Abstract
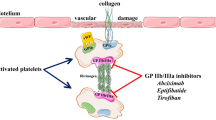
Tirofiban is a nonpeptide tyrosine derivative that antagonises platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GP IIb/IIIa) receptors. It is one of three GP IIb/IIIa antagonists approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of patients with acute coronary syndromes. The clinical effect of tirofiban has been shown in large studies such as PRISM (Platelet Receptor Inhibition for Ischemic Syndrome Management), PRISM-PLUS (PRISM — Patients Limited by Unstable Signs and Symptoms) and RESTORE (Randomised Efficacy Study of Tirofiban for Outcomes and Restenosis).
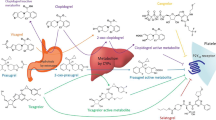
Tirofiban is administered as an intravenous infusion. Volume of distribution ranges from 21 to 87L, and binding to human plasma proteins is modest at 64%. Metabolism in humans is negligible, and most drug is excreted renally with systemic clearance ranging from 4.8 to 25.8 L/h. Renal function may influence the excretion of tirofiban, but concurrent disease or other drugs generally used in patients with ischaemia seem not to do so.
This review updates what is known about the pharmacokinetics of tirofiban in humans, especially in comparison with the monoclonal antibody against the IIb/IIIa receptor, abciximab.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peerschke EI, Zucker MB, Grant RA, et al. Correlation between fibrinogen binding to human platelets and platelet aggregability. Blood 1980 May; 55(5): 841–7
Phillips DR, Charo IF, Parise LV, et al. The platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb–IIIa complex. Blood 1988 Apr; 71(4): 831–43
Plow EF, Pierschbacher MD, Ruoslahti E, et al. The effect of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides on fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1985 Dec; 82(23): 8057–61
Pidard D, Montgomery RR, Bennett JS, et al. Interaction of AP-2, a monoclonal antibody specific for the human platelet glycoprotein IIb–IIIa complex, with intact platelets. J Biol Chem 1983 Oct 25; 258(20): 12582–6
Coller BS. A new murine monoclonal antibody reports an activation-dependent change in the conformation and/or microenvironment of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex. J Clin Invest 1985 Jul; 76(1): 101–8
Gan ZR, Gould RJ, Jacobs JW, et al. Echistatin. Apotent platelet aggregation inhibitor from the venom of the viper, Echis carinatus. J Biol Chem 1988 Dec; 263(36): 19827–32
Shebuski RJ, Ramjit DR, Bencen GH, et al. Characterization and platelet inhibitory activity of bitistatin, a potent arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-containing peptide from the venom of the viper Bitis arietans. J Biol Chem 1989 Dec; 264(36): 21550–6
Hartman GD, Egbertson MS, Halczenko W, et al. Non-peptide fibrinogen receptor antagonists. I: Discovery and design of exosite inhibitors. J Med Chem 1992 Nov; 35(24): 4640–2
PRISM Study Investigators. A comparison of aspirin plus tirofiban with aspirin plus heparin for unstable angina. N Engl J Med 1998 May; 338(21): 1498–505
PRISM-PLUS Study Investigators. Inhibition of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor with tirofiban in unstable angina and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1998 May; 338(21): 1488–97
RESTORE Investigators. Effects of platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa blockade with tirofiban on adverse cardiac events in patients with unstable angina or acute myocardial infarction undergoing coronary angioplasty. Circulation 1997 Sep; 96(5): 1445–53
EPIC Investigators. Use of a monoclonal antibody directed against the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor in high-risk coronary angioplasty. N Engl J Med 1994 Apr; 330(14): 956–61
EPILOG Investigators. Platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor blockade and low-dose heparin during percutaneous coronary revascularization. N Engl J Med 1997 Jun; 336(24): 1689–96
CAPTURE Investigators. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of abciximab before and during coronary intervention in refractory unstable angina: the CAPTURE Study. Lancet 1997 May; 349(9063): 1429–35
RAPPORT Investigators. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa blockade with primary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 1998 Aug; 98(8): 734–41
Topol EJ, Ferguson JJ, Weisman HF, et al. Long-term protection from myocardial ischemic events in a randomized trial of brief integrin beta3 blockade with percutaneous coronary intervention. JAMA 1997; 30: 149–56
Adgey AA. An overview of the results of clinical trials with glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors. Eur Heart J 1998 Apr; 19 Suppl. D: D10–21
Herrmann HC. Tirofiban: an overview of the phase III trials. J Invasive Cardiol 1999 Dec; 11 Suppl. C: C7–13
White HD. Newer antiplatelet agents in acute coronary syndromes. Am Heart J 1999 Dec; 138 (6 Pt 2): S570–6
Topol EJ, Moliterno DJ, Herrmann HC, et al. TARGET Investigators. Comparison of two platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors, tirofiban and abciximab, for the prevention of ischemic events with percutaneous coronary revascularization. N Engl J Med 2001; 344(25): 1888–94
Lehne G, Nordal KP, Midtvedt K, et al. Increased potency and decreased elimination of lamifiban, a GPIIb–IIIa antagonist, in patients with severe renal dysfunction. Thromb Haemost 1998 Jun; 79(6): 1119–25
Ferguson JJ, Kereiakes DJ, Adgey AA, et al. Safe use of platelet GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors. Eur Heart J 1998 Apr; 19 Suppl. D: D40–51
Dunn A. Abciximab, eptifibatide, and tirofiban: comparison of parenteral glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors. Conn Med 1999 Aug; 63(8): 483–7
Tcheng JE. Differences among the parenteral platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors and implications for treatment. Am J Cardiol 1999 May; 83(9A): E7–11
Peerlinck K, De Lepeleire I, Goldberg M, et al. MK-383 (L-700,462), a selective nonpeptide platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonist, is active in man. Circulation 1993 Oct; 88 (4 Pt 1): 1512–7
Barrett JS, Murphy G, Peerlinck K, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of MK-383, a selective non-peptide platelet glycoprotein-IIb/IIIa receptor antagonist, in healthy men. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1994 Oct; 56(4): 377–88
Tcheng JE, Ellis SG, George BS, et al. Pharmacodynamics of chimeric glycoprotein IIb/IIIa integrin antiplatelet antibody Fab 7E3 in high-risk coronary angioplasty. Circulation 1994 Oct; 90(4): 1757–64
Mascelli MA, Lance ET, Damaraju L, et al. Pharmacodynamic profile of short-term abciximab treatment demonstrates prolonged platelet inhibition with gradual recovery from GP IIb/IIIa receptor blockade. Circulation 1998 May 5; 97(17): 1680–8
Kleiman NS, Raizner AE, Jordan R, et al. Differential inhibition of platelet aggregation induced by adenosine diphosphate or a thrombin receptor-activating peptide in patients treated with bolus chimeric 7E3 Fab: implications for inhibition of the internal pool of GPIIb/IIIa receptors. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995 Dec; 26(7): 1665–71
Reverter JC, Beguin S, Kessels H, et al. Inhibition of platelet-mediated, tissue factor-induced thrombin generation by the mouse/human chimeric 7E3 antibody. Potential implications for the effect of c7E3 Fab treatment on acute thrombosis and ‘clinical restenosi’. J Clin Invest 1996 Aug; 98(3): 863–74
Tam SH, Sassoli PM, Jordan RE, et al. Abciximab (ReoPro, chimeric 7E3 Fab) demonstrates equivalent affinity and functional blockade of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa and alpha(v)beta3 integrins. Circulation 1998 Sep; 98(11): 1085–91
Umemura K, Kondo K, Ikeda Y, et al. Enhancement by ticlopidine of the inhibitory effect on in vitro platelet aggregation of the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor tirofiban. Thromb Haemost 1997; 78: 1381–4
Cohen M, Theroux P, Weber S, et al. Combination therapy with tirofiban and enoxaparin in acute coronary syndromes. Int J Cardiol 1999 Dec; 71(3): 273–81
Hand EL, Gilbert JD, Yuan AS, et al. Determination of MK-383, a non-peptide fibrinogen receptor antagonist, in human plasma and urine by radioimmunoassay. J Pharm Biomed Anal 1994 Aug; 12(8): 1047–53
Tcheng JE. Clinical challenges of platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitor therapy: bleeding, reversal, thrombocytopenia, and retreatment. Am Heart J 2000 Feb; 139 (2 Pt 2): S38–45
Vickers S, Theoharides AD, Arison B, et al. In vitro and in vivo studies on the metabolism of tirofiban. Drug Metab Dispos 1999 Nov; 27(11): 1360–6
Frishman WH, Burns B, Atac B, et al. Novel antiplatelet therapies for treatment of patients with ischemic heart disease: inhibitors of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa integrin receptor. Am Heart J 1995 Oct; 130(4): 877–92
Kleiman NS. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of glycoprotein IIb–IIIa inhibitors. Am Heart J 1999 Oct; 138 (4 Pt 2): 263–75
Cohen I, Burk D, Fullerton RJ, et al. Nonenzymatic glycation of human blood platelet proteins. Thromb Res 1989 Aug; 55(3): 341–9
Steinhubl SR, Kottke-Marchant K, Moliterno DJ, et al. Attainment and maintenance of platelet inhibition through standard dosing of abciximab in diabetic and nondiabetic patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation 1999 Nov; 100(19): 1977–82
McClellan KJ, Goa KL. Tirofiban: a review of its use in acute coronary syndromes. Drugs 1998 Dec; 56(6): 1067–80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondo, K., Umemura, K. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Tirofiban, a Nonpeptide Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Receptor Antagonist. Clin Pharmacokinet 41, 187–195 (2002). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200241030-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200241030-00003