Abstract
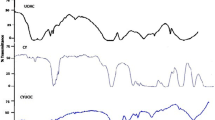
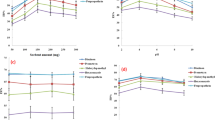
This study reports research on pesticide suspension rheology and a new rheological parameter, the relative value of approach, which has great advantage for judging the physical stability of a pesticide suspension concentrate. Experiments showed that the system can form stable dispersions when the value of the relative value of approach (S r) is less than 0.1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brian, V., 1980. The stability of particulate suspensions. Chemistry and Industry, 18(3):218–224.
Chen, Q.W., Tan, C.X., Shen, K.G., 2002. The Rheology Token of Physical Stability of Pesticide Suspension Concentrates. In: Zhang, X. (Ed.), The Progress in Botanical Pesticide and Pharmacological Toxicology. Publishing House of Chinese Agriculture Science and Technology, Beijing, p.384–387 (in Chinese).
Cheng, C.H., 1980. Sedimentation of suspensions and storage stability. Chemistry and Industry, 18(5):407–413.
Guido, B., Tadros, T.F., 2000. Fundamental aspects of suspension stabilization and some of their applications. Chim Ind (Milan), 82(7):E2/1-E2/8.
John, T., 1987. The stability of multiphase suspensions. Diss Abstr Int B, 48(2):512–513.
Kanellopulos, A.G., 1974. Additives in herbicide formulations. Chemistry and Industry, 12(7):951–955.
Luckham, P.F., 1989. The physical stability of suspension concentrates with particular reference to pharmaceutical and pesticide formulations. Pestic Sci, 45(25):25–34.
Makarov, A.S., Gamera, A.V., Vasil’ev, V.V., Sushko, V.A., 1988. Stability of structureless and structurized highly concentrated suspension. Dokl Akad Nauk Ukr SSR B: Geol, Khim Biol Nauki, (7):51–53.
Mulqueen, P.J., Paterson, E.S., Smith, G.W., 1990. Recent development in suspoemulsions. Pestic Sci, 46(29):451–465.
Seaman, D., 1990. Trends in the formulation of pesticide-an overview. Pestic Sci, 46(29):437–449.
Tadros, T.F., 1980. Control and assessment of the physical stability of pesticide suspension concentrates. Chemistry and Industry, 18(3):211–218.
Wigger, A., Guckel, W., 1989. Some investigations of suspoemulsions. Pestic Sci, 45(25):401–409.
Winzeler, H.B., Vogel, R., Dudler, A., 1980. Rheological measurements in development and quality of suspension concentrates. World Pesticides, 19(6):1–6 (in Chinese).
Woldemar, B., Piotr, C., Leszek, D., 1984. Evaluation of the state of a suspension in a mixer. Pr Nauk Politech Szczecin, 273:21–24.
Zhang, X., 2002. The Progress in Botanical Pesticide and Pharmacological Toxicology. Publishing House of Chinese Agriculture Science and Technology, Beijing, p.405–409 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Cx., Shen, Dl., Weng, Jq. et al. Research on the rheological properties of pesticide suspension concentrate. J. Zheijang Univ.-Sci. 5, 1604–1607 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2004.1604
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2004.1604