Abstract
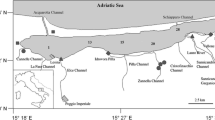
The Lagoon of Venice is a wide, shallow coastal basin that extends for about 50 km along the northwest coast of the Adriatic Sea. The lagoon has been substantially modified through the actions of man over the last century through the artificial control of the hydraulic dynamics of the laggon including the construction of channels to facilitate navigation. The lagoon is subjected to considerable pollutant loading through the drainage of land under cultivation, municipal sewage, and industrial effluents. In this paper are reported the results of observations designed to document recent changes in macroalgal species composition, seasonal cycles of primary producers and nutrient levels, and the effects of the macroalgal community on concentrations of organic and inorganic pollutants. The dominant macroalgae in the lagoon wasUlva rigida, and the levels of plant nutrients and pollutants were influenced by the seasonal cycles of the macroalgal community.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Aspila, K., H. Agemian, andA. S. J. Char. 1976. A semi-automated method for the determination of inorganic, organic and total phosphorus in sediments.Analyst 101:187–197.
Battaglia, B., C. Datei, C. Dejak, G. Gambaretto, G. B. Guarise, G. Perin, E. Vianello, andF. Zingales. 1983. Hydrothermodynamic and Biological Investigations to Determine the Environmental Consequences of the Functionality at Full Working-Order of the ENEL Thermoelectric Plant in Porto Marghera (in Italian). Vol. 4. Regione Veneto, Venezia.
Battiston, L., A. Giommoni, L. Pilan, and S. Vincenzi. 1983. Salinity exchange induced by tide in the Venice Lagoon (in Italian), p. 1–7.In Conference Proceedings on Five Centuries of Water Management in the Venice Territory, Venice.
Bressan, G. 1991. Some space and time changes on the flora and vegetational zones of the northern Adriatic Sea (in Italian), p. 28–29.In F. Galli (ed.), II. Rassegna del Mare “Formazione professionale per la gestione e la protezione dell’ambiente marino.” Italprogram Viareggio, Trieste.
Ceretti, G., U. Ferrarese, andM. Scattolin. 1985. Chironomidae in the Venice Lagoon (in Italian). Arsenale, Venezia. p. 59.
Consorzio Venezia Nuova. 1989. The agricultural pollution in the Venice Lagoon (in Italian). Società Cooperativa ipografica Padova, Padova. 144 p.
Cossu, R., D. Degobbis, R. Donazzolo, E. Maslowska, A. A. Orio, andB. Pavoni. 1983. Nutrient release from the sediments of the Venice Lagoon.Ingegneria Sanitaria 5/6:16–23.
Degobbis, D., M. Gilmartin, andA. A. Orio. 1986. The relation of nutrient regeneration in the sediments of the northern Adriatic to eutrophication, with special reference to the Lagoon of Venice.Science of the Total Environment 56: 201–210.
ENEA. 1988. Integrative elements on the polluting inputs in the lagoon. Final report (in Italian). Report No. 1.3.3, Consorzio Venezia Nuova.
ENEA. 1990. Final report on the actual conditions of the lagoon ecosystem (in Italian). Report No. 1.3.9, Consorzio Venezia Nuova.
Förstner, U. 1989. Contaminated Sediments. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg. 157 p.
Giordani Soika, A. and G. Perin. 1970. Changes of chemical characteristics and population variation in the lagoon sediments in the last twenty years. I. Changes of animal populations (in Italian), p. 135–139.In XI Conference Proceedings. A.N.L.S.B., Venezia.
Giordani Soika, A., andG. Perin. 1974a. The pollution of the Venice Lagoon: Study of the chemical changes and population variations in the lagoon sediments in the last twenty years (in Italian).Bullettino Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Venezia 26:25–68.
Giordani Soika, A. and G. Perin. 1974b. The pollution of the Venice Lagoon: Study of the chemical changes and population variations in the lagoon sediments in the last twenty years (in Italian).Bullettino Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Venezia 26(2). [29 charts of the Venice lagoon]
Golterman, A. L.. 1973. Vertical movement of phosphate in fresh water, p. 509–538.In E. J. Griffith, A. Beeton, J. M. Spencer, and D. T. Mitchell (eds.), Environmental Phosphorus Handbook. Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Henriksen, K., J. I. Hansen, andT. H. Blackburn. 1981. Rates of nitrification, distribution of nitrifying bacteria, and nitrate fluxes in different types of sediment from Danish waters.Marine Biology 61:299–304.
Kornfeldt, R. A. 1982. Relation between nitrogen and phosphorus content of macroalgae and the waters of northern Oresund.Botanica Marina 25:197–201.
Marcomini, A., andW. Giger. 1987. Simultaneous determination of linear alkylbenzenesulfonates, alkylphenol polyethoxilates and nonylphenol by high-performance liquid chromatography.Analytical Chemistry 59:1709–1715.
Marcomini, A., B. Pavoni, A. Sfriso, andA. A. Orio. 1990. Persistent metabolites of alkylphenol polyethoxilates in the marine environment.Marine Chemistry 29:307–323.
Marcomini, A., G. Rampazzo, A. Sfriso, M. Zanette, andA. A. Orio. 1990. Spatial and time distribution of heavy metals in the Venice Lagoon, p. 315–318.In J. Barceló (ed.), Environmental Contamination. CEP Consultants Ltd., Edinburgh, United Kingdom.
Ministry of Public Works, Magistrato alle Acque, Consorzio Venezia Nuova. 1985. Information on the pollution of the Venice Lagoon (in Italian). Venezia. 4 vols.
Miozzi, E. 1980. Venice in the centuries: The lagoon (in Italian). Libeccio, Venezia. 545 p.
Nixon, S. W., J. R. Kelly, B. N. Fumas, C. A. Oviatt, andS. S. Hale. 1979. Phosphorus regeneration and the metabolism of coastal marine bottom communities, p. 219–241.In R. K. Tenore and B. C. Coull (eds.), Marine Benthic Dynamics. University of South Carolina Press, Columbia, South Carolina.
Orio, A. A. andR. Donazzolo. 1987. Toxic and eutrophicating substances in the lagoon and the Gulf of Venice (in Italian).Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere ed Arti 11:149–215.
Oxner, M.. 1962. The Determination of Chlorinity by the Knudsen Method and Hydrographical Tables. G. Manufacturing Co., New York. 63 p.
Pavoni, B., C. Calvo, A. Sfriso, andA. A. Orio. 1990. Time trend of PCB concentrations in surface sediments from a hypertrophic macroalgae populated area of the Lagoon of Venice.Science of the Total Environment 91:13–21.
Pavoni, B., A. Sfriso, andS. Raccanelli. 1991. Quantification of PCBs in environmental samples: Comparison of results obtained with different analytical instruments (GC-ECD, GC-MS) and standards.International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry 44:11–20.
Perin, G. 1975. The Pollution of the Venice Lagoon. Summary of Seven Research Years (in Italian). Atti Tavola Rotonda C.D.A. 47 p.
Pignatti, S.. 1962. Associations of marine algae on the Venice littorals (in Italian).Memorie Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere ed Arti 32:1–134.
Schiffner, V. and A. Vatova. 1938. The algae of the lagoon:Chlorophyceae, Phaeophyceae, Rhodophyceae, Myxophyceae, p. 250.In M. Minio (ed.), The Lagoon of Venice, Vol. 3. Venezia Iin Italian).
Sfriso, A.. 1987. Flora and vertical distribution of macroalgae in the Lagoon of Venice: A comparison with previous studies.Giornale Botanico Italiano 121:69–85.
Sfriso, A., A. Marcomini, andB. Pavoni. 1987. Relationship between macroalgal biomass and nutrient concentrations in a hypertrophic area of the Venice Lagoon.Marine Environmental Research 22:287–312.
Sfriso, A., A. Marcomini, B. Pavoni, andA. A. Orio. 1988b. Macroalgal production and nutrient recycling in the Lagoon of Venice.Ingegneria Sanitaria 5:255–266.
Sfriso, A., A. Marcomini, B. Pavoni, andA. A. Orio 1990a. Eutrophication and macroalgae: The Lagoon of Venice as study case (in Italian).Inquinamento 4:63–78.
Sfriso, A., A. Marcomini, M. Zanette, andA. A. Orio. 1990b. Mapping heavy metals in surface sediment, p. 322–325.In J. Barceló (ed.), Environmental Contamination. CEP Consultants Ltd., Edinburgh, United Kingdom.
Sfriso, A., B. Pavoni, andA. Marcomini. 1989. Macroalgae and phytoplankton standing crops in the central Venice Lagoon: Primary production and nutrient balance.Science of the Total Environment 80:139–159.
Sfriso, A., B. Pavoni, A. Marcomini, andA. A. Orio. 1988a. Annual variation of nutrients in a lagoon hypertrophic area.Marine Pollution Bulletin 19:54–60.
Sfriso, A., S. Raccanelli, B. Pavoni, andA. Marcomini. 1991. Sampling strategies for measuring macroalgal biomass in the shallow waters of the Venice Lagoon.Environmental Technology 12:263–269.
Strickland, J. D. H., andT. R. Parsons. 1972. A practical handbook of seawater analyses. Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Ottawa. 310 p.
Thorne-Miller, B., andM. M. Harlin. 1984. The production ofZostera marina L. and other submerged macrophytes in a coastal lagoon in Rhode Island, U.S.A.Botanica Marina 27: 539–546.
Vatova A.. 1940. The animal benthic associations of the Venice Lagoon (in Italian).Istituto Italo Germanico di Biologia Marina 3:1–25.
Vazzoler, S., F. Costa, andS. Bernardi. 1987. Lagoon of Venice and transfer of fresh water and pollutants (in Italian).Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere ed Arti 11:81–124.
Zanette, M. 1990. Space and time trends of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the central part of the Venice Lagoon. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Venice, Venice.
Zucchetta, G. 1983. The pollution of the Venice Lagoon (in Italian).Ateneo Veneto 21:1–44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sfriso, A., Pavoni, B., Marcomini, A. et al. Macroalgae, nutrient cycles, and pollutants in the Lagoon of Venice. Estuaries 15, 517–528 (1992). https://doi.org/10.2307/1352394
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/1352394