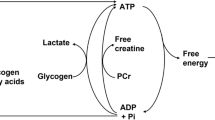
Summary
The anaerobic threshold consists of a lactate threshold and a ventilatory threshold. In some conditions there may actually be 2 ventilatory thresholds.
Much of the work detailing the lacatate threshold is strongly based on blood lactate concentration. Since, in most cases, blood lactate concentration does not reflect production in active skeletal muscle, inferences about the metabolic state of contracting muscle will not be valid based only on blood lactate concentration measurements.
Numerous possible mechanisms may be postulated as generating a lactate threshold. However, it is very difficult to design a study to influence only one variable. One may ask, does reducing F1O2 cause an earlier occurrence of a lactate threshold during progressive exercise by reducing oxygen availability at the mitochondria? By stimulating catecholamine production? By shifting more blood flow away from tissues which remove lactate from the blood? Or by some other mechanism? Processes considered essential to the generation of a lactate threshold include: (a) substrate utilisation in which the ability of contracting muscle cells to oxidise fats reaches maximal power at lactate threshold; and (b) catecholaminergic stimulation, for without the presence of catecholamines it appears a lactate threshold cannot be generated. Other mechanisms discussed which probably enhance the lacate threshold, but are not considered essential initiators are: (a) oxygen limitation; (b) motor unit recruitment order; (c) lactate removal; (d) muscle temperature receptors; (e) metabolic stimulation; and (f) a threshold of lactase efflux.
Some mechanisms reviewed which may induce or contribute to a ventilatory threshold are the effect of: (a) the carotid bodies; (b) respiratory mechanics; (c) temperature; and (d) skeletal muscle receptors. It is not yet possible to determine the hierarchy of effects essential for generating a ventilatory threshold. This may indicate that the central nervous system integrates a broad range of input signals in order to generate a non-linear increase in ventilaion.
Evidence indicates that the occurrence of the lactate threshold and the ventilatory threshold may be dissociated: sometimes the occurrence of the lactate threshold significantly precedes the ventilatory threshold and at other times the ventilatory threshold significantly precedes the lactate threshold. It is concluded that the 2 threshold are not subserved by the same mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlborg G, Felig P. Lactate and glucose exchange across the forearm, legs, and splanchnic bed during and after prolonged leg exercise. Journal of Clinical Investigations 69: 45–54, 1982
Ahlborg G, Hangenfeldt L, Wahren J. Substrate utilization by the inactive leg during oneleg or arm exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 39: 718–723, 1975
Alberti KGMM, Cuthbert C. The hydrogen ion in normal metabolism: a review. In Metabolic acidosis, Ciba Foundation Symposium 87, pp. 1–19, 1982
Arnall DA, Marker JC, Conlee RK, Winder WW. Effect of infusing epinephrine on liver and muscle glycogenosis during exercise in rats. American Journal of Physiology 250: E641–E649, 1986
Ashby B, Frieden C. Interaction of AMP-aminohydrolase with myosin and its subfragments. Journal of Biological Chemistry 252: 1869–1872, 1977
Ashby B, Freiden C, Bischoff R. Immunofluorescent and histochemical localization of AMP deaminase in skeletal muscle. Journal of Cell Biology 81: 361–373, 1979
Asmussen E. Control of ventilation in exercise. In Terjung (Ed.) Exercise and sport sciences reviews, American College of Sports Medicine Series 11, pp. 24–54, 1983
Asmussen E, Johansen SH, Jorgensen M, Nielsen M. On the nervous factors controlling respiration and circulation during exercise. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 63: 343–350, 1965
Aunola S, Rusko H. Aerobic and anaerobic thresholds determined from venous lactate or from ventilation and gas exchange in relation to muscle fiber composition. International Journal of Sports Medicine 7: 161–166, 1986
Babij P, Matthews SM, Rennie MJ. Changes in blood ammonia, lactate and amino acids in relation to workload during bicycle ergometer exercise in man. European Journal of Applied Physiology 50: 405–411, 1983
Baldwin KM, Campbell PJ, Cooke DA. Glycogen, lactate, and alanine changes in muscle fiber types during graded exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 43: 288–291, 1977
Baldwin KM, Hooker AM, Herrick RE. Lactate oxidative capacity in different types of muscle. Biochemical and Biophysical Communications 83: 151–157, 1978
Band DM, Linton RAF, Kent R, Kurer FL. The effect of peripheral chemodenervation on the ventilatory response to potassium. Respiration Physiology 60: 217–225, 1985
Banister EW, Allen ME, Mekjavic IB, Singh AK, Legge B, et al. The time course of ammonia and lactate accumulation in blood during bicycle exercise. European Journal of Applied Physiology 51: 195–202, 1983
Banister EW, Taunton JE, Patrick T, Ofarsagd P, Duncan WR. Effect of oxygen at high pressure at rest and during severe exercise. Respiration Physiology 10: 74–84, 1970
Barbee RW, Stainsby WN, Chirtel SJ. Dynamics of O2, CO2, lactate and acid exchange during contractions and recovery. Journal of Applied Physiology 54: 1687–1692, 1983
Baron PG, Iies RA, Cohen RD. Effect of varying PC02 on intracellular pH and lactate consumption in the isolated perfused rat liver. Clinical Science and Molecular Medicine 55: 175–181, 1978
Barshop BA, Frieden C. Analysis of the interaction of rabbit skeletal muscle adenylate deaminase with myosin subfragments. Journal of Biological Chemistry 259: 60–66, 1984
Barter TJ, Clarkson PM, Melchionda A. The relationship of forearm flexion isometric strength, endurance, and fiber composition; and the effect of heating. International Journal of Sports Medicine 3: 159–162, 1982
Bass A, Brdiczka D, Eyer P, Hofer S, Pette D. Metabolic differentiation of distinct muscle types at the level of enzymatic organization. European Journal of Biochemistry 10: 198–206, 1969
Bassols AM, Carreras J, Cusso R. Changes in glucose 1,6-bis-phosphate content in rat skeletal muscle during contraction. Biochemical Journal 240: 747–751, 1986
Bauer HP, Birkel G, Hofer HW. The concentrations of glucose 1,6-bisphosphate and other regulatory metabolites, and the activities of enzymes of the glycogen in the perfused rabbit psoas muscle. International Journal of Biochemistry 18: 73–77, 1986a
Bauer HP, Reichmann H, Hofer W. Perfusion of the psoas muscle of the rabbit: metabolism of a homogeneous muscle composed of ‘fast glycolytic’ fibres. International Journal of Biochemistry 18: 67–72, 1986b
Beitner R, Haberman A, Nordenberg J. The effect of epinephrine and dibutyryl cyclic AMP on glucose 1,6,-biphosphate levels and the activities of hexokinase, phosphofructokinase and phosphoglucomutase in the isolated rat diaphragm. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 10: 135–147, 1978
Beicastro AN, Bonen A. Lactic acid removal rates during controlled and uncontrolled recovery exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 39: 932–936, 1975
Benade AJS, Heisler N. Comparison of efflux rates of hydrogen and lactate ions from isolated muscles in vitro. Respiration Physiology 32: 369–380, 1978
Bergstrom J, Hermansen L, Hultman E, Saltin B. Diet, muscle glycogen and physical performance. Acta Physiologica Scandinavia 71: 140–150, 1967
Bergstrom J, Hultman E. A study of the glycogen metabolism during exercise in man. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigations 19: 218–228, 1967
Bessman SP, Carpenter CL. The creatine-creatine phosphate energy shuttle. Annual Review of Biochemistry 54: 831–862, 1985
Bhambhani Y, Singh M. Ventilatory thresholds during a graded exercise test. Respiration 47: 120–128, 1985
Birkel G, Bauer HP, Hofer HW. Phosphofructokinase activity and the binding of enzymes to glycogen particles in the perfused psoas muscle of the rabbit. International Journal of Biochemistry 18: 79–83, 1986
Bolstad G, Ersland A. Energy metabolism in different human skeletal muscles during voluntary isometric contractions. European Journal of Applied Physiology 38: 171–179, 1978
Borison HL, Gonsalves SF, Montgomery SP, McCarthy LE. Dynamics of respiratory VT response to isocapnic pHa forcing in chemodenervated cats. Journal of Applied Physiology 45: 502–511, 1978
Brooks GA. Anaerobic threshold: review of the concept and directions for future research. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 17: 22–31, 1985
Buono MJ, Clancy TR, Cook JR. Blood lactate and ammonium ion accumulation during graded exercise in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology 57: 135–139, 1984
Buono MJ, Roby FB. Acid-base, metabolic, and ventilatory responses to repeated bouts of exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 53: 436–439, 1982
Bylund-Fellenius AC, Walker PM, Elander A, Holm S, Holm J, et al. Energy metabolism in relation to oxygen partial pressure in human skeletal muscle during exercise. Biochemical Journal 200: 247–255, 1981
Caiozzo V, Davis J, Ellis J, Azus J, Vandagriff R, et al. A comparison of gas exchange indices used to detect the anaerobic threshold. Journal of Applied Physiology 53: 1184–1189, 1982
Callow M, Morton A, Guppy M. Marathon fatigue: the role of plasma fatty acids, muscle glycogen and blood glucose. European Journal of Applied Physiology 55: 654–661, 1986
Carlson KI, Marker JC, Arnall DA, Terry ML, Yang HT, et al. Epinephrine is unessential for stimulation of liver glycogenosis during exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 58: 544–548, 1985
Cartier L-J, Gollnick PD. Sympathoadrenal system and activation of glycogenosis during muscular activity. Journal of Applied Physiology 58: 1122–1127, 1985
Celsing F, Ekblom B. Anemia causes a relative decrease in blood lactate concentration during exercise. European Journal of Applied Physiology 55: 74–78, 1986
Chance B, Quistorff B. Study of tissue O2 gradients by single and multiple indicators. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 94: 331–338, 1978
Chasiotis D. Effects of adrenaline infusion on cAMP and glycogen Phosphorylase in fast-twitch and slow-twitch rat muscles. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 125: 537–540, 1985
Chirtel SJ, Barbee RW, Stainsby WN. Net O2, CO2, lactate and acid exchange by muscle during progressive working contractions. Journal of Applied Physiology 56: 161–165, 1984
Christensen NJ, Galbo H. Sympathetic nervous activity during exercise. Annual Review of Physiology 45: 139–153, 1983
Clancy RL, Gonzalez NC, Fenton RA. Effect of beta-adrenore-ceptor blockade on rat cardiac skeletal pH. American Journal of Physiology 230: 959–964, 1976
Clausen JP. Circulatory adjustments to dynamic exercise and effect of physical training in normal subjects and in patients with coronary artery disease. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases 18: 459–495, 1976
Clausen JP, Klausen K, Rasmussen B, Trap-Jensen J. Central and peripheral circulatory changes after training of the arms of legs. American Journal of Physiology 255: 675–682, 1973
Clifford PS, Litzow JT, von Colditz JH, Coon RL. Effect of chronic pulmonary denervation on ventilatory responses to exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 61: 603–610, 1986
Cohen P. The role of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase in the regulation of glycogen metabolism in mammalian skeletal muscle. Current Topics in Cellular Regulation 14: 117–196, 1978
Connett RJ, Gayeski TEJ, Honig CR. Lactate accumulation in fully aerobic, working, dog gracilis muscle. American Journal of Physiology 246: H120–H128, 1984
Connett RJ, Gayeski TE, Honig CR. Energy sources in fully aerobic rest-work transitions: a new role for glycolysis. American Journal of Physiology 248: H922–H929, 1985
Connett RJ, Gayeski TEJ, Honig CR. Lactate efflux is unrelated to intracellular P02 in a working red muscle in situ. Journal of Applied Physiology 61: 402–408, 1986
Costill DL, Coyle E, Dalsky G, Evans W, Fink W, et al. Effects of elevated plasma FFA and insulin on muscle glycogen usage during exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 43: 695–699, 1977
Cross BA, Davey A, Guz A, Katona PG, Maclean M, et al. The pH oscillations in arterial blood during exercise; a potential signal for the ventilatory response in the dog. Journal of Physiology 329: 57–73, 1982
Cunningham DJC, O’Riordan JLH. The effect of a rise in the temperature of the body on the respiratory response to carbon dioxide at rest. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology 42: 329–345, 1957
Davies CTM, Few J, Foster KG, Sargeant AJ. Plasma catecholamine concentration during dynamic exercise involving different muscle groups. European Journal of Applied Physiology 32: 195–206, 1974
Davies CTM, Young K. Effect of temperature on the contractile properties and muscle power of triceps surae in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology 55: 191–195, 1983
Davies ST, Iber C, Keene SA, McArthur CD, Path MJ. Effect of respiratory alkalosis during exercise on blood lactate. Journal of Applied Physiology 61: 948–952, 1986
Davis HA, Gass GC. The anaerobic threshold as determined before and during lactic acidosis. European Journal of Applied Physiology 47: 141–149, 1981
Davis JA. Anaerobic threshold: review of the concept and directions for future research. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 17: 6–18, 1985
Davis JA, Vodak P, Wilmore JH, Vodak J, Kurtz P. Anaerobic threshold and maximal aerobic power for three modes of exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 41: 544–550, 1976
Davis JA, Whipp BJ, Lamarra N, Huntsman DJ, Frank MH, et al. Effect of ramp slope on determination of aerobic parameters from the exercise test. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 14: 339–343, 1982
Dejours P. Control of respiration by arterial chemoreceptors. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 109: 682–695, 1963
Dempsey JA, Vidruk EH, Mitchell GS. Pulmonary control systems in exercise: update. Federation Proceedings 44: 2260–2270, 1985
Depocas F, Minaire Y, Chatonnet J. Rates of formation and oxidation of lactic acid in dogs at rest and during moderate exercise. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 47: 603–610, 1969
Donovan CM, Brooks GA. Endurance training affects lactate clearance, not lactate production. American Journal of Physiology 244: E83–E92, 1983
Dudley GA, Staron RS, Murray TF, Hagerman FC, Luginbuhl A. Muscle fiber composition and blood ammonia levels after intense exercise in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology 54: 582–586, 1983
Dudley GA, Terjung RL. Influence of acidosis on AMP deaminase activity in contracting fast-twitch muscle. American Journal of Physiology 248: C43–C50, 1985
Eagle GR, Scopes RK. Inhibition of muscle Phosphorylase α by natural components of the sarcoplasm. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 210: 540–548, 1981
Eldridge FL. Relationship between turnover rate and blood concentration of lactate in exercising dogs. Journal of Applied Physiology 39: 231–234, 1975
Eldridge FL, Millhorn DE, Kiley JP, Waldrop TG. Stimulation by central command of locomotion, respiration and circulation during exercise. Respiration Physiology 59: 313–337, 1985
Essen B, Haggmark. Lactate concentration in type I and II muscle fibres during muscular contraction in man. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 95: 344–346, 1975
Essen B, Pernow B, Gollnick PD, Saltin B. Muscle glycogen content and lactate uptake in exercising muscles. In Howald & Poortmans (Eds) Metabolic adaptation to prolonged physical exercise, pp. 130–134, J R Birkhauser Verlag, Basel, 1975
Exton JH, Park CR. Control of gluconeogenesis in liver. I. General features of gluconeogenesis in the perfused livers of rats. Journal of Biological Chemistry 242: 2622–2636, 1967
Farrell SW, Ivy JL. Lactate acidosis and the increase in V̇2 during incremental exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 62: 1551–1555, 1987
Favier RJ, Constable SH, Chen M, Holloszy JO. Endurance exercise training reduces lactate production. Journal of Applied Physiology 61: 885–889, 1986
Feraudi M, Kolb J, Hassel M, Weicker H. ATP-ADP-dependent phosphorylations of glycolysis metabolites, creatine and glycerol: their compartition and thermodynamic relationship in gastrocnemius muscle cell of exercised guinea pigs. Archives Internationale de Physiologie et de Biochimie 91: 351–360, 1983
Fishbein WN, Armbrustmacher VW, Griffen JL. Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency: a new disease of muscle. Science 200: 545–548, 1978
Fishbein WN, Armbrustmacher VW, Griffen JL, Davis JL, Foster WD. Levels of adenylate deaminase, adenylate kinase and creatinase in frozen human muscle biopsy specimens relative to type 1-type 2 fiber distribution: evidence for a carrier state of myoadenylate deaminase deficiency. Annals of Neurology 15: 271–277, 1984
Flandrois R, Favier R, Pequignot JM. Role of adrenaline in gas exchanges and respiratory control in the dog at rest and exercise. Respiration Physiology 30: 291–303, 1977
Frisk-Holmberg M, Jorfeldt L, Juhlin-Dannfelt A. Metabolic effects in muscle during antihypertensive therapy with β1-and β1/β2-adrenoceptor blockers. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 30: 611–618, 1981
Gaesser GA, Poole DC. Lactate and ventilatory thresholds: disparity in time course of adaptations to training. Journal of Applied Physiology 61: 999–1004, 1986
Gaesser GA, Poole DC, Gardner BP. Dissociation between V̇2max and ventilatory responses to endurance training. European Journal of Applied Physiology 53: 242–247, 1984
Galbo H, Richter EA, Christensen NJ, Holst JJ. Sympathetic control of metabolic and hormonal responses to exercise in rats. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 102: 441–449, 1978
Gallagher CG, Brown E, Younes M. Breathing pattern during maximal exercise and during submaximal exercise with hypercapnia. Journal of Applied Physiology 63: 238–244, 1987
Gayeski TEJ, Connett RJ, Honig CR. Oxygen transport in rest-work transition illustrates new functions for myoglobin. American Journal of Physiology 248: H914–H921, 1985
George P, Rutman RJ. The ‘high energy phosphate bond’ concept. Progress in Biophysics and Biophysical Chemistry 10: 1–53, 1960
Gevers W. Generation of protons by metabolic processes in heart cells. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 9: 867–874, 1977
Gollnick PD. Metabolic regulation in skeletal muscle: influence of endurance training as exerted by mitochondrial protein concentration. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 128 (Suppl. 556): 53–66, 1986
Gollnick PD, Riedy M, Quintinskie JJ, Bertocci LA. Differences in metabolic potential of skeletal muscle fibres and their significance for metabolic control. Journal of Experimental Biology 115: 191–199, 1985
Goodman MN, Lowenstein JM. The purine nucleotide cycle: studies of ammonia production by skeletal muscle in situ and in perfused preparations. Journal of Biological Chemistry 252: 5054–5060, 1977
Gorski J. Glycogenolytic effect of adrenaline in skeletal muscle of rats adapted to endurance exercise. Acta Physiologica Polonica 29: 437–441, 1978
Gorski J, Sikorska J. Effect of pH and lactate on glucose uptake by red and white skeletal muscle in vitro. Acta Physiologica Polonica 28: 441–444, 1977
Graham TE, Barclay JK, Wilson BA. Skeletal muscle lactate release and glycolytic intermediates during hypercapnia. Journal of Applied Physiology 60: 568–575, 1986
Graham TE, Sinclair DG, Chapler CK. Metabolic intermediates and lactate diffusion in active dog skeletal muscle. American Journal of Physiology 231: 766–771, 1976
Graham T, Sjogaard G, Lollgen H, Saltin B. NAD in muscle of man at rest and during exercise. Pflügers Archiv 376: 35–39, 1978
Green HJ, Hughson RL. Letter to the editor-in-chief. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 17: 621–622, 1985
Green HJ, Hughson RL, Orr GW, Ranney DA. Anaerobic threshold, blood lactate, and muscle metabolites in progressive exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 54: 1032–1038, 1983
Griffiths JR, Rahim ZHA. Glycogen as a fuel for skeletal muscle. Biochemical Society Transactions 6: 530–534, 1978
Hagberg JM, Coyle EF, Carroll JE, Miller JM, Martin WH, et al. Exercise hyperventilation in patients with McArdle’s disease. Journal of Applied Physiology 52: 991–994, 1982
Heigenhauser GJF, Sutton JR, Jones NL. Effect of glycogen depletion on the ventilatory response to exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 54: 470–474, 1983
Heilmeyer Jr LMG, Meyer F, Haschke RH, Fischer EH. Control of Phosphorylase activity in a muscle glycogen particle. II. Activation by calcium. Journal of Biological Chemistry 245: 6649–6656, 1970
Heisler N. Kinetics of the efflux of hydrogen and lactate ions from isolated rat diaphragms stimulated in anoxia. (Abstract.) Pflüger Archiv 339: R51, 1973
Heistad DD, Wheeler RC, Mark AL, Schmid PG, Abboud FM. Effects of adrenergic stimulation on ventilation in man. Journal of Clinical Investigation 51: 1469–1475, 1972
Helmrich E, Cori CF. Regulation of glycolysis in muscle. In Weber (Ed.) Advances in enzyme regulation, pp. 91–107, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1965
Henneman E. Relation between size of neurons and their susceptibility to discharge. Science 126: 1345–1347, 1957
Henneman E, Mendell LM. Functional organization of motorneuron pool and its inputs. In Brookhart & Mountcastle (Eds) Handbook of physiology, section 1: The nervous system, Vol. II, Motor control, part 1, pp. 423–507, American Physiological Society, Bethesda, 1981
Henneman E, Somjen G, Carpenter DO. Functional significance of cell size in spinal motor neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology 28: 560–580, 1965
Henriksson J. Training induced adaptation of skeletal muscle and metabolism during submaximal exercise. Journal of Physiology 270: 661–675, 1977
Henriksson J, Reitman JS. Time course of changes in human skeletal muscle succinate dehydrogenase and cytochrome oxidase activities and maximal oxygen uptake with physical activity and inactivity. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 99: 91–97, 1977
Henritze J, Weltman A, Schurrer RL, Barlow K. Effects of training at and above the lactate threshold on the lactate threshold and maximal oxygen uptake. European Journal of Applied Physiology 54: 84–88, 1985
Hermansen L, Osnes J-B. Blood and muscle pH after maximal exercise in man. Journal of Applied Physiology 32: 304–308, 1972
Hermansen L, Stensvold I. Production and removal of lactate during exercise in man. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 86: 191–201, 1972
Hespel P, Lijnen P, Vanhees L, Fagard R, Fiocchi R, et al. Differentiation of exercise-induced metabolic response during selective β1-and β2-antagonism. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 18: 186–191, 1986
Hesse B, Kanstrup I-L, Christensen NJ, Ingemann-Hansen T, Hansen JF, et al. Reduced norepinephrine response to dynamic exercise in human subjects during O2 breathing. Journal of Applied Physiology 51: 176–178, 1981
Hill AV, Lupton H. Muscular exercise, lactic acid and supply and utilization of oxygen. Quarterly Journal of Medicine 16: 135–171, 1923
Hirche H, Grun D, Waller W. Utilization of carbohydrates and free fatty acids by the gastrocnemius of the dog during long lasting rhythmical exercise. Pflügers Archiv 321: 121–132, 1970
Hirche H, Hombach V, Langohr HD, Wacker U, Busse J. Lactic acid permeation rate in working gastrocnemii of dogs during metabolic alkalosis and acidosis. Pflügers Archiv 356: 209–222, 1975
Hirche U, Wacker U, Langohr HD. Lactic acid formation in the working gastrocnemius of the dog. Internationale Zeitschrift für Angewandte Physiologie 30: 52–64, 1971
Hochachka PW. Fuels and pathways as designed systems for support of muscle work. Journal of Experimental Biology 115: 149–164, 1985
Hochachka PW, Mommsen TP. Protons and anaerobiosis. Science 219: 1391–1397, 1983
Hogan MC, Welch HG. Effect of altered arterial O2 tensions on muscle metabolism in dog skeletal muscle during fatiguing work. American Journal of Physiology 251: C216–C222, 1986
Hogan MC, Welch HG. Effect of varied lactate levels on bicycle ergometer performance. Journal of Applied Physiology 57: 505–513, 1984
Holloszy JO. Biochemical adaptations in muscle: effects of exercise on mitochondrial oxygen uptake and respiratory enzyme activity in skeletal muscle. Journal of Biological Chemistry 212: 2278–2282, 1967
Holloszy JO. Biochemical adaptations to exercise: aerobic metabolism. In Wilmore (Ed.) Exercise and sport sciences reviews, Vol, vn1, pp. 45–72, Academic Press, New York
Holloszy JO. Adaptations of muscular tissue to training. Progress in Cardiovascular Disease 18: 445–458, 1976
Hoppeler H, Hudlicka O, Uhlmann E. Relationship between mitochondria and oxygen consumption in isolated cat muscles. Journal of Physiology 385: 661–675, 1987
Horita T, Ishiko T. Relationships between muscle lactate accumulation and surface EMG activities during isokinetic contractions in man. European Journal of Applied Physiology 56: 18–23, 1987
Horn RS, Haugaard ES, Haugaard N. The mechanism of the inhibition of glycolysis by oxygen in rat heart homogenate. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 99: 549–552, 1965
Hubbard JL. The effect of exercise on lactate metabolism. Journal of Physiology 231: 1–18, 1973
Hughes EF, Turner SC, Brooks GA. Effects of glycogen depletion and pedalling speed on ‘anaerobic threshold’. Journal of Applied Physiology 52: 1598–1607, 1982
Hughson RL, Weisiger KH, Swanson GD. Blood lactate concentration increases as a continuous function in progressive exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 62: 1975–1981, 1987
Hussain SNA, Pardy RL, Dempsey JA. Mechanical impedance as determinant of inspiratory neural drive during exercise in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology 59: 365–375, 1985
Huszczuk A, Whipp BJ, Oren A, Shors EC, Pokorski M, et al. Ventilatory responses to partial cardiopulmonary bypass at rest and exercise in dogs. Journal of Applied Physiology 61: 575–583, 1986
Idstrom J-P, Subramanian VH, Chance B, Schersten T, Bylund-Fellenius AC. Oxygen dependence of energy metabolism in contracting and recovering rat skeletal muscle. American Journal of Physiology 248: H40–H48, 1985
Issekutz B, Miller HI, Rodahl K. Lipid and carbohydrate metabolism during exercise. Federation Proceedings 25: 1415–1420, 1966
Issekutz Jr B. Effect of β-adrenergic blockade on lactate turnover in exercising dogs. Journal of Applied Physiology 57: 1754–1759, 1984
Ivy JL, Costili DL, Van Handel PJ, Essig DA, Lower RW. Alteration in the lactate threshold with changes in substrate availability. International Journal of Sports Medicine 2: 139–142, 1981
Ivy JL, Withers RT, Van Handel PJ, Elger DH, Costili DL. Muscle respiratory capacity and fiber type as determinants of the lactate threshold. Journal of Applied Physiology 48: 523–527, 1980
Jacobs I, Kaiser P. Lactate in blood, mixed skeletal muscle, and FT or ST fibres during cycle exercise. Acta Physiologica Scaninavica 114: 461–466, 1982
Jacobus WE. Respiratory control and the integration of heart highenergy phosphate metabolism by mitochondrial creatine kinase. Annual Review of Biochemistry 54: 707–725, 1985
Jansson E, Hjemdahl P, Kaijser L. Diet induced changes in sympathoadrenal activity during submaximal exercise in relation to substrate utilization in man. Acta Physiologica Scandinavia 114: 171–178, 1982
Jansson E, Hjemdahl P, Kaijser L. Epinephrine-induced changes in muscle carbohydrate metabolism during exercise in male subjects. Journal of Applied Physiology 60: 1466–1470, 1986
Javaheri SA, Clendening A, Papadakis N, Brody JS. Changes in brain surface pH during acute isocapnic metabolic acidosis and alkalosis. Journal of Applied Physiology 51: 276–281, 1981
Jeyaranjan R, Goode R, Beamish S, Duffin J. The contribution of peripheral chemoreceptors to ventilation during heavy exercise. Respiration Physiology 68: 203–213, 1987
Jezova D, Vigas M, Tatar P, Kvetnansky R, Nazar K, et al. Plasma testosterone and catecholamine responses to physical exercise of different intensities in men. European Journal of Physiology 54: 62–66, 1985
Jobsis FF, Stainsby WN. Oxidation of NADH during contractions of circulated mammalian skeletal muscle. Respiration Physiology 4: 292–300, 1968
Joels N, White H. The contribution of the arterial chemoreceptors to the stimulation of respiration by adrenaline and noradrenaline in the cat. Journal of Physiology 197: 1–23, 1968
Jones NL. Hydrogen ion balance during exercise. Clinical Science 59: 85–91, 1980
Jones NL, Heigenhauser GJF, Kuksis A, Matsos CG, Sutton JR, et al. Fat metabolism in heavy exercise. Clinical Science 59: 469–478, 1980
Jones NL, McHardy GJR, Naimark A, Campbell EJM. Physiological dead space and alveolar-arterial gas pressure differences during exercise. Clinical Science 31: 19–29, 1966
Jong Y-SA, Davis EJ. Reconstruction of steady state in cell-free systems: interactions between glycolysis and mitochondrial metabolism; regulation of the redox and phosphorylation states. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 222: 179–191, 1983
Jorfeldt L. Metabolism of L (+)-lactate in human skeletal muscle during exercise. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica (Suppl. 338): 1–67, 1970
Jorfeldt L, Juhlin-Dannfelt A, Karlsson J. Lactate release in relation to tissue lactate in human skeletal muscle during exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 44: 350–352, 1978
Kaehny WD, Jackson JT. Respiratory response to HCl acidosis in dogs after carotid body denervation. Journal of Applied Physiology 46: 1138–1142, 1979
Kaijser L. Limiting factors for aerobic muscle performance. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica (Suppl. 346): 1–96, 1970
Karlsson J, Nordesjo L-O, Jordfeldt L, Saltin B. Muscle lactate, ATP, and CP levels during exercise after physical training in man. Journal of Applied Physiology 33: 199–203, 1972
Katz A, Sahlin K, Juhlin-Dannfelt A. Effect of β-adrenoceptor blockade on H+ and K+ flux in exercising humans. Journal of Applied Physiology 59: 336–341, 1985
Kaufman MP, Rybicki KJ. Muscular contraction reflexly relaxes tracheal smooth muscle in dogs. Respiration Physiology 56: 61–72, 1984
Kindermann W, Simon G, Keul J. The significance of the aerobic-anaerobic transition for the determination of work load intensities during endurance training. European Journal of Applied Physiology 42: 25–34, 1979
Kniffki KD, Mense S, Schmidt RF. Muscle receptors with fine afferent fibers which may evoke circulatory reflexes. Circulation Research 48 (Suppl. 1): 1-25–1-31, 1981
Knuttgen HG, Saltin B. Muscle metabolites and oxygen uptake in short-term submaximal exercise in man. Journal of Applied Physiology 32: 690–694, 1972
Kobayashi K, Necly JR. Control of maximum rates of glycolysis in rat cardiac muscle. Circulation Research 44: 166–175, 1979
Kotchen TA, Hartley LH, Rice TW, Moughey EH, Jones LG, et al. Renin, norepinephrine, and epinephrine responses to graded exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 31: 178–184, 1971
Kozlowski S, Brezinska Z, Kruk B, Kaciuba-Uscilko H, Greenleaf JE et al. Exercise hyperthermia as a factor limiting physical performance; temperature effect on muscle metabolism. Journal of Applied Physiology 59: 766–773, 1985
Kozlowski S, Brezinska Z, Nazar K, Turlejska E. Carbohydrate availability for the brain and muscles as a factor modifying sympathetic activity during exercise in dogs. In Poortmans & Niset (Eds) Biochemistry of exercise IV, pp. 54–62, University Park Press, Baltimore, 1979
Kozlowski S, Nazar K, Brzezinska Z, Stephens D, Kaciuba-Uscilko J, et al. Mechanism of sympathetic activation during prolonged physical exercise in dogs. The role of hepatic glucore-ceptors. Pflügers Archiv 399: 63–67, 1983
Kruk B, Kaciuba-Uscilko H, Nazar K, Greenleaf JE, Kozlowski S. Hypothalamic, rectal, muscle temperatures in exercising dogs: effect of cooling. Journal of Applied Physiology 58: 1444–1448, 1985
Kula RW, Brumback RA, Engel WK, Line BR. Ischemic contracture in muscle phosphylase deficiency: clinical scanning and histochemical autoradiographic studies. Abstract. Neurology 27: 401–402, 1977
Lehmann M, Berg A, Keul J. Sex-related differences in free plasma catecholamines in individuals of similar performance ability during graded ergometrie exercise. European Journal of Applied Physiology 55: 54–58, 1986
Lehmann M, Kapp R, Himmelsbach M, Keul J, Time and intensity dependent catecholamine responses during graduated exercise as an indicator of fatigue and exhaustion. In Knuttgen et al. (Eds) Biochemistry of exercise, Vol. 13, pp. 738–748, Human Kinetics Publishers, Champaign, Illinois, 1983
Lehmann M, Keul J, Berg A, Stippig S. Plasma catecholamines and aerobic-anaerobic capacity in women during graduated treadmill exercise. European Journal of Applied Physiology 46: 305–315, 1981
Lewis S, Thompsen P, Areskog N-H, Vodak P, Marconyak M, et al. Transfer effects or endurance training to exercise with untrained limbs. European Journal of Applied Physiology 44: 25–34, 1980
Lind FG. Respiratory drive and breathing pattern during exercise in man. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica (Suppl. 533): 1–47, 1984
Linton RAF, Band BM. The effect of potassium on carotid chemoreceptor activity and ventilation in the cat. Respiration Physiology 59: 65–70, 1985
Linton RAF, Lim M, Wolff CB, Wilmshurst P, Band DM. Arterial plasma potassiuim measured continuously during exercise in man. Clinical Science 67: 427–431, 1984
Lloyd MH, Iles RA, Simpson BR, Strunin JM, Layton JM, et al. The effect of simulated metabolic acidosis on intracellular pH and lactate metabolism in the isolated perfused rat liver. Clinical Science 45: 543–549, 1973
Mackova EV, Melichna J, Vondra K, Jurimae T, Paul T, et al. The relationship between anaerobic performance and muscle metabolic capacity and fibre distribution. European Journal of Applied Physiology 54: 413–415, 1985
Mahler M. First-order kinetics of muscle oxygen consumption, and an equivalent proportionality between QO2 and phos-phorylcreatine level: implications for the control of respiration. Journal of General Physiology 86: 135–165, 1985
Mainwood GW, Worsley-Brown P. The effects of extracellular pH and buffer concentration on the efflux of lactate from frog sartorius muscle. Journal of Physiology 250: 1–22, 1975
Manhem P, Lecerof H, Hokfelt B. Plasma catecholamine levels in the coronary sinus, the left renal vein and peripheral vessels in healthy males at rest and during exercise. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 104: 364–369, 1978
Marrin D, Gledhill N. Effect of the low exercise ventilation observed in athletes on endurance performance. (Abstract). Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 18: S84–S85, 1986
Martin BJ, Sparks KE, Zwillich CW, Weil JV. Low exercise ventilation in endurance atheletes. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 11: 181–185, 1979
Martin BJ, Weil JV. CO2 and exercise tidal volume. Journal of Applied Physiology 46: 322–325, 1979
McArdle B. Myopathy due to a defect in muscle glycogen breakdown. Clinical Science 10: 13–18, 1951
McCloskey DI, Mitchell JH. Reflex cardiovascular and respiratory responses originating in exercising muscle. Journal of Physiology 224: 173–186, 1972
McGilvery RW. The use of fuels for muscular work. In Howald & Poortmans (Eds) Metabolic adaptation to prolonged physical exercise, pp. 12–30, J.R. Birkhauser Verlag, Basel, 1975
Meyer RA, Dudley GA, Terjung RT. Ammonia and IMP in different skeletal muscle fibers after exercise in rats. Journal of Applied Physiology 49: 1037–1041, 1980
Meyer RA, Terjung RL. Differences in ammonia and adenylate metabolism in contracting fast and slow muscle. American Journal of Physiology 237: C111–C118, 1979
Meyer RA, Terjung RL. AMP deamination and IMP reamination in working skeletal muscle. American Journal of Physiology 239: C32–C38, 1980
Mitchell JH, Reardon WC, McCloskey DI. Reflex effects on circulation and respiration from contracting skeletal muscle. American Journal of Physiology 233: H374–H378, 1977
Mohsenifar Z, Brown HV, Koerner SK. Effect of breathing pattern on dead space ventilation VD/VT during exercise. Respiration 47: 232–236, 1985
Moruzzi EV, Bergamini E, Bergamini ZG. Glycogen metabolism and the function of fast and slow muscles of the rat. Pflügers Archiv 391: 338–342, 1981
Musch TA, Haidet GC, Friedman DB, Pitetti KH, Stray-Gundersen et al. Distribution of regional blood flow at different percentages of maximal oxygen consumption in the untrained dog. (Abstract.) Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 16: 178, 1984
Mutch BJC, Bannister EW. Ammonia metabolism in exercise and fatigue: a review. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 15: 41–50, 1983
Nagata A, Muro M, Montani T, Toshida T. Anaerobic threshold determination by blood lactate and myoelectric signals. Japanese Journal of Physiology 31: 585–597, 1981
Naveri H. Blood hormone and metabolite levels during graded cycle ergometer exercise. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation 45: 599–603, 1985
Naylor JM, Kronfeld DS, Freeman DE, Richardson D. Hepatic and extrahepatic lactate metabolism in sheep: effects of lactate loading and pH. American Journal of Physiology 247: E747–E755, 1984
Neary PJ, MacDougall JD, Bachus R, Wenger HA. The relationship between lactate and ventilatory thresholds: coincidental or cause and effect? European Journal of Applied Physiology 54: 104–108, 1985
Neary PJ, Wenger HA. The effects of one- and two-legged exercise on the lactate and ventilatory threshold. European Journal of Applied Physiology 54: 591–595, 1986
Newman EV, Dill DB, Edwards HT, Webster FA. The rate of lactic acid removal in exercise. American Journal of Physiology 118:457–462, 1937
Ogasahara S, Yorifuji S, Nishikawa Y, Takahashi M, Wada K, et al. Improvement of abnormal pyruvate metabolism and cardiac conduction defect with coenzyme Q10 in Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Neurology 35: 372–377, 1985
Pack AI, Ogilvie MD, Davies RO, Galante RJ. Responses of pulmonary stretch receptors during ramp inflations of the lung. Journal of Applied Physiology 61: 344–352, 1986
Palka MJ, Rogozinski A. Standards and predicted values of anaerobic threshold. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 54: 643–646, 1986
Pande SV. On rate-controlled factors of long chain fatty acid oxidation. Journal of Biological Chemistry 246: 5384–5390, 1971
Paschen W, Djuricic B, Miles G, Schmidt-Kästner R, Linn F. Lactate and pH in the brain: association and dissociation in different pathophysiological states. Journal of Neurochemistry 48: 154–159, 1987
Paul P. FFA metabolism of normal dogs during steady state exercise at different work loads. Journal of Applied Physiology 28: 127–132, 1970
Pedersen PK. Individual blood lactate response during exercise and its relation to muscle fibre composition. (Abstract). Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 102: 57A–58A, 1978
Peronnet F, Cleroux J, Perrault H, Cousineau D, Champlain DE, et al. Plasma norepinephrine response to exercise before and after training in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology 51: 812–815, 1981a
Peronnet F, Nadeau RA, Champlain DE, Magrassi P, Chatrand C. Exercise plasma catecholamines in dogs: role of adrenals and cardiac nerve endings. American Journal of Physiology 241: H243–H247, 1981b
Petrofsky JS. The influence of recruitment order and temperature on muscle contraction with special reference to motor unit fatigue. European Journal of Applied Physiology 47: 17–25, 1981
Petrofsky JS, Lind AR. The influence of temperature on the isometric characteristics of fast and slow muscle in the cat. Pflügers Archiv 389: 149–154, 1981
Poole DC, Gaesser GA. Response of ventilatory and lactate thresholds to continuous and interval training. Journal of Applied Physiology 58: 1115–1121, 1985
Poortmans JR, Delescaille-Vanden Bossche J, Leclercq R. Lactate uptake by inactive forearm during progressive leg exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 45: 835–839, 1978
Powers SK, Jacques M, Richard R, Beadly RE. Effects of breathing on normoxic He-O2 gas mixture on exercise tolerance and VO2 max. International Journal of Sports Medicine 7: 217–221, 1986
Rahim ZHA, Lutaya G, Griffiths JR. Activation of AMP aminohydrolase during skeletal-muscle contraction. Biochemical Journal 184: 173–176, 1979
Randle PJ, Fuel selection in animals. Biochemical Society of Transactions 14: 799–806, 1986
Rausch SM, Ward SA, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ. Effect of altered F1O2 on breathing pattern relationships during exercise. (Abstract). Federation Proceedings 45: 1126, 1986
Reinhard U, Muller PH, Schmulling R-M. Determination of anaerobic threshold by the ventilation equivalent in normal individuals. Respiration 38: 36–42, 1979
Rennie MJ, Winder WW, Holloszy JO. A sparing effect of increased plasma fatty acids on muscle and liver glycogen content in the exercising rat. Biochemical Journal 156: 647–655, 1976
Reybrouck T, Weymans M, Stijns H, Knops J, van der Hauwaert L. Ventilatory anaerobic threshold in healthy children. European Journal of Applied Physiology 54: 278–284, 1985
Ribeiro, JP, Hughes V, Fielding RA, Holden W, Evans W, et al. Metabolic and ventilatory responses to steady state exercise relative to lactate thresholds. European Journal of Applied Physiology 55: 215–221, 1986
Richter EA, Galbo H. High glycogen levels enhance glycogen breakdown in isolated contracting skeletal muscle. Journal of Applied Physiology 61: 827–831, 1986
Richter EA, Galbo H, Christensen NJ. Control of exercise-induced muscular glycogenosis by adrenal medullary hormones in rats. Journal of Applied Physiology 50: 21–26, 1981
Richter EA, Ruderman NB, Galbo H. Alpha and beta adrenergic effects on muscle metabolism in contracting, perfused muscle. In Knuttgen et al. (Eds) Biochemistry of exercise, Vol 13, pp. 766–772, Human Kinetics Publishers Inc., Champaign, 1983
Richter EA, Sonne B, Christensen NJ, Galbo H. Role of epinephrine for muscular glycogenosis and pancreatic hormonal secretion in running rats. American Journal of Physiology 240: E526–E532, 1981
Ronca-Testoni S, Raggi A, Ronca G. Muscle AMP aminohydrolase. III. A comparative study on the regulatory properties of skeletal muscle enzyme from various species. Biochimica Biophysica Acta 198: 101–112, 1970
Rosier K, Hoppeler H, Conley KE, Claassen H, Gehr P, et al. Transfer effects in endurance exercise. European Journal of Applied Physiology 54: 355–362, 1985
Rowell LB. Circulation. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 1: 15–22, 1969
Rowell LB, Blackman JR, Bruce RA. Indocyanine green clearance and estimated hepatic blood flow during mild to maximal exercise in upright man. Journal of Clinical Investigation 43: 1677–1690, 1964
Rowell LB, Kraning II KK, Evans TO, Kennedy JW, Blackmon JR et al. Splanchnic removal of lactate and pyruvate during prolonged exercise in man. Journal of Applied Physiology 21: 1773–1783, 1966
Rusko H, Luhtanen P, Rahkila P, Viitasalo J, Rehunen S, et al. Muscle metabolism, blood lactate and oxygen uptake in steady state exercise at aerobic and anaerobic thresholds. European Journal of Applied Physiology 55: 181–186, 1986
Rybicki KJ, Kaufman MP. Stimulation of group III and IV muscle afférents reflexly decreases total pulmonary resistance in dogs. Respiration Physiology 59: 185–195, 1985
Rybicki KJ, Waldrop TG, Kaufman MP. Increasing gracialis muscle interstitial potassium concentrations stimulate group III and IV afferents. Journal of Applied Physiology 58: 936–991, 1985
Sahlin K. NADH in human skeletal muscle during short-term intense exercise. Pflügers Archiv 403: 193–196, 1985
Sahlin K, Harris RC, Nylind B, Hultman E. Lactate content and pH in muscle samples obtained after dyamic exercise. Pflügers Archiv 367: 143–149, 1976
Sahlin K, Henriksson J, Juhlin-Dannfelt A. Intracellular pH and electrolytes in human skeletal muscle during adrenaline and insulin infusions. Clinical Science 67: 461–464, 1984
Sahlin K, Palmskog G, Hultman E. Adenine nucleotide and IMP contents of the quadriceps muscle in man after exercise. Pflügers Archiv 374: 193–198, 1978
Saltin B, Karlsson J. Muscle glycogen utilization during work of different intensities. In Pernow & Saltin (Eds) Muscle metabolism during exercise, pp. 289–299, Plenum, New York, 1971a
Saltin B, Karlsson J. Muscle ATP, CP and lactate during exercise after physical conditioning. In Pernow & Saltin (Eds) Muscle metabolism during exercise, pp. 395–399, Plenum, New York, 1971b
Saltin B, Nazar K, Costili DL, Stein E, Jansson E, et al. The nature of the training responses: peripheral and central adaptations to one-legged exercise. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 96: 289–305, 1976
Sawka MN, Miles DS, Petrofsky JS, Wilde SW, Glaser RM. Ventilation and acid-base equilibrium for upper body and lower body exercise. Aviation Space and Environmental Medicine 53: 354–359, 1982
Schantz PG, Sjoberg B, Svendenhag J. Malate-aspartate and alpha-glycerophosphate shuttle enzyme levels in human skeletal muscle: methodological considerations and effect of endurance training. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica 128: 397–407, 1986
Schoener EP, Frankel HM. Effect of hyperthermia and PaCo2 on the slowly adapting pulmonary stretch receptor. American Journal of Physiology 222: 68–72, 1972
Schuitmaker JJ, Berkenbosch A, De Goede J, Olievier CN. Effects of CO2 and H+ on the ventilatory response to peripheral chemoreceptor stimulation. Respiration Physiology 64: 69–79, 1986
Sachwert GW, Winer AD. Lactate dehydrogenase. In Boyer et al. (Eds) The enzymes, pp. 127–148, Academic Press, New York, 1963
Semple SJG. The role of oscillations in arterial CO2 tension in the chemical control of breathing at rest and on exercise. Clinical Science 66: 639–642, 1984
Shors EC, Hudszczuk A, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ. Ventilatory responses to venous CO2 unloading during steady-state exercise in the dog. (Abstract) Federation Proceedings 39: 583, 1980
Siafakas N, Morris AJR, Prime FJ. The rate of change of mouth occulsion pressure during exercise. Clinical Science 56: 455–461, 1979
Simon J, Young JL, Blood DK, Segal KR, Case RB, et al. Plasma lactate and ventilation thresholds in trained and untrained cyclists. Journal of Applied Physiology 60: 777–781, 1986
Simon J, Young JL, Gutin B, Blood DK, Case RB. Lactate accumulation relative to the anaerobic and respiratory compensation thresholds. Journal of Applied Physiology 54: 13–17, 1983
Skinner JS, McLennan TH. The transition from aerobic to anaerobic metabolism. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport 51: 234–248, 1980
Solano C, Coffee CJ. Differential response of AMP deaminase isozymes to changes in the adenylate energy charge. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 85: 564–571, 1978
Stainsby WN, Sumners C, Andrew GM. Plasma catecholamines and their effect on blood lactate and muscle lactate output. Journal of Applied Physiology 57: 321–325, 1984
Stainsby WN, Sumners C, Eitzman PD. Effects of catecholamines on lactic acid output during progressive working contractions. Journal of Applied Physiology 59: 1809–1814, 1985
Stainsby WN, Sumners C, Eitzman PD. Effects of adrenergic agonists and antagonists on muscle O2 uptake and lactate metabolism. Journal of Applied Physiology 62: 1845–1851, 1987
Twentyman OP, Disley A, Gribbin HR, Alberti KGMM, Tattersfield AE. Effect of β-adrenergic blockade on respiratory and metabolic responses to exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 51: 788–793, 1981
VanBenthuysen KM, Swanson GD, Weil JV. Role of venous CO2 flow in exercise in hyperpnea. (Abstract). Federation Proceedings 39: 584, 1980
Van Meerhaeghe A, Sergysels R, De Coster A. Assessment of the anaerobic threshold during exercise by normal man by means of the occlusion pressure as compared to conventional noninvasive techniques. Respiration 46: 346–353, 1984
Vogel JA, Gleser MA. Effect of carbon monoxide on oxygen transport during exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 32: 234–239, 1972
Waldrop TG, Mullins DC, Millhorn DE. Control of respiration by the hypothalamus and by feedback from contracting muscles in cats. Respiration Physiology 64: 317–328, 1986
Ward SA, Whipp BJ, Poon C-S. Density-dependent airflow and ventilatory control during exercise. Respiration Physiology 49: 267–277, 1982
Wasserman DH, Whipp BJ. Coupling of ventilation to pulmonary gas exchange during non steady-state work in men. Journal of Applied Physiology 54: 587–593, 1983
Wasserman K. Testing regulation of ventilation with exercise. Chest 70: 173–178, 1976
Wasserman K, Beaver WL, Davis JA, Pong J-Z, Heber D, et al. Lactate, pyruvate, and lactate-to-pyruvate ratio during exercise and recovery. Journal of Applied Physiology 59: 935–940, 1985
Wasserman K, Hansen JE, Sue DY, Whipp BJ. Principles of Exercise Testing and Interpretation, Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, 1987
Wasserman K, Mcllroy MB. Detecting the threshold of anaerobic metabolism in cardiac patients during exercise. American Journal of Cardiology 14: 844–859, 1964
Wasserman K, Whipp BJ, Casaburi R, Golden M, Beaver WL. Ventilatory control during exercise in man. Bulletin Européen Physiopathologie Respiratoire 15: 27–47, 1979
Wasserman K, Whipp BJ, Castagna J. Cardiodynamic hypernea; hypernea secondary to cardiac output increase. Journal of Applied Physiology 36: 457–464, 1974
Wasserman K, Whipp BJ, Koyal SN, Beaver WL. Anaerobic threshold and respiratory gas exchange during exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 35: 236–243, 1973
Wasserman K, Whipp BJ, Koyal SN, Cleary MG. Effect of carotid body resection on ventilatory and acid base control during exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 39: 354–358, 1975
Wheeler TJ, Lowenstein JM. Adenylate deaminase from rat skeletal muscle. Journal of Biological Chemistry 254: 8994–8999, 1979
Whipp BJ. The hypernea of dynamic muscular exercise. In Sutton RS (Ed.) Exercise and sport science reviews, pp. 295–311, Journal Publishing Affiliates, Santa Barbara, 1977
Whipp BJ, Davis JA, Torres F, Wasserman K. A test to determine parameters of aerobic function during exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 50: 217–221, 1981
Whipp BJ, Davis JA, Wasserman K. Ventilatory control of the ‘isocapnic buffering’ region of incremental exercise tests. (Abstract). Federation Proceedings 45: 1126, 1986
Whipp BJ, Ward SA. Ventilatory control dynamics during muscular exercise in man. International Journal of Sports Medicine 1: 146–159, 1980
Whipp BJ, Ward SA, Wasserman K. Ventilation to exercise and their control in man. American Review of Respiratory Disease 129(Suppl.):S17–S20, 1984
Whipp BJ, Wasserman K. Effect of body temperature on the ventilatory response to exercise. Respiratory Physiology 8: 354–360, 1970
Wieland OH. The mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; structure and regulation. Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry, and Pharmacology 96: 123–170, 1983
Wilkerson JE, Batterton DL, Horvath SM. Exercise-induced changes in blood ammonia levels in humans. European Journal of Applied Physiology 37: 255–263, 1977
Wilson DF, Erecinska M, Drown C, Silver IA. The oxygen dependence of cellular energy metabolism. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 195: 485–493, 1979
Winder WW, Terjung RL, Baldwin KM, Holloszy JO. Effect of exercise on AMP deaminase and adenylosuccinase in rat skeletal muscle. American Journal of Physiology 227: 1411–1414, 1974
Winder WW, Terry ML, Mitchell VM. Role of plasma epinephrine in fasted exercising rats. American Journal of Physiology 248: R302–R307, 1985
Winning AJ, Hamilton RD, Shea SA, Knott C, Guz A. The effect of airway anaesthesia on the control of breathing and the sensation of breathlessness in man. Clinical Science 68: 215–225, 1985
Woodson RD, Wills RE, Lenfant C. Effect of acute and established anemia on O2 transport at rest, submaximal and maximal work. Journal of Applied Physiology 44: 36–43, 1978
Wu T-FL, Davis EJ. Regulation of glycolytic flux in an energetically controlled cell-free system; the effects of adenine nucleotide ratios on inorganic phosphate, pH, and citrate. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 209: 85–99, 1981
Yeh MP, Gardner RM, Adams TD, Yanowitz FG, Crapo RO ‘Anaerobic threshold’: problems of determination and validation. Journal of Applied Physiology 55: 1178–1186, 1983
Yoshida T. Effect of dietary modifications on lactate threshold and onset of blood lactate accumulation during incremental exercise. European Journal of Applied Physiology 53: 200–205, 1984
Yoshida T, Suda Y, Takeuchi N. Endurance training regimen based upon arterial blood lactate: effects on anaerobic threshold. European Journal of Physiology 49: 223–230, 1982
Young K, Maughan RJ. Physical training in humans: a central or peripheral effect. In Knuttgen et al. (Eds) Biochemistry of Exercise, Vol 13, pp. 433–438, Human Kinetics Publishers Inc., Champaign, 1982
Yudkin J, Cohen RD. The contribution of the kidney to the removal of a lactic acid load under normal and acidotic conditions in the conscious rat. Clinical Science and Molecular Medicine 48: 121–131, 1975
Zilva JF. The origin of the acidosis in hyperlactataemia. Annals of Clinical Biochemistry 15: 40–43, 1978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walsh, M.L., Banister, E.W. Possible Mechanisms of the Anaerobic Threshold. Sports Medicine 5, 269–302 (1988). https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-198805050-00001
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-198805050-00001