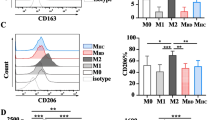
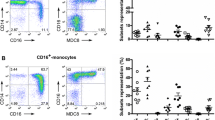
Abstract
Macrophages are widely distributed immune cells that contribute to tissue homeostasis. Human THP-1 cells have been widely used in various macrophage-associated studies, especially those involving pro-inflammatory M1 and anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes. However, the molecular characterization of four M2 subtypes (M2a, M2b, M2c, and M2d) derived from THP-1 has not been fully investigated. In this study, we systematically analyzed the protein expression profiles of human THP-1-derived macrophages (M0, M1, M2a, M2b, M2c, and M2d) using quantitative proteomics approaches. The commonly and specially regulated proteins of the four M2 subtypes and their potential biological functions were further investigated. The results showed that M2a and M2b, and M2c and M2d have very similar protein expression profiles. These data could serve as an important resource for studies of macrophages using THP-1 cells, and provide a reference to distinguish different M2 subtypes in macrophage-associated diseases for subsequent clinical research.
概要
目的
探究THP-1来源的四种M2巨噬细胞亚型的蛋白质组学特征, 为进一步区分M2亚型以及使用THP-1来源的巨噬细胞作为临床前研究的细胞模型提供数据基础。
创新点
首次系统性地对四种M2巨噬细胞亚型的蛋白质组进行了分析, 并提供潜在的候选标志物用于不同M2亚型的鉴定, 为巨噬细胞的可塑性、相关疾病以及免疫机制等方面的研究提供参考。
方法
在体外诱导THP-1单核细胞分化为M0、M1、M2a、M2b、M2c和M2d巨噬细胞, 并利用基于质谱的无标记定量技术揭示了其蛋白质组学特征。结合数据库与生物信息学分析四种M2亚型共同或特异的生物学功能及疾病关联。此外, 通过靶向蛋白质组学技术分析了四种M2巨噬细胞亚型中共同或特异上调的蛋白。
结论
本研究首次揭示了THP-1衍生的四种M2巨噬细胞亚型的蛋白质组学特征。不仅验证了几个已知的巨噬细胞标记物, 也提供了一份新的候选标记物列表, 用于识别M2a、M2b、M2c和M2d巨噬细胞。一个主要发现是M2a和M2c以及M2b和M2d的蛋白表达谱非常相似。本研究的数据为未来研究巨噬细胞相关疾病的免疫调节机制以及使用THP-1来源的巨噬细胞模型进行临床前研究提供了宝贵的资源。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avila-Ponce de León U, Vazquez-Jimenez A, Matadamas-Guzman M, et al., 2021. Transcriptional and microenvironmental landscape of macrophage transition in cancer: a boolean analysis. Front Immunol, 12:642842. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.642842
Bader GD, Hogue CWV, 2003. An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics, 4:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-4-2
Batchu S, 2020. Progressive multiple sclerosis transcriptome deconvolution indicates increased M2 macrophages in inactive lesions. Eur Neurol, 83(4):433–435. https://doi.org/10.1159/000510075
Baumeier C, Escher F, Aleshcheva G, et al., 2021. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 reduces cardiac fibrosis and promotes M2 macrophage polarization in inflammatory cardiomyopathy. Basic Res Cardiol, 116:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-020-00840-w
Ben-Ari Fuchs S, Lieder I, Stelzer G, et al., 2016. GeneAnalytics: an integrative gene set analysis tool for next generation sequencing, RNAseq and microarray data. OMICS, 20(3):139–151. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2015.0168
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, et al., 2009. ClueGO: a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics, 25(8):1091–1093. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp101
Busch S, Talamini M, Brenner S, et al., 2019. Circulating monocytes and tumor-associated macrophages express recombined immunoglobulins in glioblastoma patients. Clin Transl Med, 8(1):e18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40169-019-0235-8
Chanput W, Mes JJ, Wichers HJ, 2014. THP-1 cell line: an in vitro cell model for immune modulation approach. Int Immunopharmacol, 23(1):37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2014.08.002
Colin S, Chinetti-Gbaguidi G, Staels B, 2014. Macrophage phenotypes in atherosclerosis. Immunol Rev, 262(1):153–166. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12218
Chen YB, Song YC, Du W, et al., 2019. Tumor-associated macrophages: an accomplice in solid tumor progression. J Biomed Sci, 26:78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-019-0568-z
de Morrée A, Flix B, Bagaric I, et al., 2013. Dysferlin regulates cell adhesion in human monocytes. J Biol Chem, 288(20):14147–14157. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.448589
Dennis G, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, et al., 2003. DAVID: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol, 4(5):3.
di Paolo NC, Shayakhmetov DM, 2016. Interleukin 1α and the inflammatory process. Nat Immunol, 17(8):906–913. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3503
Drazic A, Aksnes H, Marie M, et al., 2018. NAA80 is actin’s N-terminal acetyltransferase and regulates cytoskeleton assembly and cell motility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 115(17):4399–4404. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1718336115
Eligini S, Fiorelli S, Tremoli E, et al., 2016. Inhibition of transglutaminase 2 reduces efferocytosis in human macrophages: role of CD14 and SR-AI receptors. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, 26(10):922–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2016.05.011
Epelman S, Lavine KJ, Randolph GJ, 2014. Origin and functions of tissue macrophages. Immunity, 41(1):21–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.013
Ferrante CJ, Leibovich SJ, 2012. Regulation of macrophage polarization and wound healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle), 1(1):10–16. https://doi.org/10.1089/wound.2011.0307
Ferrante CJ, Pinhal-Enfield G, Elson G, et al., 2013. The adenosine-dependent angiogenic switch of macrophages to an M2-like phenotype is independent of interleukin-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα) signaling. Inflammation, 36(4): 921–931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9621-3
Guo MM, Härtlova A, Gierliński M, et al., 2019. Triggering MSR1 promotes JNK-mediated inflammation in IL-4-activated macrophages. EMBO J, 38(11):e100299. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2018100299
Hendricks CM, Cordeiro T, Gomes AP, et al., 2021. The interplay of HIV-1 and macrophages in viral persistence. Front Microbiol, 12:646447. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.646447
Huang C, Lewis C, Borg NA, et al., 2018. Proteomic identification of interferon-induced proteins with tetratricopeptide repeats as markers of M1 macrophage polarization. J Proteome Res, 17(4):1485–1499. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00828
Huang X, Li Y, Fu MG, et al., 2018. Polarizing macrophages in vitro. In: Rousselet G (Ed.), Macrophages: Methods and Protocols. Humana Press, New York, p.119–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7837-3_12
Ivashkiv LB, 2018. IFNγ: signalling, epigenetics and roles in immunity, metabolism, disease and cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol, 18(9):545–558. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-018-0029-z
Knudsen E, Iversen PO, van Rooijen N, et al., 2002. Macrophage-dependent regulation of neutrophil mobilization and chemotaxis during development of sterile peritonitis in the rat. Eur J Haematol, 69(5–6):284–296. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0609.2002.02657.x
Kuo CL, Chou HY, Chiu YC, et al., 2020. Mitochondrial oxidative stress by Lon-PYCR1 maintains an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment that promotes cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Lett, 474:138–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.01.019
Lee J, French B, Morgan T, et al., 2014. The liver is populated by a broad spectrum of markers for macrophages. In alcoholic hepatitis the macrophages are M1 and M2. Exp Mol Pathol, 96(1):118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2013.09.004
Lewis CE, Leek R, Harris A, et al., 1995. Cytokine regulation of angiogenesis in breast cancer: the role of tumor-associated macrophages. J Leukoc Biol, 57(5):747–751. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlb.57.5.747
Li GM, Li YF, Liu HM, et al., 2020. Genetic heterogeneity of pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus with lymphoproliferation. Medicine (Baltimore), 99(20):e20232. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000020232
Li GQ, Jin FQ, Du JX, et al., 2019. Macrophage-secreted TSLP and MMP9 promote bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 366:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2019.01.011
Li PF, Hao ZF, Liu HH, et al., 2021. Quantitative proteomics analysis of berberine-treated colon cancer cells reveals potential therapy targets. Biology, 10(3):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030250
Liao CW, Chou CH, Wu XM, et al., 2020. Interleukin-6 plays a critical role in aldosterone-induced macrophage recruitment and infiltration in the myocardium. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 1866(3):165627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165627
Liu YC, Zou XB, Chai YF, et al., 2014. Macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases. Int J Biol Sci, 10(5):520–529. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.8879
Lu JY, Cao Q, Zheng D, et al., 2013. Discrete functions of M2a and M2c macrophage subsets determine their relative efficacy in treating chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int, 84(4):745–755. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2013.135
MacLean B, Tomazela DM, Shulman N, et al., 2010. Skyline: an open source document editor for creating and analyzing targeted proteomics experiments. Bioinformatics, 26(7): 966–968. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq054
Martinez FO, Helming L, Milde R, et al., 2013. Genetic programs expressed in resting and IL-4 alternatively activated mouse and human macrophages: similarities and differences. Blood, 121(9):e57–e69. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-06-436212
Menzel K, Hausmann M, Obermeier F, et al., 2006. Cathepsins B, L and D in inflammatory bowel disease macrophages and potential therapeutic effects of cathepsin inhibition in vivo. Clin Exp Immunol, 146(1):169–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03188.x
Minoia F, Tibaldi J, Muratore V, et al., 2021. Thrombotic microangiopathy associated with macrophage activation syndrome: a multinational study of 23 patients. J Pediatr, 235:196–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.04.004
Mosser DM, Edwards JP, 2008. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol, 8(12):958–969. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2448
Murray PJ, 2017. Macrophage polarization. Annu Rev Physiol, 79:541–566. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034339
Neven Q, Boulanger C, Bruwier A, et al., 2021. Clinical spectrum of Ras-associated autoimmune leukoproliferative disorder (RALD). J Clin Immunol, 41(1):51–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-020-00883-7
Nosaka M, Ishida Y, Kimura A, et al., 2020. Crucial involvement of IL-6 in thrombus resolution in mice via macrophage recruitment and the induction of proteolytic enzymes. Front Immunol, 10:3150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.03150
Ouimet M, Ediriweera HN, Gundra UM, et al., 2015. MicroRNA-33-dependent regulation of macrophage metabolism directs immune cell polarization in atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest, 125(12):4334–4348. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI81676
Peterson AC, Russell JD, Bailey DJ, et al., 2012. Parallel reaction monitoring for high resolution and high mass accuracy quantitative, targeted proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics, 11(11):1475–1488. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.O112.020131
Prosper F, Vanoverbeke K, Stroncek D, et al., 1997. Primitive long-term culture initiating cells (LTC-ICs) in granulocyte colony-stimulating factor mobilized peripheral blood progenitor cells have similar potential for ex vivo expansion as primitive LTC-ICs in steady state bone marrow. Blood, 89(11):3991–3997.
Rabinowitz J, Sharifi HJ, Martin H, et al., 2021. xCT/SLC7A11 antiporter function inhibits HIV-1 infection. Virology, 556:149–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2021.01.008
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S, Vazini H, et al., 2018. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol, 233(9):6425–6440. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26429
Sica A, Mantovani A, 2012. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest, 122(3):787–795. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI59643
Snel B, Lehmann G, Bork P, et al., 2000. STRING: a webserver to retrieve and display the repeatedly occurring neighbourhood of a gene. Nucleic Acids Res, 28(18): 3442–3444. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.18.3442
Song QQ, Hawkins GA, Wudel L, et al., 2019. Dissecting intratumoral myeloid cell plasticity by single cell RNA-seq. Cancer Med, 8(6):3072–3085. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2113
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, et al., 2015. STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res, 43(D1):D447–D452. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1003
Vago JP, Sugimoto MA, Lima KM, et al., 2019. Plasminogen and the plasminogen receptor, Plg-RKT, regulate macrophage phenotypic, and functional changes. Front Immunol, 10: 1458. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01458
Wang LX, Zhang SX, Wu HJ, et al., 2019. M2b macrophage polarization and its roles in diseases. J Leukoc Biol, 106(2):345–358. https://doi.org/10.1002/JLB.3RU1018-378RR
Wang QS, Ni H, Lan L, et al., 2010. Fra-1 protooncogene regulates IL-6 expression in macrophages and promotes the generation of M2d macrophages. Cell Res, 20(6):701–712. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2010.52
White MJV, Gomer RH, 2015. Trypsin, tryptase, and thrombin polarize macrophages towards a pro-fibrotic M2a phenotype. PLoS ONE, 10(9):e0138748. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138748
Wu SY, Romero-Ramírez L, Mey J, 2021. Retinoic acid increases phagocytosis of myelin by macrophages. J Cell Physiol, 236(5):3929–3945. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.30137
Wynn TA, Vannella KM, 2016. Macrophages in tissue repair, regeneration, and fibrosis. Immunity, 44(3):450–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2016.02.015
Wynn TA, Chawla A, Pollard JW, 2013. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature, 496(7446):445–455. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12034
Zhao Y, Zhang BZ, Zhang QQ, et al., 2021. Tumor-associated macrophages in osteosarcoma. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 22(11):885–892. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100029
Zizzo G, Hilliard BA, Monestier M, et al., 2012. Efficient clearance of early apoptotic cells by human macrophages requires M2c polarization and MerTK induction. J Immunol, 189(7):3508–3520. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1200662
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFA0905200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 91853123, 81773180, 81800655, and 21705127), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Nos. 2019M653715, 2019TQ0260, and 2019M663798).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Availability of data and materials
The mass spectrometry data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium (http://proteomecentral.proteomexchange.org) via the PRIDE partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD022320.
Author contributions
Pengfei LI and Shisheng SUN designed the experiments. Pengfei LI, Chen MA, Zhifang HAO, and Jing LI performed experiments. Chen MA, Jingyu WU, and Yuan ZHI performed mass spectrometry analysis. Chen MA, Jing LI, Shanshan YOU, and Lin CHEN analyzed data. Pengfei LI, Chen MA, and Shisheng SUN wrote the manuscript. Liuyi DANG and Jun LI revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Pengfei LI, Chen MA, Jing LI, Shanshan YOU, Liuyi DANG, Jingyu WU, Zhifang HAO, Jun LI, Yuan ZHI, Lin CHEN, and Shisheng SUN declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Supplementary information
Figs. S1 and S2; Tables S1–S8
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Ma, C., Li, J. et al. Proteomic characterization of four subtypes of M2 macrophages derived from human THP-1 cells. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 23, 407–422 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100930
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2100930