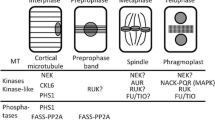
Abstract
The nearest plant homologues of animal protein kinase BRSK were identified using the methods of classical and structural bioinformatics. The selection was performed based on the sequence comparison, results of phylogenetic clustering, and analysis of domain architecture. Spatial structures of human BRSK1 and KIN10 from A. thaliana were compared. The relationship between KIN10 and the regulation of primary microtubule nucleation centers in A. thaliana was revealed. Obvious homology of plant KIN10 and mammalian BRSK1 evidence to suggest that this plant protein kinase is associated with the regulation of the structure and function of primary microtubule nucleation centers and is able to phosphorylate γ-tubulin from Arabidopsis (TUBG1 and TUBG2) at Ser131, affecting the γTuSC monomer structure as well as the γTuRC complex assembly. The effect of the modification on the TUBG1-GACP3 interaction was suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amos, L.A., http://www.els.net/09.04.2010.
Kollman, J.M., Merdes, A., Mourey, L., and Agard, D.A., Microtubule nucleation by-tubulin complexes, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2011, vol. 12, no. 11, pp. 709–721.
Nyporko, A.Yu., Demchuk, O.N., and Blume, Ya.B., Cold adaptation of plant microtubules: structural interpretation of primary sequence changes in a highly conserved region of-tubulin, Cell Biol. Int., 2003, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 241–243.
Karpov, P.A. and Blume, Y.B., Bioinformatic search for plant homologues of animal structural maps in the arabidopsis thaliana genome, in The Plant Cytoskeleton: A Key Tool for Agro-Biotechnology, Blume, Y.B., Baird, W.V., Yemets, A.I., and Breviario, D., Eds, Netherlands: Springer, 2008, pp. 373–397.
Blume, Ya.B., Plant tubulin phosphorylation and its role in cell cycle progression, in The Plant Cytoskeleton: A Key Tool for Agro-Biotechnology, Blume, Y.B., Baird, W.V., Yemets, A.I., and Breviario, D., Eds, Netherlands: Springer, 2008, pp. 145–159.
Karpov, P.A., Nadezhdina, E.S., Yemets, A.I., Matusov, V.G., Nyporko, A.Yu., Shashina, N.Yu., and Blume, Ya.B., Bioinformatic search of plant protein kinases, participating in microtubule protein phosphorylation and cell division regulation, Tsitol. Genet., 2009, vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 63–79.
Karpov, P.A., Yemets, A.I., Matusov, V.G., Nyporko, A.Yu., Nadezhdina, E.S., and Blume, Ya.B., Bioinformatic search for plant homologs of Ste20-like serine/threonine protein kinases, Tsitol. Genet., 2009, vol. 43, no. 6, pp. 68–71.
Bryantseva, S.A., Gavryushina, E.S., Yemets, A.I., Karpov, P.A., Blume, Ya.B., Drygin, Yu.F., and Nadezhdina, E.S., MAST2-like protein kinase from grape Vitis vinifera: cloning of catalytic domain cDNA, Cytol. Genet, 2010, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 227–232.
Karpov, P.A., Nadezhdina, E.S., Yemets, A.I., Matusov, V.G., Nyporko, A.Yu., Shashina, N.Yu., and Blume, Ya.B., Bioinformatic search of plant microtubule- and cell cycle related serine-threonine protein kinases, BMC Genom., 2010, vol. 11, suppl. 1, p. 14. doi 10.1186/1471-2164-11-S1-S14
Karpov, P.A., Rayevsky, A.V., and Blume, Ya.B., Bioinformatic search for plant homologs of the protein kinase Bub1—a key component of the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint, Cytol. Genet, 2010, vol. 44, no. 6, pp. 376–388.
Karpov, P., Raevsky, A., Korablyov, M., and Blume, Ya., Identification of plant homologues of dual specificity Yak1-related kinases, Comp. Biol. J., 2014.
Chen, D. and Vogel, J., SAD kinase keeps centrosomes lonely, Nat. Cell Biol., 2009, vol. 11, no. 9, pp. 1047–1048.
Alvarado-Kristensson, M., Rodriguez, M.J., Silio, V., Valpuesta, J.M., and Carrera, A.C., SADB phosphorylation of γ-tubulin regulates centrosome duplication, Nat. Cell Biol., 2009, vol. 11, no. 9, pp. 1081–1092.
Eklund, G., Lang, S., Glindre, J., Ehlen, A., and Alvarado-Kristensson, M., The nuclear localization of γ-tubulin is regulated by SadB-mediated phosphorylation, J. Biol. Chem., 2014, vol. 289, no. 31, pp. 21360–21373.
UniProt Consortium, The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt), Nucleic Acids Res., 2, vol. 35, pp. D193–D197.
Claverie, J.-M. and Notredame, C., Bioinformatics for Dummies, 2nd ed., New York: Wiley Publ., 2006.
Korf, I., Yandell, M., and Bedell, J., BLAST, Sebastopol: O’Reilly and Associates, 2003.
Larkin, M.A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N.P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P.A., McWilliam, H., Valentin, F., Wallace, I.M., Wilm, A., Lopez, R., Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., and Higgins, D.G., Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0, Bioinformatics, 2007, vol. 23, no. 21, pp. 2947–2948.
Letunic, I., Doerks, T., and Bork, P., Smart: recent updates, new developments and status in 2015, Nucleic Acids Res., 2015, vol. 43, pp. D257–260.
Letunic, I., Copley, R.R., Pils, B., Pinkert, S., Schultz, J., and Bork, P., SMART 5: domains in the context of genomes and networks, Nucleic Acids Res., 2006, vol. 34, pp. D257–D260. doi 10.1093/nar/gkj079
Finn, R.D., Coggill, P., Eberhardt, R.Y., Eddy, S.R., Mistry, J., Mitchell, A.L., Potter, S.C., Punta, M., Qureshi, M., Sangrador-Vegas, A., Salazar, G.A., Tate, J., and Bateman, A., The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future, Nucleic Acids Res., 2016, vol. 44, pp. D279–D285.
DeCastro, E., Sigrist, C.J.A., Gattiker, A., Bulliard, V., Langendijk-Genevaux, P.S., Gasteiger, E., Bairoch, A., and Hulo, N., ScanProsite: detection of PROSITE signature matches and ProRule-associated functional and structural residues in proteins, Nucleic Acids Res., 2006, vol. 34, pp. W362–W365.
Finn, R.D., Attwood, T.K., Babbitt, P.C., Bateman, A., Bork, P., Bridge, A.J., et al., InterPro in 2017—beyond protein family and domain annotations, Nucleic Acids Res., 2017, vol. 45, pp. D190–199.
Hanks, S.K. and Quinn, A.M., Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members, Methods Enzymol., 1991, vol. 200, pp. 38–62.
Atteson, K., The performance of neighbor-joining algorithms of phylogeny reconstruction, in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Jiang, T. and Lee, D., Eds., Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1997, vol. 1276, pp. 101–110.
Nei, M. and Kumar, S., Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics, New York: Oxford Univ. Press, 2000.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., and Tamura, K., MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2016, vol. 33, no. 7, pp. 1870–1874.
Huang, H.D., Lee, T.Y., Tseng, S.W., and Horng, J.T., KinasePhos: a web tool for identifying protein kinasespecific phosphorylation sites, Nucleic Acids Res., 2005, vol. 33, pp. W226–W229.
Yang, J., Yan, R., Roy, A., Xu, D., Poisson, J., and Zhang, Y., The I-TASSER suite: protein structure and function prediction, Nature Methods, 2015, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 7–8.
Eswar, N., Webb, B., Marti-Renom, M.A., Madhusudhan, M.S., Eramian, D., Shen, M., Pieper, U., and Sali, A., Comparative protein structure modeling using MODELLER, Curr. Prot. Bioinform, 2006, suppl. 15, pp. 5.6.1–5.6.30. doi 10.1002/0471250953.bi0506s15.
Kuntal, B.K., Aparoy, P., and Reddanna, P., Easy- Modeller: a graphical interface to MODELLER, BMC Res. Notes, 2010, vol. 3, p. 226.
Hildebrand, P.W., Goede, A., Bauer, R.A., Gruening, B., Ismer, J., Michalsky, E., and Preissner, R., Super- Looper—a prediction server for the modeling of loops in globular and membrane proteins, Nucleic Acids Res., 2009, vol. 37, pp. W571–W574.
Dominguez, C., Boelens, R., and Bonvin, A.M., HADDOCK: a protein-protein docking approach based on biochemical and/or biophysical information, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, vol. 125, no. 7, pp. 1731–1737.
Kollman, J.M., Zelter, A., Muller, E.G., Fox, B., Rice, L.M., Davis, T.N., and Agard, D.A., The structure of the gamma-tubulin small complex: implications of its architecture and flexibility for microtubule nucleation, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2008, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 207–215.
Kollman, J.M., Greenberg, C.H., Li, S., Moritz, M., Zelter, A., Fong, K.K., Fernandez, J.-J., Sali, A., Kilmartin, J., Davis, T.N., and Agard, D.A., Ring closure activates yeast TuRC for species-specific microtubule nucleation, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 2015, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 132–137.
Stacklies, W., Seifert, C., and Graeter, F., Implementation of force distribution analysis for molecular dynamics simulations, BMC Bioinform., 2011, vol. 12, no. 1. doi 10.1186/1471-2105-12-101
Davis, I.W., Leaver-Fay, A., Chen, V.B., Block, J.N., Kapral, G.J., Wang, X., Murray, L.W., Arendall, W.B.III., Snoeyink, J., Richardson, J.S., and Richardson, D.C., MolProbity: all-atom contacts and structure validation for proteins and nucleic acids, Nucleic Acids Res., 2007, vol. 35, pp. W375–383.
Benkert, P., Kunzli, M., and Schwede, T., QMEAN server for protein model quality estimation, Nucleic Acids Res., 2009, vol. 37, pp. W510–W514.
Karpov, P.A., Bryrsun, V.M., Demchuk, O.M., Pydiura, N.O., Ozheredov, S.P., Samofalova, D.A., Spivak, S.I., Yemets, A.I., Kalchenko, V.I., Blume, Ya.B., and Rayevsky, A.V., High-throughput screening of new antimitotic compounds based on CSLabGrid virtual organization, Sci. Innov., 2015, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 92–100.
Pettersen, E.F., Goddard, T.D., Huang, C.C., Couch, G.S., Greenblatt, D.M., Meng, E.C., and Ferrin, T.E., UCSF chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis, J. Comput. Chem., 2004, vol. 25, no. 13, pp. 1605–1612.
Marx, A., Nugoor, C., Panneerselvam, S., and Mandelkow, E., Structure and function of polarity-inducing kinase family MARK/Par-1 within the branch of AMPK/Snf1-related kinases, FASEB J., 2010, vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 1637–1648.
Naz, F., Anjum, F., Islam, A., Ahmad, F., and Hassan, M.I., Microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 4: structure, function, and regulation, Cell Biochem. Biophys., 2013, vol. 67, no. 2, pp. 485–499.
Tassan, J.P. and Le Goff, X., An overview of the KIN1/PAR-1/MARK kinase family, Biol. Cell., 2004, vol. 96, no. 3, pp. 193–199.
Elbert, M., Rossi, G., and Brennwald, P., The yeast par-1 homologs kin1 and kin2 show genetic and physical interactions with components of the exocytic machinery, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2005, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 532–549.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © P.A. Karpov, A.V. Rayevsky, E.E. Krasnoperova, S.V. Isayenkov, A.I. Yemets, Ya.B. Blume, 2017, published in Tsitologiya i Genetika, 2017, Vol. 51, No. 6, pp. 3–11.
About this article
Cite this article
Karpov, P.A., Rayevsky, A.V., Krasnoperova, E.E. et al. Protein kinase KIN10 from Arabidopsis thaliana as a potential regulator of primary microtubule nucleation centers in plants. Cytol. Genet. 51, 415–421 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452717060056
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452717060056