and its Mixed-Matrix Membranes as a Fluorescent Sensor for Quantitative Ratiometric pH and Folic Acid Detection, and Visible Fingerprint Identifying. Inorg. Chem. Front. 8 (22), 4924–4932. doi:10.1039/D1QI00840D
Jin, H.-G., Zong, W., Yuan, L., and Zhang, X.-B. (2018). Nanoscale Zeolitic Imidazole Framework-90: Selective, Sensitive and Dual-Excitation Ratiometric Fluorescent Detection of Hazardous Cr(vi) Anions in Aqueous media. New J. Chem. 42 (15), 12549–12556. doi:10.1039/C8NJ02047G
Lai, X., Sun, D., Hou, Y., Zuo, Y., Li, Y., and Zhang, L. (2018). Amino-Functionalized Multilayer Core-Shell Mesoporous Organosilica Nanospheres for Cr(VI) Removal. Adv. Mater. Inter. 5 (18), 1800630. doi:10.1002/admi.201800630
Lei, C., Zhu, X., Zhu, B., Jiang, C., Le, Y., and Yu, J. (2017). Superb Adsorption Capacity of Hierarchical Calcined Ni/Mg/Al Layered Double Hydroxides for Congo Red and Cr(VI) Ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 321, 801–811. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.070
Levine, M. (2021). Fluorescence-Based Sensing of Pesticides Using Supramolecular Chemistry. Front. Chem. 9, 27. doi:10.3389/fchem.2021.616815
Li, H., Zhang, L., He, H., Yang, Y., Cui, Y., and Qian, G. (2021). Tunable Nonlinear Optical Responses Based on Host-Guest MOF Hybrid Materials. Sci. China Mater. 64 (3), 698–705. doi:10.1007/s40843-020-1455-6
Li, J., Wang, X., Zhao, G., Chen, C., Chai, Z., Alsaedi, A., et al. (2018). Metal-Organic Framework-Based Materials: Superior Adsorbents for the Capture of Toxic and Radioactive Metal Ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47 (7), 2322–2356. doi:10.1039/C7CS00543A
Li, Q.-Y., Li, Y.-A., Guan, Q., Li, W.-Y., Dong, X.-J., and Dong, Y.-B. (2019). UiO-68-PT MOF-Based Sensor and its Mixed Matrix Membrane for Detection of HClO in Water. Inorg. Chem. 58 (15), 9890–9896. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01032
Lin, Z.-J., Zheng, H.-Q., Zheng, H.-Y., Lin, L.-P., Xin, Q., and Cao, R. (2017). Efficient Capture and Effective Sensing of Cr2O72- from Water Using a Zirconium Metal-Organic Framework. Inorg. Chem. 56 (22), 14178–14188. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b02327
Liu, J., Ye, Y., Sun, X., Liu, B., Li, G., Liang, Z., et al. (2019). A Multifunctional Zr(iv)-Based Metal-Organic Framework for Highly Efficient Elimination of Cr(vi) from the Aqueous Phase. J. Mater. Chem. A. 7 (28), 16833–16841. doi:10.1039/C9TA04026A
Liu, W., Wang, Y., Bai, Z., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, L., et al. (2017). Hydrolytically Stable Luminescent Cationic Metal Organic Framework for Highly Sensitive and Selective Sensing of Chromate Anions in Natural Water Systems. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 9 (19), 16448–16457. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b03914
Lv, X.-L., Feng, L., Xie, L.-H., He, T., Wu, W., Wang, K.-Y., et al. (2021). Linker Desymmetrization: Access to a Series of Rare-Earth Tetracarboxylate Frameworks with Eight-Connected Hexanuclear Nodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143 (7), 2784–2791. doi:10.1021/jacs.0c11546
Mi, X., Sheng, D., Yu, Y. e., Wang, Y., Zhao, L., Lu, J., et al. (2019). Tunable Light Emission and Multiresponsive Luminescent Sensitivities in Aqueous Solutions of Two Series of Lanthanide Metal-Organic Frameworks Based on Structurally Related Ligands. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 11 (8), 7914–7926. doi:10.1021/acsami.8b18320
Muthukumaraswamy Rangaraj, V., Wahab, M. A., Reddy, K. S. K., Kakosimos, G., Abdalla, O., Favvas, E. P., et al. (2020). Metal Organic Framework - Based Mixed Matrix Membranes for Carbon Dioxide Separation: Recent Advances and Future Directions. Front. Chem. 8, 534. doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.00534
Qin, B., Zhang, X., Qiu, J., Gahungu, G., Yuan, H., and Zhang, J. (2021). Water-Robust Zinc-Organic Framework with Mixed Nodes and its Handy Mixed-Matrix Membrane for Highly Effective Luminescent Detection of Fe3+, CrO42-, and Cr2O72- in Aqueous Solution. Inorg. Chem. 60 (3), 1716–1725. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c03214
Qiu, L., Ma, Z., Li, P., Hu, X., Chen, C., Zhu, X., et al. (2021). Sensitive and Selective Detection of Chromium (VI) Based on Two-Dimensional Luminescence Metal Organic Framework Nanosheets via the Mechanism Integrating Chemical Oxidation-Reduction and Inner Filter Effect. J. Hazard. Mater. 419, 126443. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126443
Semino, R., Ramsahye, N. A., Ghoufi, A., and Maurin, G. (2016). Microscopic Model of the Metal-Organic Framework/Polymer Interface: A First Step toward Understanding the Compatibility in Mixed Matrix Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 8 (1), 809–819. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b10150
Shen, X., Ma, S., Xia, H., Shi, Z., Mu, Y., and Liu, X. (2018). Cationic Porous Organic Polymers as an Excellent Platform for Highly Efficient Removal of Pollutants from Water. J. Mater. Chem. A. 6 (42), 20653–20658. doi:10.1039/C8TA09145E
Sousaraei, A., Queirós, C., Moscoso, F. G., Lopes-Costa, T., Pedrosa, J. M., Silva, A. M. G., et al. (2019). Subppm Amine Detection via Absorption and Luminescence Turn-On Caused by Ligand Exchange in Metal Organic Frameworks. Anal. Chem. 91 (24), 15853–15859. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04291
Wang, H., Lustig, W. P., and Li, J. (2018). Sensing and Capture of Toxic and Hazardous Gases and Vapors by Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47 (13), 4729–4756. doi:10.1039/C7CS00885F
Wang, Y., Ma, J.-X., Zhang, Y., Xu, N., and Wang, X.-L. (2021). A Series of Cobalt-Based Coordination Polymer Crystalline Materials as Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Sensors for Detecting Trace Cr(VI), Fe(III) Ions, and Ascorbic Acid. Cryst. Growth Des. 21 (8), 4390–4397. doi:10.1021/acs.cgd.1c00311
Wiwasuku, T., Boonmak, J., Siriwong, K., Ervithayasuporn, V., and Youngme, S. (2019). Highly Sensitive and Selective Fluorescent Sensor Based on a Multi-Responsive Ultrastable Amino-Functionalized Zn(II)-MOF for Hazardous Chemicals. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 284, 403–413. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.094
Wu, L., Huang, C., Emery, B. P., Sedgwick, A. C., Bull, S. D., He, X.-P., et al. (2020a). Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)-based Small-Molecule Sensors and Imaging Agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49 (15), 5110–5139. doi:10.1039/C9CS00318E
Wu, S., Min, H., Shi, W., and Cheng, P. (2020b). Multicenter Metal-Organic Framework‐Based Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensors. Adv. Mater. 32 (3), 1805871. doi:10.1002/adma.201805871
Wu, S., Ren, D., Zhou, K., Xia, H.-L., Liu, X.-Y., Wang, X., et al. (2021). Linker Engineering toward Full-Color Emission of UiO-68 Type Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143 (28), 10547–10552. doi:10.1021/jacs.1c04810
Wu, T., Prasetya, N., and Li, K. (2020c). Recent Advances in Aluminium-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOF) and its Membrane Applications. J. Membr. Sci. 615, 118493. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118493
Xiao, J., Liu, J., Gao, X., Ji, G., Wang, D., and Liu, Z. (2018). A Multi-Chemosensor Based on Zn-MOF: Ratio-dependent Color Transition Detection of Hg (II) and Highly Sensitive Sensor of Cr (VI). Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 269, 164–172. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2018.04.129
Xu, Y.-K., Meng, M.-M., Xi, J.-M., Wang, L.-F., Zhu, R., Liu, X.-G., et al. (2021). Mixed Matrix Membranes Containing Fluorescent Coordination Polymers for Detecting Cr2O72− with High Sensitivity, Stability and Recyclability. Dalton Trans. 50 (23), 7944–7948. doi:10.1039/D1DT00894C
Zhang, F., Yao, H., Zhao, Y., Li, X., Zhang, G., and Yang, Y. (2017). Mixed Matrix Membranes Incorporated with Ln-MOF for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Nitrofuran Antibiotics Based on Inner Filter Effect. Talanta 174, 660–666. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2017.07.007
Zhang, F., Zou, X., Gao, X., Fan, S., Sun, F., Ren, H., et al. (2012). Hydrogen Selective NH2-MIL-53(Al) MOF Membranes with High Permeability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22 (17), 3583–3590. doi:10.1002/adfm.201200084
Zhang, Q., Yu, J., Cai, J., Zhang, L., Cui, Y., Yang, Y., et al. (2015). A Porous Zr-Cluster-Based Cationic Metal-Organic Framework for Highly Efficient Cr2O72− Removal from Water. Chem. Commun. 51 (79), 14732–14734. doi:10.1039/C5CC05927E
Zhang, X., Zhang, Q., Yue, D., Zhang, J., Wang, J., Li, B., et al. (2018). Flexible Metal-Organic Framework-Based Mixed-Matrix Membranes: A New Platform for H2 S Sensors. Small 14 (37), 1801563. doi:10.1002/smll.201801563
Zheng, H.-Q., Liu, C.-Y., Zeng, X.-Y., Chen, J., Lü, J., Lin, R.-G., et al. (2018). MOF-808: A Metal-Organic Framework with Intrinsic Peroxidase-like Catalytic Activity at Neutral pH for Colorimetric Biosensing. Inorg. Chem. 57 (15), 9096–9104. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b01097
Keywords: metal–organic frameworks, mixed-matrix membranes, removal, fluorescence sensing, Cr2O72
Citation: Zhang S, Zheng H, Yang Y, Qian G and Cui Y (2022) Cationic Metal–Organic Framework-Based Mixed-Matrix Membranes for Fast Sensing and Removal of Cr2O72− Within Water. Front. Chem. 10:852402. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.852402
Received: 11 January 2022; Accepted: 10 February 2022;
Published: 28 February 2022.
Edited by:
Liming Fan, North University of China, ChinaReviewed by:
Guocheng Liu, Bohai University, ChinaJianqiang Liu, Guangdong Medical University, China
Suna Wang, Liaocheng University, China
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Zheng, Yang, Qian and Cui. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yu Yang, yuyang@zju.edu.cn; Yuanjing Cui, cuiyj@zju.edu.cn
 Shuyun Zhang
Shuyun Zhang  Heqi Zheng
Heqi Zheng Yuanjing Cui
Yuanjing Cui