Abstract
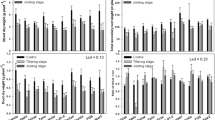
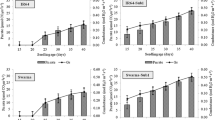
To study the effect of high temperature, rice seedlings 20, 30, 40 and 50 d were kept at 5, 10, 15 and 20 cm water depth in a water pool. Meteorological findings indicated that water temperature varied up to 10 cm but became stable below this depth. Deep water inflicted higher tiller mortality, minimal increase in dry weight of aerial parts and leaf area, decrease in root length, and decrease in root dry weight especially at 20 cm water depth and produced an unbalanced T/R ratio (top versus root dry weight). However, deep water tended to increase plant length. These parameters, however, excel in shallow water. Older seedlings, with the exception of root dry weight, could not perform well compared to young seedlings in all physiological and morphological aspects. The study revealed that seedlings, particularly young ones, and stand well in shallow water and can cope with high temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adak, M.K., Gupta, D.K.D., 2002. Metabolic activities in some rice varieties under submergence stress.Indian Journal of Plant Physiology,6(3):312–316.
De Datta, S.K., 1981. Principles and Practices of Rice Production. International Rice Research Institute, John Willy & Sons, Inc., New York, USA.
Gun, W.J., 1999. Tillering, lodging and yield under deep water treatment in direct seeded rice. Plant Production Science.Fukuoka,2(3):200–205.
Hoshikawa, K., 1975. Growth of Rice. Nouson Gyoson Bunka Kyoukai Co., Noubunkyo, p. 90–91 (in Japanese).
Kanzaki, M., Toriu, K., Oishi, H., Shirakawa, N., 2001. Factors influencing the phytotoxicity of cafenstroile to transplanted rice plants in paddy field.Journal of Weed Science and Technology,46(3):169–174.
Lal, M., Roy, R.K., 1996. Effect of nursery seeding densities and fertilizer on seedling growth and yield of rice (Oryza Sativa L).Indian journal of Agronomy,41(4):642–644.
Matsushima, S., Tanaka, T., Hoshino, T., 1968. Combined Effect of Air Temperatures and Water Temperatures at Different Stages of Growth on the Grain Yield and Its Components of Lowland Rice. National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Konosu, Saitama, Japan, p. 57–58.
Morita, S., Shiratsuchi, H., Takansh, J., Fujita, K., 2002. Effect of high temperature on ripening in rice plants.Japanese Journal of Grop Science,71(1):102–109.
Nishiki, T., 1987. Stable and High Yielding Techniques. Bull Yamagata Agric. Exp. Station, Yamagata, Japan, p. 33–34.
Ogasawara, M., Nozaki, T., Takeuchi, Y., Konnai, M., 1998. Influence of environmental factors in the development of root systems in young seedlings of rice (Oryza sativa L.) and barnyard grass (Echinochloa Crus-galli L.), (Beauvar Crus-galli).Journal of Weed Science and Technology,43(4):328–333.
Ohe, M., Mimoto, H., 1999. Changes in dry matter production of Japonica-type paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.) due to deep water treatment.Japanese Journal of Crop Science,68(4):482–486.
Padalia, C.R., 1980. Effect of age of seedling on the growth and yield of transplanted rice.Oryza,81:165–167.
Purba, D., 1993. Effect of Deep Water on Tiller and Yield of Rice. Report of Experiments. TIATC (JICA), Tsukuba, Japan, p. 61–74.
Quayyum, H.A., Gomosta, A.R., Hoque, M.Z., 1981. Effect of seedling age on total plant elongation and internode elongation of deep water rice.International Rice Research Newsletter,6(5):9–10.
Sinha, S.K., 2002. Tiller phonology and grain yield of low land rice (Oryza sativa) varieties under different water depth.Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences,72(5):285–287.
Sugai, K., Goto, Y., Saito, M., Nakamura, S., Kato, T., Nishiyama, I., 1998. Changes in Leaf Colour of Rice during Ripening Stage in Water Storage Type Deep Irrigation Method. Tohoku-Journal of Crop Science, Morioka, Japan,41:29–39.
Thanomthin, C., Zada, A., Said, A., 2002. Effect of high temperature at heading stage on growth and yield of four rice varieties.Sarhad Journal of Agriculture,18(3):291–294.
Williams, R.L., Angus, J.F., 1994. Deep floodwater protects high nitrogen rice crops from low temperature damage.Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture,34(7):927–932.
Zakria, S., Matsuda, T., Tajima, S., Nitta, Y., 2002. Effect of high temperature at ripening stage on the reserve accumulation in seed in some rice cultivars.Plant Production Science,5(2):160–168.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khakwani, A.A., Shiraishi, M., Zubair, M. et al. Effect of seedling age and water depth on morphological and physiological aspects of transplanted rice under high temperature. J Zheijang Univ Sci B 6, 389–395 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B0389
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B0389