Abstract
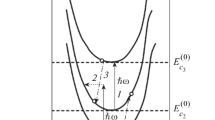
The applicability of the resonant tunneling phenomenon for efficient extraction of photogenerated carriers from quantum wells in the electric field of the p–i–n junction is studied. It was found and shown that the efficient functioning of the considered mechanism of photocarrier extraction from quantum wells requires not only a resonant tunnel channel only for electrons; an identical tunnel channel for holes should be implemented. Quantum-well structures implementing the resonant-tunneling mechanism of photoelectron and photohole extraction are developed and proposed.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Barnham, K.W.J. and Duggan, G., A new approach to high efficiency multibandgap solar cells, J. Appl. Phys., 1990, vol. 67, pp. 3490–3493. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.345339
Barnham, K.W.J., Ballard, I., Connolly, J.P., Ekins-Daukes, N.J., Kluftinger, B.G., Nelson, J., and Rohr, C., Quantum well solar cells, Physica E, 2002, vol. 14, pp. 27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1386-9477(02)00356-9
Green, M.A., Third generation photovoltaics: solar cells for 2020 and beyond, Physica E, 2002, vol. 14, pp. 65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1386-9477(02)00361-2
Jani, O. and Honsberg, C., Absorption and transport via tunneling in quantum-well solar cells, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2006, vol. 90, pp. 3464–3470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2006.01.004
Aeberhard, U., A microscopic theory of quantum well photovoltaics, PhD Dissertation, Zürich: Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, Zürich, 2008.
Brown, G.F. and Wu, J., Third generation photovoltaics, Laser Photon. Rev., 2009, vol. 3, pp. 394–405. https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.200810039
Tsakalakos, L., Ed., Nanotechnology for Photovoltaics, Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2010.
Aeberhard, U. and Morf, R.H., Photovoltaic Effects in Quantum Confined Systems: Microscopic Theory and Numerical Simulation in “Physics of Nanostructured Solar Cells,” Nova Science Publ., 2010.
Aeberhard, U., Spectral properties of photogenerated carriers in quantum well solar cells, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2010, vol. 94, 1897—1902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2010.06.020
Adams, J.G.J., Browne, B.C., Ballard, I.M., Connolly, J.P., Chan, N.L.A., Ioannides, A., Elder, W., Stavri-nou, P.N., Barnham, K.W.J., and Ekins-Daukes, N.J., Recent results for single-junction and tandem quantum well solar cells, Prog. Photovoltaics Res. Appl., 2011, vol. 19, no. 7, pp. 865–877. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.1069
Fara, L. and Yahaguchi, M., Eds., Advanced Solar Cell Materials, Technology, Modeling, and Simulation, Hershey: IGI Global, 2013.
Telenkov, M.P. and Mityagin, Yu.A., Resonant-tunneling structure of quantum wells in the p–i–n photovoltaic element, Bull. Lebedev Phys. Inst., 2013, vol. 40, no. 12, pp. 346–353. https://doi.org/10.3103/S106833561312004X
Aeberhard, U., Simulation of nanostructure-based high-efficiency solar cells: challenges, existing approaches and future directions, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron., 2013, vol. 19, p. 4000411. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTQE.2013.2257701
Aeberhard, U., Simulation of absorption, photogeneration and carrier extraction in nanostructure-based and ultra-thin film solar cell devices beyond the classical picture, Proc. SPIE, 2014, vol. 8981, p. 898103. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2040610
Fujii, H., Toprasertpong, K., Wang, Y., Watanabe, K., Sugiyama, M., and Nakano, Y., 100-period, 1.23-eV bandgap InGaAs/GaAsP quantum wells for high-efficiency GaAs solar cells: toward current-matched Ge-based tandem cells, Prog. Photovoltaics Res. Appl., 2014, vol. 22, no. 7, pp. 784–795. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.2454
Jian-Ya, L., Xin-He, Z., Nai-Ming, W., Xi, C., Bao-Ji, L., Shu-Long, L., and Hui, Y., GaNAs/InGaAs superlattice solar cells with high N content in the barrier grown by all solid-state molecular beam epitaxy, Chin. Phys. Lett., 2015, vol. 32, p. 057301. https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307x/32/5/057301
Fujii, H., Katoh, T., Toprasertpong, K., Sodabanlu, H., Watanabe, K., Sugiyama, M., Nakano, Y., Thickness-modulated InGaAs/GaAsP superlattice solar cells on vicinal substrates, J. Appl. Phys., 2015, vol. 117, h. 154501. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4917535
Nagaraja, K.K., Telenkov, M.P., Kazakov, I.P., Savinov, S.A., and Mityagin, Yu.A., Development of GaAs/AlGaAs quantum well structures providing a resonant tunneling regime in an electric field of p–i–n junction, Mater. Today: Proc., 2016, vol. 3, no. 8, pp. 2744–2747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2016.06.021
Shan, H., Chen, B., Li, X., Lin, Z., Xu, S., Hao, Y., and Zhang, J., The performance enhancement of an InGaN/GaN multiple-quantum-well solar cell by superlattice structure, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2017, vol. 56, no. 11, p. 110305. https://doi.org/10.7567/JJAP.56.110305
Sayed, I.E.H., Jain, N., Steiner, M.A., Geisz, J.F., and Bedair, S.M., 100-period InGaAsP/InGaP superlattice solar cell with sub-bandgap quantum efficiency approaching 80%, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2017, vol. 111, p. 082107. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4993888
Aeberhard, U., Gonzalo, A., and Ulloa, J.M., Photocarrier extraction in GaAsSb/GaAsN type-II QW superlattice solar cells, Appl. Phys. Rev., 2018, vol. 12, p. 213904. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5030625
Welser, R.E., Polly, S.J., Kacharia, M., Fedorenko, A., Sood, A.K., and Hubbard, S.M., Design and demonstration of high efficiency quantum well solar cells employing thin strained superlattices, Sci. Rep., 2019, vol. 9, p. 1395. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50321-x
Telenkov, M.P., Klemmer, P.S., and Mityagin, Yu.A., Resonant tunneling in GaAs/AlGaAs quantum well system for solar photovoltaics, Superlatt. Microstruct., 2020, vol. 140, p. 106472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2020.106472
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project no. 18-02-00874-a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Mityagin, Y.A., Klemmer, P.S., Telenkov, M.P. et al. Kinetics of Photostimulated Transport in Resonant Tunneling Quantum Well Structures in the Electric Field of a p–i–n Photovoltaic Cell. Bull. Lebedev Phys. Inst. 49, 151–157 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068335622060069
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068335622060069