Abstract
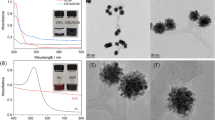
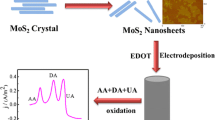
As a nutrient in body functions, folic acid (FA) plays a very important role for human health, and thus developing a highly sensitive method for its determination is of great significance. In the present work, carbon hollow nanospheres decorated with molybdenum disulfide nanosheets (CHN@MoS2) nanomaterials were produced through a simple method and adopted to modify a glassy carbon electrode for assembling a highly sensitive electrochemical sensor of FA. After characterizing the prepared nanomaterials using scanning-/transmission-electron microscopy and Raman spectra, as well as optimizing various testing conditions, including the pH value of the buffer solution, the accumulation time and amount of nanomaterials on electrode surface, and the electrochemical determination of FA was carried out using a CHN@MoS2 electrode. Owing to the coordinative advantages from CHN and MoS2, the results show that CHN@MoS2 exhibits excellent sensing responses for FA, and it has a wide linear range from 0.08 to 10.0 μM coupled with a low detection limit of 0.02 μM. Finally, the proposed method for FA detection was successfully applied in human urine analysis. The obtained results are satisfactory, revealing that the developed method based on CHN@MoS2 nanomaterials has important applications for FA determination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Akbar, A. Anwar, and Q. Kanwal, Anal. Biochem., 2016, 510, 98.
M. Venu, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2018, 11702.
H. Rajabi, and M. Noroozifar, Mater. Sci. and Eng. C, 2017, 75, 791.
S. Güney, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2019, 854, 113518.
F. Chekin, F. Teodorescu, Y. Coffinier, G.-H. Pan, A. Barras, R. Boukherroub, and S. Szunerits, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2016, 85, 807.
W. Ren, Y. Fang, and E. Wang, ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 6425.
S. Ulusoy, H. Acidereli, S. Erdoḡan, and H. İbrahim Ulusoy, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 40115.
X. Li and L. Chen, ACS appl. mater. interfaces, 2016, 8, 31832.
A. A. Abdelwahab and Y. Shim, Sens. Actuators, 2015, 221, 659.
Q. Wang, H. Si, L. Zhang, L. Li, X. Wang, and S. Wang, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2020, 1104, 69.
J. P. Winiarski, R. Rampanelli, J. C. Bassani, D. Z. Mezalira, and C. L. Jost, J. Food Compos. Anal, 2020, 92, 103511.
Y. Yi, D. Zhang, Y. Ma, X. Wu, and G. Zhu, Anal. Chem., 2019, 91, 2908.
J. Hu, K. T. Ho, X. U. Zou, W. H. Smyrl, A. Stein, and P. Buhlmann, Anal. Chem., 2015, 87, 2981.
K. Hsieh, B. S. Ferguson, M. Eisenstein, K. W. Plaxco, and H. T. Soh, Acc. Chem. Res., 2015, 48, 911.
A. Kotani, M. Kaneko, K. Machida, K. Yamamoto, and H. Hakamata, Anal. Sci., 2020, 10.2116/analsci.2120p2049.
O. Parlak, A. Incel, L. Uzun, A. P. F. Turner, and A. Tiwari, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, 89, 545.
A. Sinha, Dhanjai, B. Tan, Y. Huang, H. Zhao, X. Dang, J. Chen, and R. Jain, TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2018, 102, 75.
M. Sharifuzzaman, S. C. Barman, M. A. Zahed, N. J. San, and J. Y. Park, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2019, 166, B249.
D. Zhang, Y. Ma, O. J. Kingsford, J. Qian, and Y. Yi, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2019, 166, B1392.
B. Mao, B. Wang, F. Yu, K. Zhang, Z. Zhang, J. Hao, J. Zhong, Y. Liu, and W. Shi, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43, 11038.
L. Xing and Z. Ma, Microchim. Acta, 2015, 183, 257.
Y. Wang, G. Ning, H. Bi, Y. Wu, G. Liu, and Y. Zhao, Electrochim. Acta, 2018, 285, 120.
S. K. Tuteja, T. Duffield, and S. Neethirajan, Nanoscale, 2017, 9, 10886.
S. Wang, B. Y. Guan, L. Yu, and X. W. D. Lou, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29.
L. Song, X. Wang, F. Wen, L. Niu, X. Shi, and J. Yan, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41, 18942.
P. Jing, H. Yi, S. Xue, Y. Chai, R. Yuan, and W. Xu, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2015, 853, 234.
A. Ambrosi, Z. Sofer, and M. Pumera, Small, 2014, 11, 605.
A. S. Subramanian, J. N. Tey, L. Zhang, B. H. Ng, S. Roy, J. Wei, and X. M. Hu, Polymer, 2016, 82, 285.
D. Geng, X. Bo, and L. Guo, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 244, 131.
S. Y. Park, Y. H. Kim, S. Y. Lee, W. Sohn, J. E. Lee, D. H. Kim, Y.-S. Shim, K. C. Kwon, K. S. Choi, H. J. Yoo, J. M. Suh, M. Ko, J.-H. Lee, M. J. Lee, S. Y. Kim, M. H. Lee, and H. W. Jang, J Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 5016.
Y. Li, H. Wang, L. Xie, Y. Liang, G. Hong, and H. Dai, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 7296.
H. Song, Y. Ni, and S. Kokot, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014, 56, 137.
E. B. Bahadır and M. K. Sezgintürk, TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem., 2016, 76, 1.
R. He, J. Hua, A. Zhang, C. Wang, J. Peng, W. Chen, and J. Zeng, Nano lett., 2017, 17, 4311.
L. Li, W. Zhang, X. Wang, S. Zhang, Y. Liu, M. Li, G. Zhu, Y. Zheng, Q. Zhang, T. Zhou, W. K. Pang, W. Luo, Z. Guo, and J. Yang, ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 7939.
Y. Chen, W. C. Peng, and X. Y. Li, Nanotechnology, 2017, 28, 205.
Acknowledgements
This study was financed by the Major Program of main disease in Xiamen City by Xiamen Science and Technology Bureau and Xiamen Municipal Health Commission (No. 3502Z2017050); Joint Project of health education in Fujian Province (2019-WJ-35).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, H., Song, L., Zhang, F. et al. Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Folic Acid by Using a Hollow Carbon Nanospheres@molybdenum Disulfide Modified Electrode. ANAL. SCI. 37, 575–580 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.20P297
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.20P297