Abstract
Objective
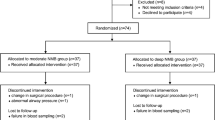
Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) requires pneumoperitoneum (Pnp) and a steep head-down position that may disturb respiratory system compliance (Crs) during surgery. Our aim was to compare the effects of different degrees of neuromuscular block (NMB) on Crs with the same Pnp pressure during RARP. Methods: One hundred patients who underwent RARP were enrolled and randomly allocated to a deep or moderate NMB group with 50 patients in each group. Rocuronium was administered to both groups: in the moderate NMB group to maintain 1–2 responses to train-of-four (TOF) stimulation; and in the deep NMB group to maintain no response to TOF stimulation and 1–2 responses in the post-tetanic count. Pnp pressure in both groups was 10 mmHg (1 mmHg=133.3 Pa). Peak inspiratory pressure (Ppeak), mean pressure (Pmean), Crs, and airway resistance (Raw) were recorded after anesthesia induction and at 0, 30, 60, and 90 min of Pnp and post-Pnp. Surgical space conditions were evaluated after the procedure on a 4-point scale.
Results
Immediately after the Pnp, Ppeak, Pmean, and Raw significantly increased, while Crs decreased and persisted during Pnp in both groups. The results did not significantly differ between the two groups at any of the time points. There was no difference in surgical space conditions between groups. Body movements occurred in 14 cases in the moderate NMB group and in one case in the deep NMB group, and all occurred during obturator lymphadenectomy. A significant difference between the two groups was observed.
Conclusions
Under the same Pnp pressure in RARP, deep and moderate NMBs resulted in similar changes in Crs, and in other respiratory mechanics and surgical space conditions. However, deep NMB significantly reduced body movements during surgery.
摘 要
目 的
机器人辅助前列腺癌根治术中需要头低位和气腹, 这将严重干扰呼吸顺应性 (Crs). 本研究比 较机器人辅助腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术在相同气腹压力下不同程度的神经肌肉阻滞对Crs 的影响.
创新点
不同深度神经肌肉阻滞对机器人辅助前列腺癌根治术 Crs 的观察.
方 法
将 100 例接受机器人辅助腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术的患者随机分配到中度神经肌肉阻滞组和深度神经肌肉阻滞组, 每组 50 例. 应用罗库溴铵维持神经肌肉阻滞. 保持对 4 个成串刺激 1–2 个反 应为中度神经肌肉阻滞组; 对 4 个成串刺激无反应, 而对强直后刺激 1–2 个反应为深度神经肌肉阻滞组. 两组气腹压力均为 10 mmHg. 记录麻醉诱导后及气腹 0、 30、 60 和 90 min 的吸气峰值压力、 平均压力、 Crs 和气道阻力. 手术结束时对手术条件进行评估.
结 论
在机器人辅助腹腔镜前列腺癌根治术中, 相同的气腹压力下, 深度神经肌肉阻滞不能改善 Crs 和手术条件, 但能显著降低术中体动.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aouad MT, Alfahel WS, Kaddoum RN, et al., 2017. Half dose sugammadex combined with neostigmine is non-inferior to full dose sugammadex for reversal ofrocuronium-induced deep neuromuscular blockade: a cost-saving strategy. BMC Anesthesiol, 17:57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-017-0348-9
Assad OM, el Sayed AA, Khalil MA, 2016. Comparison of volume-controlled ventilation and pressure-controlled ventilation volume guaranteed during laparoscopic surgery in trendelenburg position. J Clin Anesth, 34:55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinane.2016.03.053
Atkinson TM, Giraud GD, Togioka BM, et al., 2017. Cardiovascular and ventilatory consequences of laparoscopic surgery. Circulation, 135(7):700–710. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.023262
Baete S, Vercruysse G, vander Laenen M, et al., 2017. The effect of deep versus moderate neuromuscular block on surgical conditions and postoperative respiratory function in bariatric laparoscopic surgery: a randomized, double blind clinical trial. Anesth Analg, 124(5):1469–1475. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000001801
Barrio J, Errando CL, García-Ramón J, et al., 2017. Influence of depth of neuromuscular blockade on surgical conditions during low-pressure pneumoperitoneum laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized blinded study. J Clin Anesth, 42:26–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinane.2017.08.005
Basiri A, de la Rosette JJ, Tabatabaei S, et al., 2018. Comparison of retropubic, laparoscopic and robotic radical prostatectomy: who is the winner? World J Urol, 36(4): 609–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2174-1
Brandão JC, Lessa MA, Motta-Ribeiro G, et al., 2019. Global and regional respiratory mechanics during robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery: a randomized study. Anesth Analg, 129(6):1564–1573. https://doi.org/10.1213/ane.0000000000004289
Bruintjes MH, van Helden EV, Braat AE, et al., 2017. Deep neuromuscular block to optimize surgical space conditions during laparoscopic surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth, 118(6):834–842. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aex116
Cho YJ, Paik H, Jeong SY, et al., 2018. Lower intra-abdominal pressure has no cardiopulmonary benefits during laparoscopic colorectal surgery: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc, 32(11):4533–4542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6204-2
Chun EH, Baik HJ, Moon HS, et al., 2019. Comparison of low and high positive end-expiratory pressure during low tidal volume ventilation in robotic gynaecological surgical patients using electrical impedance tomography: a randomised controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol, 36(9):641–648. https://doi.org/10.1097/EJA.0000000000001047
Geldner G, Niskanen M, Laurila P, et al., 2012. A randomised controlled trial comparing sugammadex and neostigmine at different depths of neuromuscular blockade in patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. Anaesthesia, 67(9): 991–998. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.2012.07197.x
Güldner A, Kiss T, Neto AS, et al., 2015. Intraoperative protective mechanical ventilation for prevention of postoperative pulmonary complications: a comprehensive review of the role of tidal volume, positive end-expiratory pressure, and lung recruitment maneuvers. Anesthesiology, 123(3):692–713. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000000754
Kim MS, Soh S, Kim SY, et al., 2018. Comparisons of pressure-controlled ventilation with volume guarantee and volume-controlled 1:1 equal ratio ventilation on oxygenation and respiratory mechanics during robotassisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: a randomized-controlled trial. Int J Med Sci, 15(13):1522–1529. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.28442
Koo BW, Oh AY, Na HS, et al., 2018. Effects of depth of neuromuscular block on surgical conditions during laparoscopic colorectal surgery: a randomised controlled trial. Anaesthesia, 73(9):1090–1096. https://doi.org/10.1111/anae.14304
Kudoh O, Satoh D, Hori N, et al., 2019. The effects of a recruitment manoeuvre with positive end-expiratory pressure on lung compliance in patients undergoing robotassisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. J Clin Monit Comput, 34(2):303–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-019-00306-y
Madsen MV, Staehr-Rye AK, Gätke MR, et al., 2015. Neuromuscular blockade for optimising surgical conditions during abdominal and gynaecological surgery: a systematic review. Acta AnaesthesiolScand, 59(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/aas.12419
Park JS, Ahn EJ, Ko DD, et al., 2012. Effects of pneumoperitoneal pressure and position changes on respiratory mechanics during laparoscopic colectomy. Korean J Anesthesiol, 63(5):419–424. https://doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2012.63.5.419
Park SJ, Kim BG, Oh AH, et al., 2016. Effects of intraoperative protective lung ventilation on postoperative pulmonary complications in patients with laparoscopic surgery: prospective, randomized and controlled trial. Surg Endosc, 30(10):4598–4606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-4797-x
Pereira SM, Tucci MR, Morais CCA, et al., 2018. Individual positive end-expiratory pressure settings optimize intraoperative mechanical ventilation and reduce postoperative atelectasis. Anesthesiology, 129(6):1070–1081. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000002435
Rauh R, Hemmerling TM, Rist M, et al., 2001. Influence of pneumoperitoneum and patient positioning on respiratory system compliance. J Clin Anesth, 13(5):361–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0952-8180(01)00286-0
Schultz P, Ibsen M, Ostergaard D, et al., 2001. Onset and duration of action of rocuronium-from tracheal intubation, through intense block to complete recovery. Acta AnaesthesiolScand, 45(5):612–617. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-6576.2001.045005612.x
Spadaro S, Karbing DS, Mauri T, et al., 2016. Effect of positive end-expiratory pressure on pulmonary shunt and dynamic compliance during abdominal surgery. Br J Anaesth, 116(6):855–861. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aew123
Staehr-Rye AK, Rasmussen LS, Rosenberg J, et al., 2014. Surgical space conditions during low-pressure laparoscopic cholecystectomy with deep versus moderate neuromuscular blockade: a randomized clinical study. Anesth Analg, 119(5):1084–1092. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000000316
Williams WH III, Cata JP, Lasala JD, et al., 2020. Effect of reversal of deep neuromuscular block with sugammadex or moderate block by neostigmine on shoulder pain in elderly patients undergoing robotic prostatectomy. Br J Anaesth, 124(2):164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2019.09.043
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shao-jun ZHU, Xiao-lin ZHANG, and Qing XIE collected and analyzed the data. Shao-jun ZHU and Kui-rong WANG wrote the manuscript. Yan-feng ZHOU and Kui-rong WANG designed the study and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript and, therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Shao-jun ZHU, Xiao-lin ZHANG, Qing XIE, Yan-feng ZHOU, and Kui-rong WANG declare that they have no conflict of interest.
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008 (5). This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine (Hangzhou, China), and written informed consent was obtained from all enrolled patients. The trial was registered prior to patient enrolment with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (No. ChiCTR1800017660; date of registration: Aug. 1, 2018).
Additional information
Project supported by the Zhejiang Province Public Welfare Technology Application Research Project (No. LGF20H010006), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Sj., Zhang, Xl., Xie, Q. et al. Comparison of the effects of deep and moderate neuromuscular block on respiratory system compliance and surgical space conditions during robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: a randomized clinical study. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 21, 637–645 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000193
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000193
Key words
- Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP)
- Deep neuromuscular block
- Respiratory mechanics
- Surgical space condition