Abstract
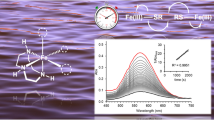
In this paper, the relationship of electronic steric factors in the active site of metallo-β-lactamase and reactivity of cephalosporin antibiotics is studied. The steric energy of the oxygen atom forming a temporary covalent bond in the structure of the transition state of the limiting stage characterizes the reactivity of the compounds. A linear relationship between this value and the macroscopic parameter of the stationary Michaelis–Menten kinetics (catalytic constant kcat) is proposed: the increase in the rate constant is associated with an increase in steric energy. Two-dimensional maps of the steric potential and steric energy density are analyzed.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Mardirossian, N. and Head-Gordon, M., Mol. Phys., 2017, vol. 115, no. 19, p. 2315.
Khrenova, M.G. and Nemukhin, A.V., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2018, vol. 122, no. 4, p. 1378.
Khrenova, M.G., Grigorenko, B.L., Kolomeisky, A.B., and Nemukhin, A.V., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2015, vol. 119, no. 40, p. 12 838.
Khrenova, M.G., Kulakova, A.M., and Nemukhin, A.V., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2018, vol. 16, no. 40, p. 7518.
Liu, S.B., J. Chem. Phys., 2007, vol. 126, 244 103.
von Weizsäcker, C.F., Z. Phys., 1935, vol. 96, p. 431.
Liu, S.B., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2013, vol. 117, no. 5, p. 962.
Wu, W.J., Wu, Z.M., Rong, C.Y., Lu, T., Huang, Y., and Liu, S.B., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2015, vol. 119, no. 29, p. 8216.
Tsirelson, V.G., Stash, A.I., and Liu, S., J. Chem. Phys., 2010, vol. 133, 114 110.
McManus-Munoz, S. and Crowder, M.W., Biochemistry, 1999, vol. 38, no. 5, p. 1547.
Crowder, M.W., Walsh, T.R., Banovic, L., Pettit, M., and Spencer, J., Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 1998, vol. 42, no. 4, p. 921.
Felici, A. and Amicosante, G., Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 1995, vol. 39, no. 1, p. 192.
Bader, R.W.F., Atoms in Molecules: A Quantum Theory, Oxford: Clarendon, 1990.
Sadovnichy, V., Tikhonravov, A., Voevodin, V., and Opanasenko, V., “Lomonosov”: Supercomputing at Moscow State University, in Contemporary High Performance Computing: From Petascale toward Exascale, Boca Raton: CRC, 2013, p. 283.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The research is carried out using the equipment of the shared research facilities of HPC computing resources at Lomonosov Moscow State University [14].
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, project no. 18-74-10056.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by M. Novikova
About this article
Cite this article
Khrenova, M.G., Tomilko, A.V. & Tsirelson, V.G. Electronic Steric Factors in the Active Site of Metallo-β-Lactamase and Reactivity of Cephalosporin Antibiotics. Moscow Univ. Chem. Bull. 74, 106–110 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0027131419030076
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0027131419030076