Abstract
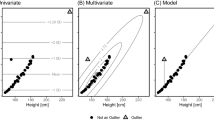
The first aim of this paper is to generalize the online estimator of a regression function introduced by Révész [26, 27] to the multivariate framework. Similarly to the univariate framework, the study of the convergence rate of the multivariate Révész’s estimator requires a tedious condition connecting the stepsize of the algorithm and the unknown value of the density of the regressor variable at the point at which the regression function is estimated. The second aim of this paper is to apply the averaging principle of stochastic approximation algorithms to remove this tedious condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Bojanic and E. Seneta, “AUnified Theory of RegularlyVarying Sequences”, Math.Z. 134, 91–106 (1973).
J. R. Blum, “Multidimensional Stochastic Approximation Methods”, Ann. Math. Statist. 25, 737–744 (1954).
H. Chen, “Lower Rate of Convergence for Locating aMaximum of a Function”, Ann. Statist. 16, 1330–1334 (1988).
H. F. Chen, T. E. Duncan, and B. Pasik–Duncan, “A Kiefer–Wolfowitz Algorithm with Randomized Differences”, IEEE Trans. Automat. Control 44, 442–453 (1999).
B. Delyon and A. B. Juditsky, “Stochastic Optimization with Averaging of Trajectories”, Stochastics Stochastic Rep. 39, 107–118 (1992).
J. Dippon, “Accelerated Randomized Stochastic Optimization”, Ann. Statist. 31, 1260–1281 (2003).
J. Dippon and J. Renz, “Weighted Means of Processes in Stochastic Approximation”, Math. Meth. Statist. 5, 32–60 (1996).
J. Dippon and J. Renz, “Weighted Means in Stochastic Approximation ofMinima”, SIAM J. Control Optim. 35, 1811–1827 (1997).
V. Fabian, “Stochastic Approximation ofMinima with Improved Asymptotic Speed”, Ann.Math. Statist. 38, 191–200 (1967).
J. Galambos and E. Seneta, “Regularly Varying Sequences”, Proc. Amer.Math. Soc. 41 110–116 (1973).
P. Hall and C. C. Heyde, Martingale Limit Theory and Its Application (Academic Press, Inc., New York–London, 1980).
P. Hall, “Effect of Bias Estimation on Coverage Accuracy of Bootstrap Confidence Intervals for a Probability Density”, Ann. Statist. 20, 675–694 (1992).
J. Kiefer and J. Wolfowitz, “Stochastic Estimation of the Maximum of a Regression Function”, Ann. Math. Statist. 23, 462–466 (1952).
H. J. Kushner and D. S. Clark, Stochastic ApproximationMethods for Constrained and Unconstrained Systems (Springer, New York, 1978).
H. J. Kushner and J. Yang, “Stochastic Approximation with Averaging of the Iterates: Optimal Asymptotic Rate of Convergence for General Processes”, SIAM J. Control Optim. 31, 1045–1062 (1993).
A. Le Breton, “About the Averaging Approach Schemes for Stochastic Approximation”, Math. Methods Statist. 2, 295–315 (1993).
A. Le Breton and A. Novikov, “Some Results about Averaging in Stochastic Approximation”, Metrika 42, 153–171 (1995).
A. Mokkadem and M. Pelletier, “A Companion for the Kiefer–Wolfowitz–Blum Stochastic Approximation Algorithm”, Annals of Statist. 35 1749–1772 (2007).
A. Mokkadem, M. Pelletier, and Y. Slaoui, “The Stochastic Approximation Method for the Estimation of a Multivariate Probability Density”, J. Statist. Plann. Inference 139, 2459–2478 (2009a).
A. Mokkadem, M. Pelletier and Y. Slaoui, “Revisiting Révész Stochastic Approximation Method for the Estimation of a Regression Function”, ALEA, Lat. Amer. J. Probab. Math. Statist. 6, 63–114 (2009b).
A. Mokkadem and M. Pelletier, “A Generalization of the Averaging Procedure: The Use of Two-Time-Scale Algorithms”, SIAM J. Control Optim. 49 (4), 1523–1543 (2011).
E. A. Nadaraya, “On Estimating Regression”, Theory Probab. Appl. 10, 186–190 (1964).
M. Pelletier, “Asymptotic Almost Sure Efficiency of Averaged Stochastic Algorithms”, SIAM J. Control Optim. 39, 49–72 (2000).
B. T. Polyak, “New Method of Stochastic Approximation Type”, Automat. Remote Control 51, 937–946 (1990).
B. T. Polyak and A. B. Juditsky, “Acceleration of Stochastic Approximation by Averaging”, SIAM J. Control Optim. 30 838–855 (1992).
P. Révész, “Robbins–Monro Procedure in a Hilbert Space and Its Application in the Theory of Learning Processes. I”, Studia Sci.Math.Hung. 8, 391–398 (1973).
P. Révész, “How to Apply the Method of Stochastic Approximation in the Nonparametric Estimation of a Regression Function”, Math. Operationsforsch. Statist., Ser. Statist. 8, 119–126 (1977).
D. Ruppert, “Almost Sure Approximations to the Robbins–Monro and Kiefer–Wolfowitz Processes with Dependent Noise”, Ann. of Probab. 10, 178–187 (1982).
D. Ruppert, “Stochastic Approximation”, in Handbook of Sequential Analysis, Ed. by B. K. Ghosh and P. K. Sen (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1991), pp. 503–529.
J. C. Spall, “A Stochastic ApproximationAlgorithmfor Large-Dimensional Systems in the Kiefer–Wolfowitz Setting”, in Proc. Conference on Decision and Control (IEEE, New York, 1988), pp. 1544–1548.
J. C. Spall, “A One-Measurement Form of Simultaneous Perturbation Stochastic Approximation”, Automatica J. IFAC 33, 109–112 (1997).
G. S. Watson, “Smooth Regression Analysis”, Sankhya Ser. A 26, 359–372 (1964).
G. Yin, “On Extensions of Polyak’s Averaging Approach to Stochastic Approximation”, Stochastics Stochastic Rep. 33, 245–264 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Mokkadem, A., Pelletier, M. The multivariate Révész’s online estimator of a regression function and its averaging. Math. Meth. Stat. 25, 151–167 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1066530716030017
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1066530716030017
Keywords
- stochastic approximation algorithm
- online estimation
- nonparametric regression
- averaging principle
- weak convergence rate