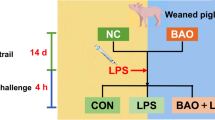
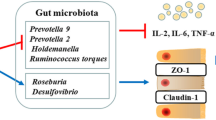
Abstract
Early weaned piglets suffer from oxidative stress and enteral infection, which usually results in gut microbial dysbiosis, serve diarrhea, and even death. Rice bran oil (RBO), a polyphenol-enriched by-product of rice processing, has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties both in vivo and in vitro. Here, we ascertained the proper RBO supplementation level, and subsequently determined its effects on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced intestinal dysfunction in weaned piglets. A total of 168 piglets were randomly allocated into four groups of seven replicates (42 piglets each group, (21±1) d of age, body weight (7.60±0.04) kg, and half males and half females) and were given basal diet (Ctrl) or basal diet supplemented with 0.01% (mass fraction) RBO (RBO1), 0.02% RBO (RBO2), or 0.03% RBO (RBO3) for 21 d. Then, seven piglets from the Ctrl and the RBO were treated with LPS (100 µg/kg body weight (BW)) as LPS group and RBO+LPS group, respectively. Meanwhile, seven piglets from the Ctrl were treated with the saline vehicle (Ctrl group). Four hours later, all treated piglets were sacrificed for taking samples of plasma, jejunum tissues, and feces. The results showed that 0.02% was the optimal dose of dietary RBO supplementation based on diarrhea, average daily gain, and average daily feed intake indices in early weaning piglets. Furthermore, RBO protected piglets against LPS-induced jejunal epithelium damage, which was indicated by the increases in villus height, villus height/crypt depth ratio, and Claudin-1 levels, as well as a decreased level of jejunal epithelium apoptosis. RBO also improved the antioxidant ability of LPS-challenged piglets, which was indicated by the elevated concentrations of catalase and superoxide dismutase, and increased total antioxidant capacity, as well as the decreased concentrations of diamine oxidase and malondialdehyde in plasma. Meanwhile, RBO improved the immune function of LPS-challenged weaned piglets, which was indicated by elevated immunoglobulin A (IgA), IgM, β-defensin-1, and lysozyme levels in the plasma. In addition, RBO supplementation improved the LPS challenge-induced dysbiosis of gut microbiota. Particularly, the indices of antioxidant capacity, intestinal damage, and immunity were significantly associated with the RBO-regulated gut microbiota. These findings suggested that 0.02% RBO is a suitable dose to protect against LPS-induced intestinal damage, oxidative stress, and jejunal microbiota dysbiosis in early weaned piglets.
摘要
早期断奶仔猪遭受氧化应激和肠道感染, 通常会导致肠道微生物失调、腹泻甚至死亡. 米糠油 (RBO) 是一种富含多酚的大米加工副产品, 在体内和体外都具有抗氧化和抗炎特性. 本研究中, 我们确定了早期断奶仔猪日粮中适当的RBO补充水平, 随后确定了它对脂多糖 (LPS) 诱导的断奶仔猪肠道功能障碍的影响. 将 168 头仔猪随机分 4 组, 每组 7 个重复 (42 头/组, (21±1) 日龄, 体重 (7.60±0.04) kg, 公母各半), 分别接受基础日粮 (Ctrl) 或补充基础日粮含 0.01% RBO (RBO1)、0.02% RBO (RBO2) 或 0.03% RBO(RBO3). 饲喂 21 天后, Ctrl 和 RBO 组的 7 头仔猪经 LPS (100 μg/kg BW) 处理 (分别为 LPS 组和 RBO+LPS 组). 同时将 Ctrl 组的 7 头仔猪用载体盐水处理作为对照 (Ctrl 组). 四小时后, 处死所有处理组仔猪并采集血浆、 空肠组织和粪便. 分别检测血浆中抗氧化和免疫指标, 评估空肠组织形态和屏障功能以及通过 16S rDNA 测序分析肠道微生物组成、 功能及多样性. 结果表明, 根据早期断奶仔猪的腹泻、 平均日增重和平均日采食量指标, 0.02% 是日粮中添加 RBO 的最佳剂量. 此外, RBO 可以缓解 LPS 诱导的仔猪空肠上皮损伤, 表现为绒毛高度、 绒毛高度/隐窝深度比和 Claudin-1 水平的增加, 以及空肠上皮细胞凋亡的改善. RBO 还提高了 LPS 应激仔猪的抗氧化能力, 表现为血浆中过氧化氢酶和超氧化物歧化酶浓度升高, 总抗氧化能力提升, 以及二胺氧化酶和丙二醛浓度降低. 同时, RBO 提高了 LPS 应激的断奶仔猪的免疫功能, 表现为血浆中 IgA、 IgM、 β-防御素-1 和溶菌酶升高. 此外, 补充 RBO 还改善了 LPS 应激引起的肠道菌群失调. 相关性分析结果发现, 仔猪抗氧化能力、 肠道损伤和免疫力指标分别与 RBO 调节的肠道微生物群显着相关. 综上所述, 0.02% RBO 是缓解 LPS 诱导的早期断奶仔猪肠道损伤、 氧化应激和空肠微生物群失调的适当剂量.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albenberg L, Esipova TV, Judge CP, et al., 2014. Correlation between intraluminal oxygen gradient and radial partitioning of intestinal microbiota. Gastroenterology, 147(5):1055–1063.e8. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.07.020
Allen HK, Levine UY, Looft T, et al., 2013. Treatment, promotion, commotion: antibiotic alternatives in food-producing animals. Trends Microbiol, 21(3):114–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2012.11.001
Bao T, Zhang M, Zhou YQ, et al., 2021. Phenolic profile of jujube fruit subjected to gut microbiota fermentation and its antioxidant potential against ethyl carbamate-induced oxidative damage. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 22(5):397–409. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000754
Bhandari SK, Xu B, Nyachoti CM, et al., 2008. Evaluation of alternatives to antibiotics using an Escherichia coli K88+ model of piglet diarrhea: effects on gut microbial ecology. J Anim Sci, 86(4):836–847. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2006-822
Boler DD, Fernández-Dueñas DM, Kutzler LW, et al., 2012. Effects of oxidized corn oil and a synthetic antioxidant blend on performance, oxidative status of tissues, and fresh meat quality in finishing barrows. J Anim Sci, 90(13):5159–5169. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2012-5266
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, et al., 2019. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol, 37(8):852–857. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
Campbell JM, Crenshaw JD, Polo J, 2013. The biological stress of early weaned piglets. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 4: 19. https://doi.org/10.1186/2049-1891-4-19
Chen CC, Wang ZB, Li JZ, et al., 2019. Dietary vitamin E affects small intestinal histomorphology, digestive enzyme activity, and the expression of nutrient transporters by inhibiting proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells within jejunum in weaned piglets. J Anim Sci, 97(3):1212–1221. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skz023
Dou S, Gadonna-Widehem P, Rome V, et al., 2017. Characterisation of early-life fecal microbiota in susceptible and healthy pigs to post-weaning diarrhoea. PLoS ONE, 12(1):e0169851. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169851
Douglas GM, Maffei VJ, Zaneveld JR, et al., 2020. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat Biotechnol, 38(6):685–688. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-020-0548-6
Fragou S, Fegeros K, Xylouri E, et al., 2004. Effect of vitamin E supplementation on various functional properties of macrophages and neutrophils obtained from weaned piglets. J Vet Med Ser A, 51(4):178–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0442.2004.00623.x
Frese SA, Parker K, Calvert CC, et al., 2015. Diet shapes the gut microbiome of pigs during nursing and weaning. Microbiome, 3:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-015-0091-8
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA, 1992. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol, 119(3):493–501. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.119.3.493
Greiner T, Bäckhed F, 2011. Effects of the gut microbiota on obesity and glucose homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 22(4):117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2011.01.002
Gresse R, Chaucheyras-Durand F, Fleury MA, et al., 2017. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in postweaning piglets: understanding the keys to health. Trends Microbiol, 25(10):851–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2017.05.004
Hu RZ, Wu SS, Li BZ, et al., 2022. Dietary ferulic acid and vanillic acid on inflammation, gut barrier function and growth performance in lipopolysaccharide-challenged piglets. Anim Nutr, 8:144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aninu.2021.06.009
Huang CY, Fan ZJ, Han DD, et al., 2021. Pyrroloquinoline quinone regulates the redox status in vitro and in vivo of weaned pigs via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 12:77. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40104-021-00595-x
Kaakoush NO, 2015. Insights into the role of Erysipelotrichaceae in the human host. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 5:84. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2015.00084
Kushwaha R, 2018. Pharmacognosy of rice bran oil—a review. Int J Green Pharm, 12(4):S784–S789. https://doi.org/10.22377/ijgp.v12i04.2255
Liu KY, Nakatsu CH, Jones-Hall Y, et al., 2021. Vitamin E alpha- and gamma-tocopherol mitigate colitis, protect intestinal barrier function and modulate the gut microbiota in mice. Free Radical Biol Med, 163:180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.12.017
Lu T, Harper AF, Zhao J, et al., 2014. Supplementing antioxidants to pigs fed diets high in oxidants: I. Effects on growth performance, liver function, and oxidative status. J Anim Sci, 92(12):5455–5463. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2013-7109
Mocchegiani E, Costarelli L, Giacconi R, et al., 2014. Vitamin E-gene interactions in aging and inflammatory age-related diseases: implications for treatment. A systematic review. Ageing Res Rev, 14:81–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2014.01.001
NRC (National Research Council), 2012. Nutrient Requirements of Swine, 11th Rev. Ed. National Academics Press, Washington, DC.
Posuwan J, Prangthip P, Leardkamolkarn V, et al., 2013. Long-term supplementation of high pigmented rice bran oil (Oryza sativa L.) on amelioration of oxidative stress and histological changes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats fed a high fat diet; Riceberry bran oil. Food Chem, 138(1):501–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.144
Prates JAM, Freire JPB, de Almeida AM, et al., 2021. Influence of dietary supplementation with an amino acid mixture on inflammatory markers, immune status and serum proteome in LPS-challenged weaned piglets. Animals, 11(4):1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041143
Punia S, Kumar M, Siroha AK, et al., 2021. Rice bran oil: emerging trends in extraction, health benefit, and its industrial application. Rice Sci, 28(3):217–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2021.04.002
Qiu YQ, Yang J, Wang L, et al., 2021. Dietary resveratrol attenuation of intestinal inflammation and oxidative damage is linked to the alteration of gut microbiota and butyrate in piglets challenged with deoxynivalenol. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 12:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40104-021-00596-w
Ren W, Yu B, Yu J, et al., 2022. Lower abundance of Bacteroides and metabolic dysfunction are highly associated with the post-weaning diarrhea in piglets. Sci China Life Sci, 65(10):2062–2075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-2068-6
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW, 2012. NIH image to imageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods, 9(7):671–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2089
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, et al., 2011. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol, 12(6):R60. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r60
Shang QS, Shan XD, Cai C, et al., 2016. Dietary fucoidan modulates the gut microbiota in mice by increasing the abundance of Lactobacillus and Ruminococcaceae. Food Funct, 7(7):3224–3232. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6FO00309E
Silva-Guillen YV, Arellano C, Boyd RD, et al., 2020. Growth performance, oxidative stress and immune status of newly weaned pigs fed peroxidized lipids with or without supplemental vitamin E or polyphenols. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 11:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40104-020-0431-9
Singh PK, Wise SY, Ducey EJ, et al., 2011. α-Tocopherol succinate protects mice against radiation-induced gastrointestinal injury. Radiat Res, 177(2):133–145. https://doi.org/10.1667/rr2627.1
Starke IC, Pieper R, Neumann K, et al., 2014. The impact of high dietary zinc oxide on the development of the intestinal microbiota in weaned piglets. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 87(2):416–427. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6941.12233
Sun X, Cui YL, Su YY, et al., 2021. Dietary fiber ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal barrier function damage in piglets by modulation of intestinal microbiome. mSystems, 6(2):e01374–20. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.01374-20
Wang XF, Tsai T, Deng FL, et al., 2019. Longitudinal investigation of the swine gut microbiome from birth to market reveals stage and growth performance associated bacteria. Microbiome, 7:109. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-019-0721-7
Wang Y, Zhang RM, Li JY, et al., 2017. Comprehensive resistome analysis reveals the prevalence of NDM and MCR-1 in Chinese poultry production. Nat Microbiol, 2(4):16260. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.260
Winter SE, Winter MG, Xavier MN, et al., 2013. Host-derived nitrate boosts growth of E. coli in the inflamed gut. Science, 339(6120):708–711. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1232467
Xu BY, Qin WX, Xu YZ, et al., 2021a. Dietary quercetin supplementation attenuates diarrhea and intestinal damage by regulating gut microbiota in weanling piglets. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021:6221012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6221012
Xu BY, Yan YQ, Yin BQ, et al., 2021b. Dietary glycyl-glutamine supplementation ameliorates intestinal integrity, inflammatory response, and oxidative status in association with the gut microbiota in LPS-challenged piglets. Food Funct, 12(8):3539–3551. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo03080e
Xu X, Wang XY, Wu HT, et al., 2018. Glycine relieves intestinal injury by maintaining mTOR signaling and suppressing AMPK, TLR4, and NOD signaling in weaned piglets after lipopolysaccharide challenge. Int J Mol Sci, 19(7):1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071980
Xu X, Hua HW, Wang LM, et al., 2020. Holly polyphenols alleviate intestinal inflammation and alter microbiota composition in lipopolysaccharide-challenged pigs. Br J Nutr, 123(8):881–891. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114520000082
Yan YQ, Xu BY, Yin BQ, et al., 2020. Modulation of gut microbial community and metabolism by dietary glycyl-glutamine supplementation may favor weaning transition in piglets. Front Microbiol, 10:3125. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.03125
Yardeni T, Tanes CE, Bittinger K, et al., 2019. Host mitochondria influence gut microbiome diversity: a role for ROS. Sci Signal, 12(588):eaaw3159. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aaw3159
Yi GF, Carroll JA, Allee GL, et al., 2005. Effect of glutamine and spray-dried plasma on growth performance, small intestinal morphology, and immune responses of Escherichia coli K88+-challenged weaned pigs. J Anim Sci, 83(3):634–643. https://doi.org/10.2527/2005.833634x
Zeng MY, Inohara N, Nuñez G, 2017. Mechanisms of inflammation-driven bacterial dysbiosis in the gut. Mucosal Immunol, 10(1):18–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2016.75
Zhang YC, Mu TQ, Jia H, et al., 2022. Protective effects of glycine against lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal apoptosis and inflammation. Amino Acids, 54(3):353–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-03011-w
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 32230099 and 31925037), the Hubei Hongshan Laboratory (No. 2021hszd018), and the Yichun Dahaigui Life Science Co., Ltd. (No. 20222ZDH04093). We thank Yan lab’s members for helpful discussion and critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Juncheng HUANG, Wenxia QIN, and Baoyang XU conducted this study, participated in the animal experiments, analyzed the samples and the data, and wrote and revised the manuscript. Haihui SUN, Fanghua JING, Yunzheng XU, Jianan ZHAO, and Yuwen CHEN participated in the animal experiments. Baoyang XU, Libao MA, and Xianghua YAN designed this study and analyzed the data. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Juncheng HUANG, Wenxia QIN, Baoyang XU, Haihui SUN, Fanghua JING, Yunzheng XU, Jianan ZHAO, Yuwen CHEN, Libao MA, and Xianghua YAN declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Our animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the Animal Experimental Ethical Inspection of Laboratory Animal Centre, Huazhong Agriculture University, Wuhan, China (No. HZAUSW20210012). All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Additional information
Supplementary information
Tables S1–S4; Fig. S1
Supplementary materials
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Qin, W., Xu, B. et al. Rice bran oil supplementation protects swine weanlings against diarrhea and lipopolysaccharide challenge. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 24, 430–441 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200565
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200565